tag > Biology
-
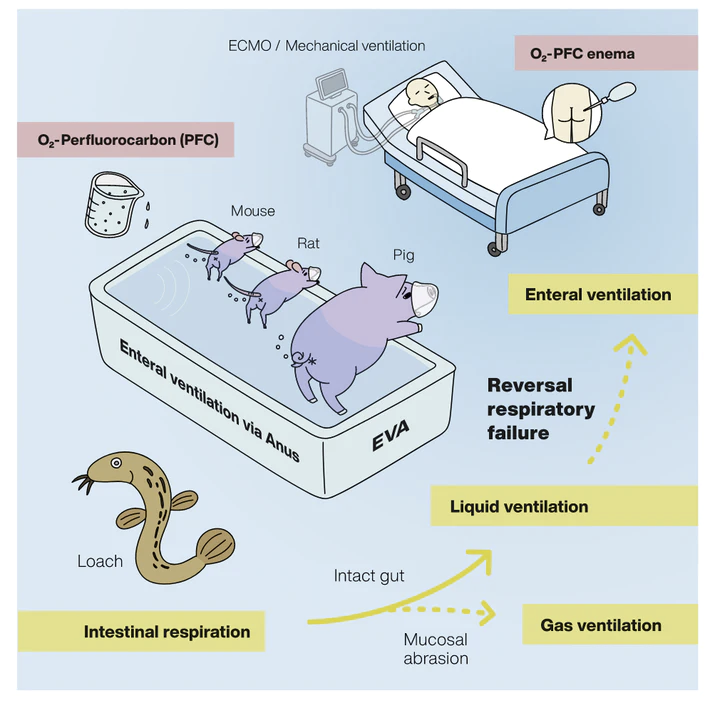
"Some mammals can breathe through their butt, scientists discover"
“We can develop a new medical device, aimed at increasing oxygen level in humans.”
-
Synthetic living machines: A new window on life (cell)

Here, we review recent advances in the emerging field of synthetic morphogenesis, the bioengineering of novel multicellular living bodies. Emphasizing emergent self-organization, tissue-level guided self-assembly, and active functionality, this work is the essential next generation of synthetic biology. Aside from useful living machines for specific functions, the rational design and analysis of new, coherent anatomies will greatly increase our understanding of foundational questions in evolutionary developmental and cell biology.
-
Magnetogenetics - "using magnetic fields to remotely control cell activity"

"Here, we show that, by complexing magnetic nanoparticles with recombinant baculoviral vectors (MNP-BVs), CRISPR–Cas9-mediated genome editing can be activated locally in vivo via a magnetic field." https://www.nature.com/articles/s41551-018-0318-7
Non-contact long-range magnetic stimulation of mechanosensitive ion channels in freely moving animals: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41563-020-00896-y
Genetically targeted magnetic control of the nervous system: https://www.nature.com/articles/nn.4265?WT.feed_name=subjects_neural-circuit
-
Yoga and Breathing Exercises Aid Children With ADHD to Focus

Yoga & breathing exercises have a positive effect on children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). After special classes, children improve their attention, decrease hyperactivity, they do not get tired longer, they can engage in complex activities longer.
-
The BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 reprograms both adaptive and innate immune responses (medrxiv)
The mRNA-based BNT162b2 vaccine from Pfizer/BioNTech was the first registered COVID-19 vaccine and has been shown to be up to 95% effective in preventing SARS-CoV-2 infections. Little is known about the broad effects of the new class of mRNA vaccines, especially whether they have combined effects on innate and adaptive immune responses. Here we confirmed that BNT162b2 vaccination of healthy individuals induced effective humoral and cellular immunity against several SARS-CoV-2 variants. Interestingly, however, the BNT162b2 vaccine also modulated the production of inflammatory cytokines by innate immune cells upon stimulation with both specific (SARS-CoV-2) and non-specific (viral, fungal and bacterial) stimuli. The response of innate immune cells to TLR4 and TLR7/8 ligands was lower after BNT162b2 vaccination, while fungi-induced cytokine responses were stronger. In conclusion, the mRNA BNT162b2 vaccine induces complex functional reprogramming of innate immune responses, which should be considered in the development and use of this new class of vaccines.
-
V.S. Ramachandran - What are Breakthroughs in Biology?
-
Christopher Alexander on Generative Systems

A generating system… is a kit of parts, with rules about the way these parts may be combined. Almost every ‘system as a whole’ is generated by a ‘generating system’. If we wish to make things which function as ‘wholes’ we shall have to invent generating systems to create them. - Christopher Alexander, 1968, “Systems Generating Systems”
If you want to make a living flower, you don't build it, you grow it from the seed. - Christopher Alexander
-
2.5 billion T. rex inhabited the planet, researchers say
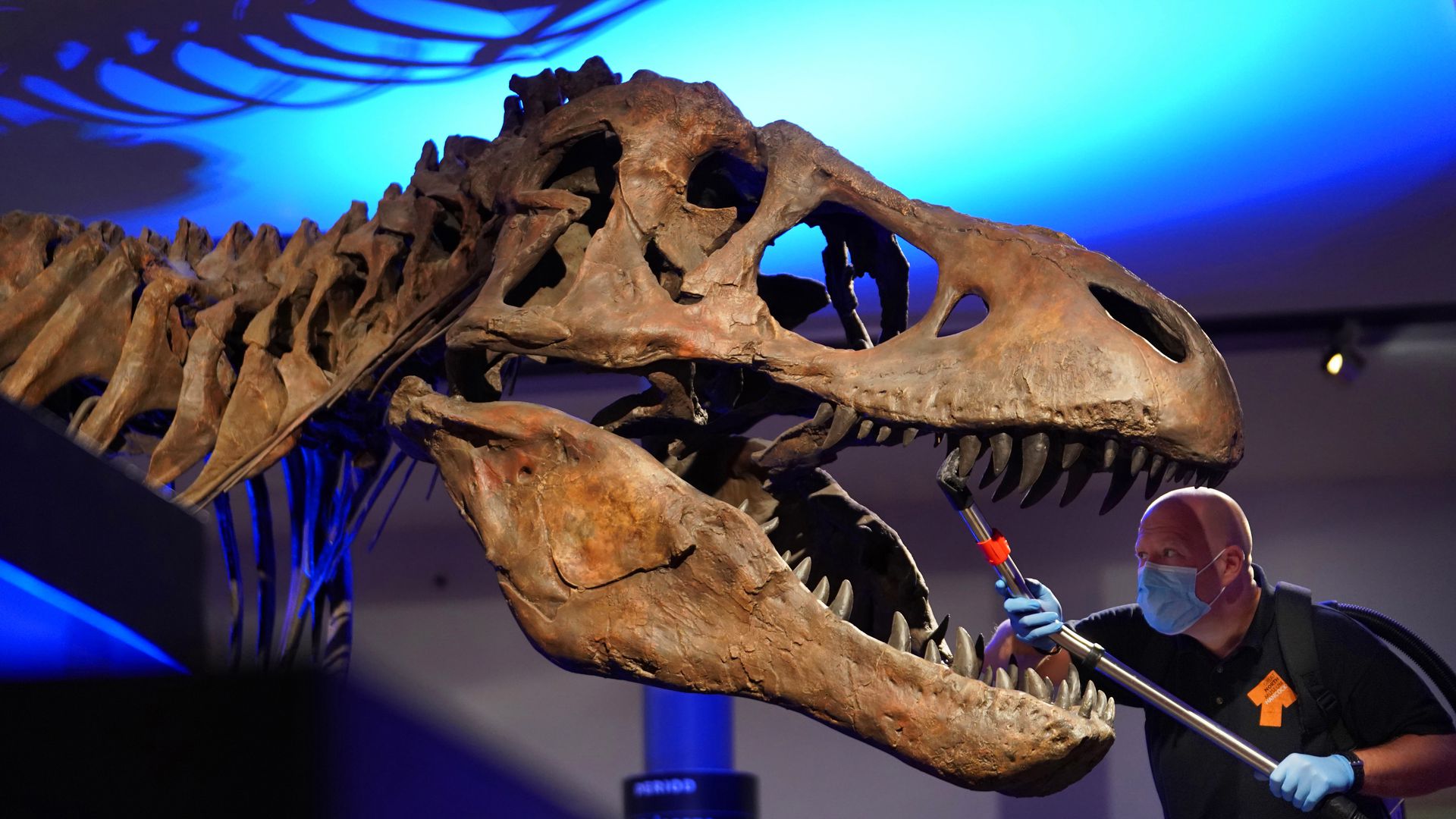

The number is staggering: 2.5 billion Tyrannosaurus rex lived and died during the roughly 2.4 million years the species survived on the planet, according to a new study set to be published in the journal Science on Friday. The study may help contextualize the fossil record and the rarity of finding certain fossilized prehistoric organisms, according to lead researcher Charles Marshall, director of the University of California Museum of Paleontology.
-
If you don't believe in miracles perhaps you've forgotten you are one.

-
The 8 Senses

- Visual (sight)
- Auditory (hearing)
- Olfactory (smell)
- Gustatory (taste)
- Tactile (touch)
- Vestibular (balance and movement)
- Proprioceptive (muscles and joints)
- Interoception ( Internal body sensations)
-
Scientists Create Simple Synthetic Cell That Grows and Divides Normally (nist.gov)
Five years ago, scientists created a single-celled synthetic organism that, with only 473 genes, was the simplest living cell ever known. However, this bacteria-like organism behaved strangely when growing and dividing, producing cells with wildly different shapes and sizes. Now, scientists have identified seven genes that can be added to tame the cells' unruly nature, causing them to neatly divide into uniform orbs.
-
There Are Hundreds of Billions of Galaxies. Where Are All the Aliens? - Comic by Maki Naro and Matthew Francis



-
Technosignatures of Intelligent Aliens Could Be “Lurking” Nearby, Study Says
A group of researchers propose searching for "unusual signatures or phenomena" on the Moon, and even around Earth.


-
Microbiome-Inspired Green Infrastructure (MIGI)
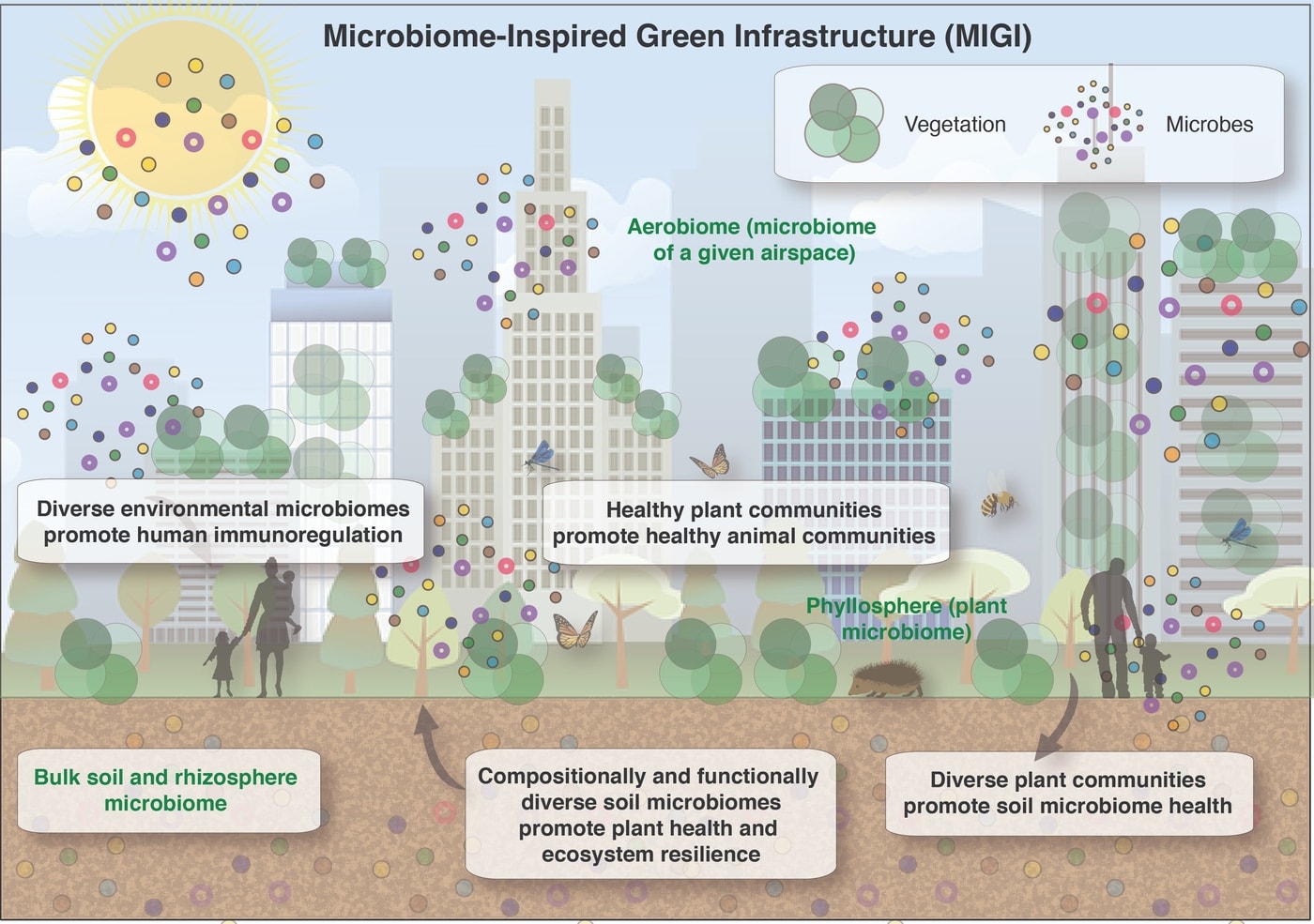
"Considerations for the microbiome (from the ground up) need to be central in urban ecosystem management. Microbes are foundational to healthy ecosystems yet are rarely considered (apart from human pathogens = <0.0001% of all microbes)"
-
Scientists discover how humans develop larger brains than other apes (phys.org)

A new study is the first to identify how human brains grow much larger, with three times as many neurons, compared with chimpanzee and gorilla brains. The study identified a key molecular switch that can make ape brain organoids grow more like human organoids, and vice versa.
-
Photosynthesis could be as old as life itself (imperial)

Researchers find the earliest bacteria had the tools to perform a crucial step in photosynthesis, showing the process previously thought to take billions of years to evolve could be as old as life itself, and suggesting other planets may have evolved complex life much earlier than previously thought