-
Planck Epoch: What is time? What is space? What is finite? What is infinite?
-
Planck’s Constant found encoded in the Great Pyramid of Giza
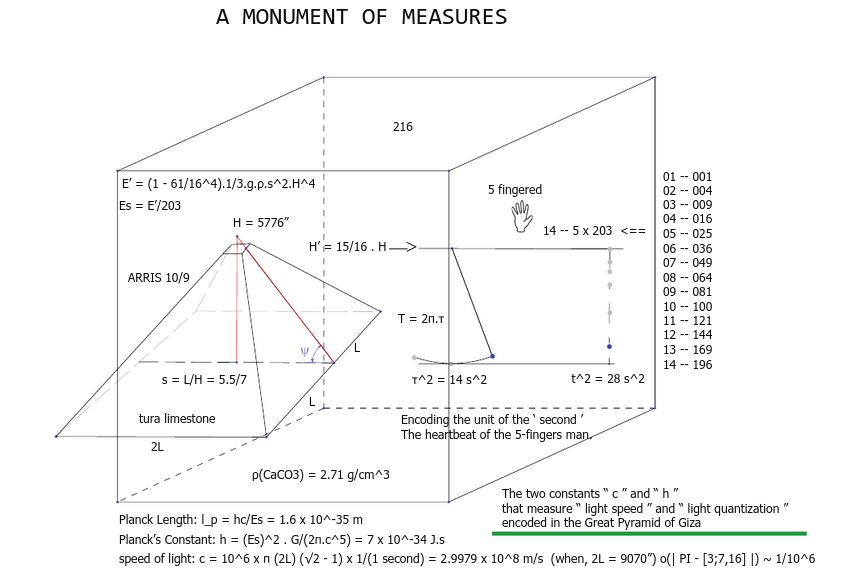
Upon computing the total energy required to raise all the stones to their respective heights in the Great Pyramid, and dividing by the number of stone steps in the construction, we obtain the energy of a photon that has the wavelength of the Planck Length. This observation enables us to calculate an estimate of Planck's Constant, h, from the measurements of the Great Pyramid of Giza, and provides a rationale for the architect's particular choice of the number of stone step layers found in the monument.
-
R.I.P. Antero Alli (1952-2023), a Finnish-American philosopher, writer, film-maker, theater director. Known for his books, incl. on the Eight-Circuit Model of Consciousness of Timothy Leary & Robert Anton Wilson.



"I have lived by a code of 'amor fati' for many years - in love with What Is; whatever fate comes my way, I accept. This is no passive acquiescence or subordination to death but a revolution of Spirit to the deep mystery pulsing at the very heart of existence itself." Antero Alli, March 17, 2023
Antero came to redefine death as "Genesis" - a new beginning, a portal into the next chapter of his journey. Our beloved Antero transcended into Genesis yesterday around 12:45pm at home in Portland, Oregon. In his words, "Honestly, I'm not one to mourn over but to celebrate..."
Arto Antero Alexander All - 11/11/1952 - 11/9/2023
-
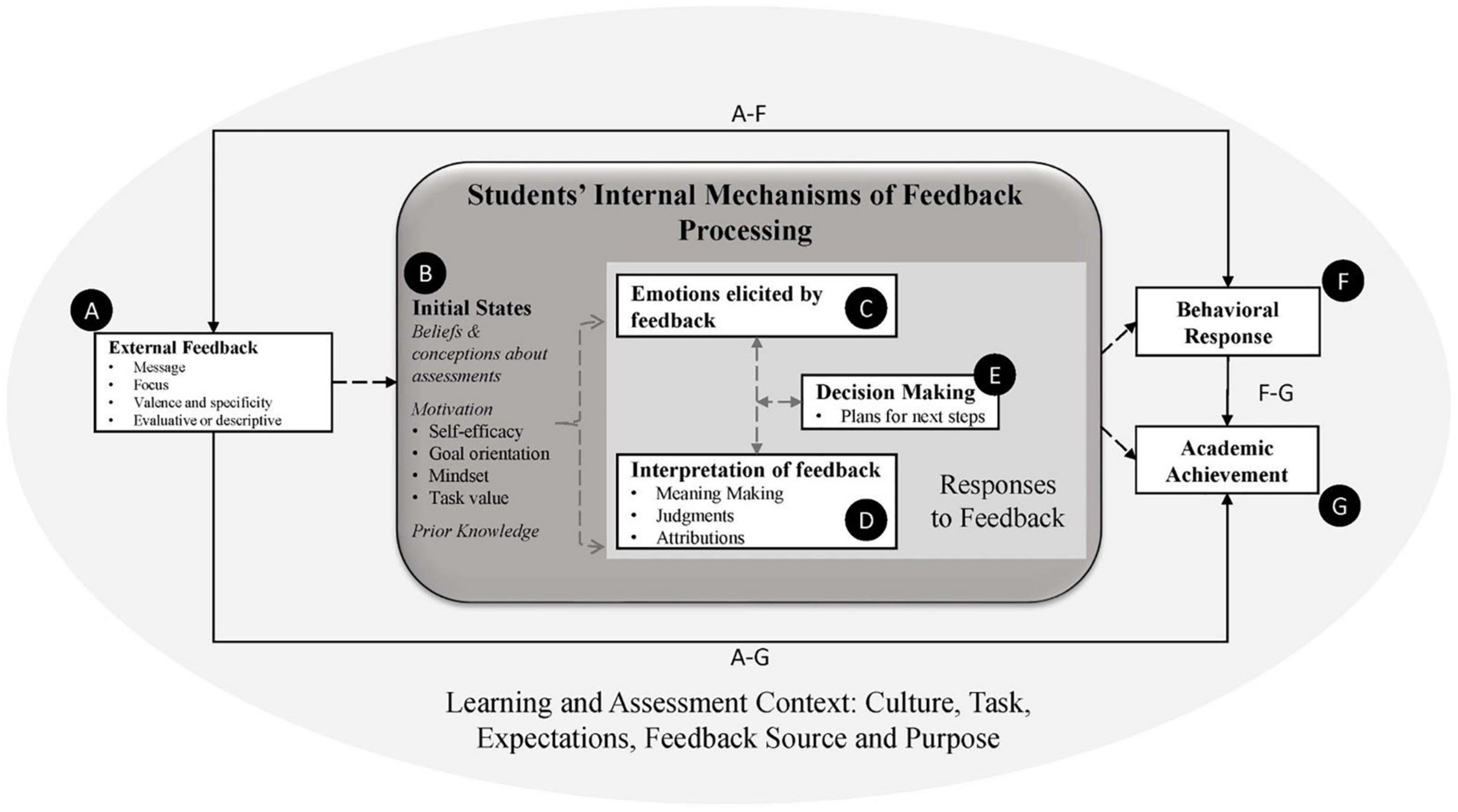
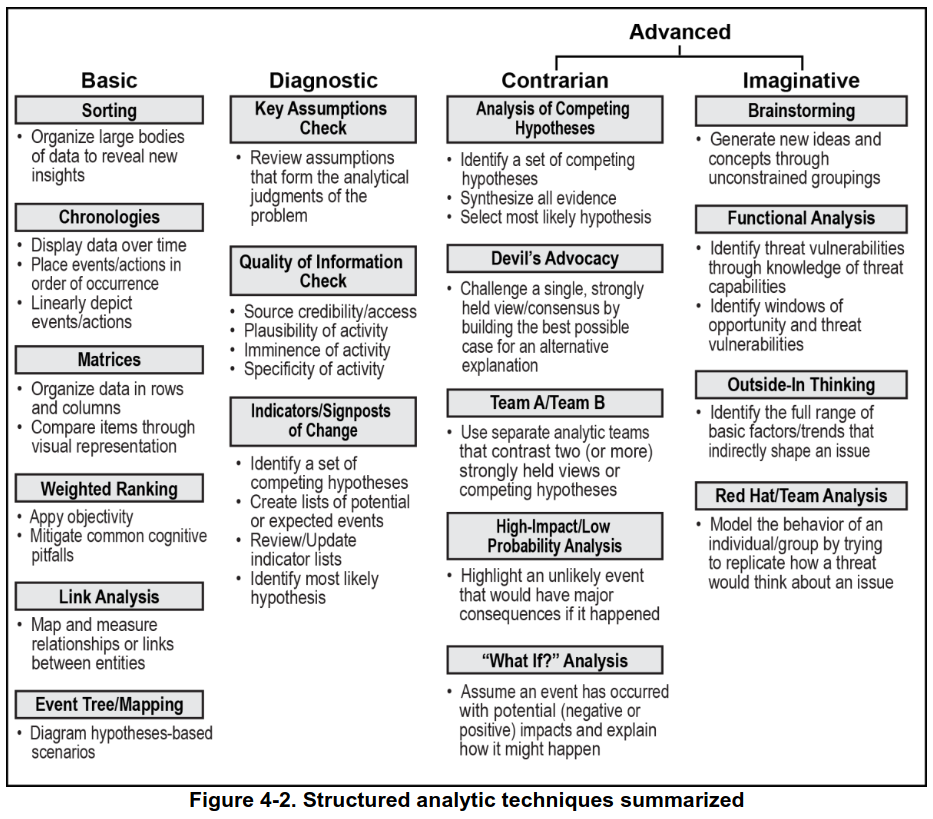
Context, Assessment, Theories, and Conclusions - a structured analytical approach often used in fields like intelligence analysis, policy analysis, academic research, and strategic planning.
Context: This is the foundational step where you establish the background and environment in which the subject of your analysis exists. It involves gathering relevant information, understanding the historical and current situation, identifying key players, and recognizing the socio-political, economic, or technological factors that might influence the subject. In intelligence and policy analysis, this might involve understanding geopolitical dynamics, while in academic research, it could involve reviewing existing literature and theories.
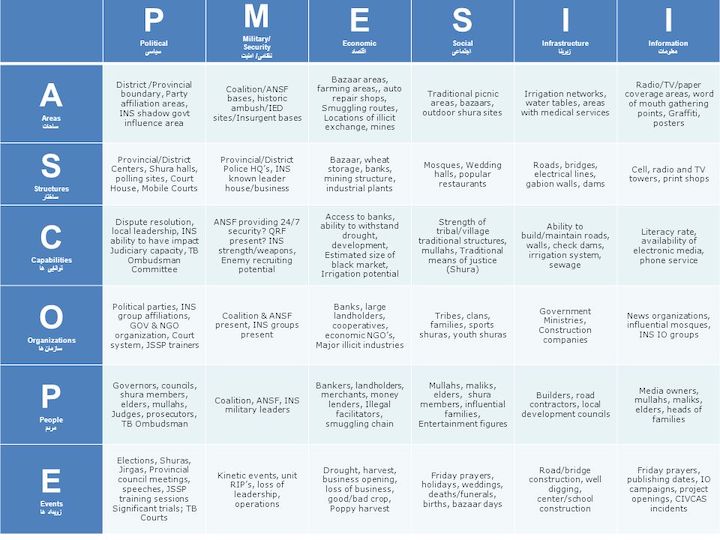
Assessment: In this phase, you evaluate the information gathered during the context phase. This involves analyzing data, identifying patterns, discrepancies, and anomalies, and understanding the relationships between different pieces of information. The assessment phase often involves critical thinking and may use specific methodologies like SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats), PESTLE analysis (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, Environmental), or other domain-specific tools.
Theories: Here, you develop hypotheses or theories to explain the observations made in the assessment phase. This could involve formulating different scenarios, proposing causal relationships, or developing models to explain the data. In intelligence analysis, this might involve creating different intelligence scenarios or forecasts. In academic research, it could involve proposing a new theory or model based on empirical data.
Conclusions: This is the phase where you draw conclusions from your analysis. It involves synthesizing the context, assessment, and theories to arrive at a comprehensive understanding of the subject. Conclusions should be supported by the evidence and analysis presented in the previous steps. This phase may also involve making recommendations or predictions based on the conclusions.
This method is particularly useful in situations requiring thorough and systematic analysis, where jumping to conclusions without a proper foundation could lead to errors or oversights. It's a method that encourages a comprehensive and multi-faceted view of a problem or situation, reducing the risk of bias or one-dimensional thinking.
-
Hindsight, Foresight, Insight
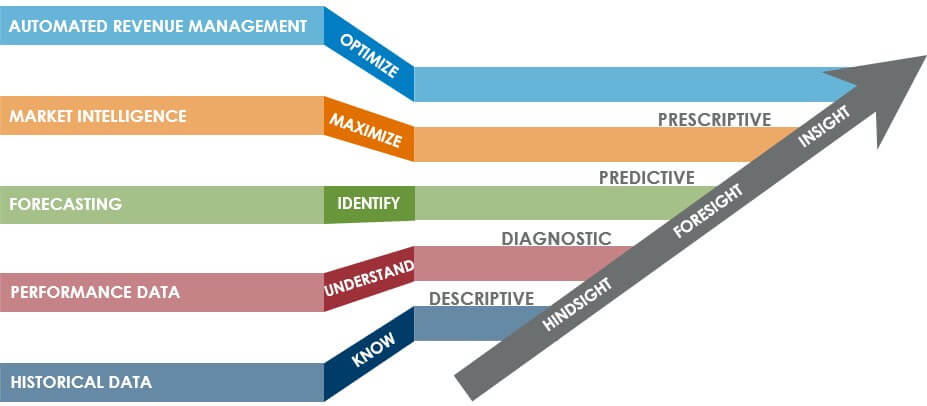
Descriptive analytics and diagnostic analytics provide revenue hindsight by evaluating historical performance data to identify what happened, when it happened and why it happened.
Predictive analytics provide revenue foresight by delivering forecasts that help you anticipate what’s going to happen next.
Prescriptive analytics go even one step further and leverage data and forward-looking intelligence data to produce automated decisions. Common examples of prescriptive analytics are advanced demand forecasts at detailed levels and automated pricing decisions.
-
The US, Swedish and UK intelligence cycle.
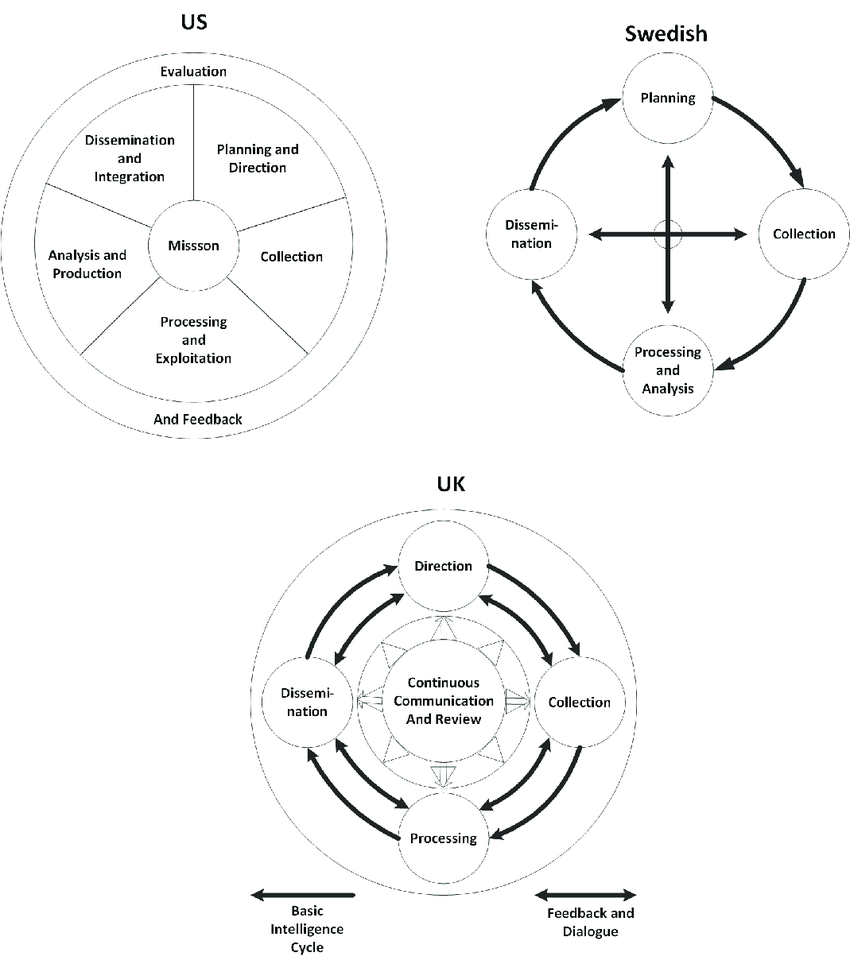
(Redrawn from the JP 2-0, Joint Intelligence, 22 October 2013; Försvarsmaktens Underrättelsereglemente, 2010; JDP 2-00: Understanding and Intelligence Support to Joint Operations, 15 May 2015).
-
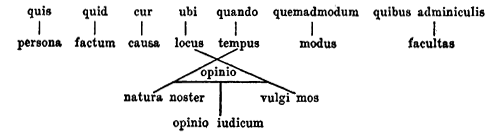
BLUF (bottom line up front) - the practice of beginning a message with its key information
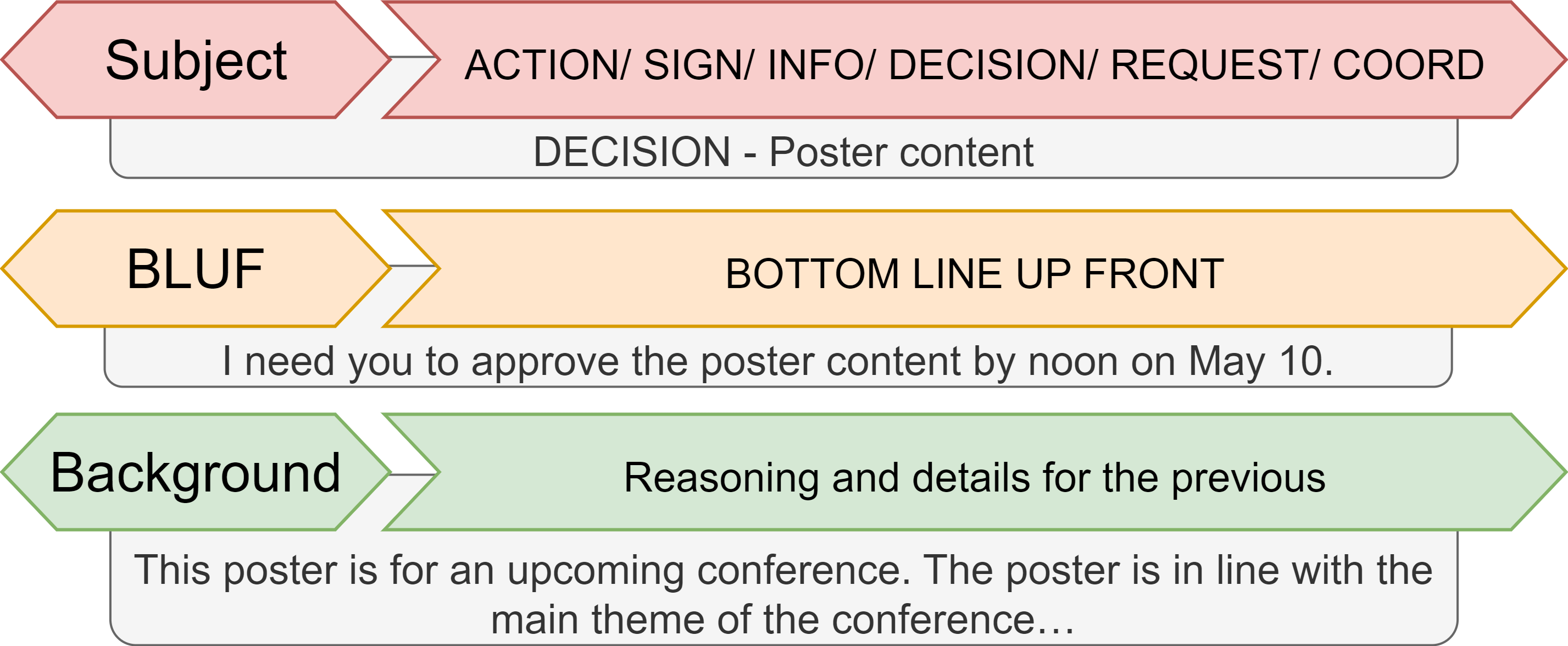
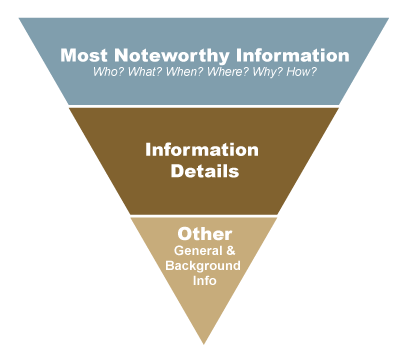
Military professionals use BLUF to send over-written messages, mostly emails. It declares the decision/question right away, and THEN explains the background and context that supports it.
The BLUF should quickly answer the five W’s: who, what, where, when, and why. An effective BLUF distills the most important information for the reader. (Sehgal, 2016)
That's because the reader doesn't necessarily want to know the whole context, but they NEED to know the decision/information.
-
80 years ago: "Machines that think called peril to man"