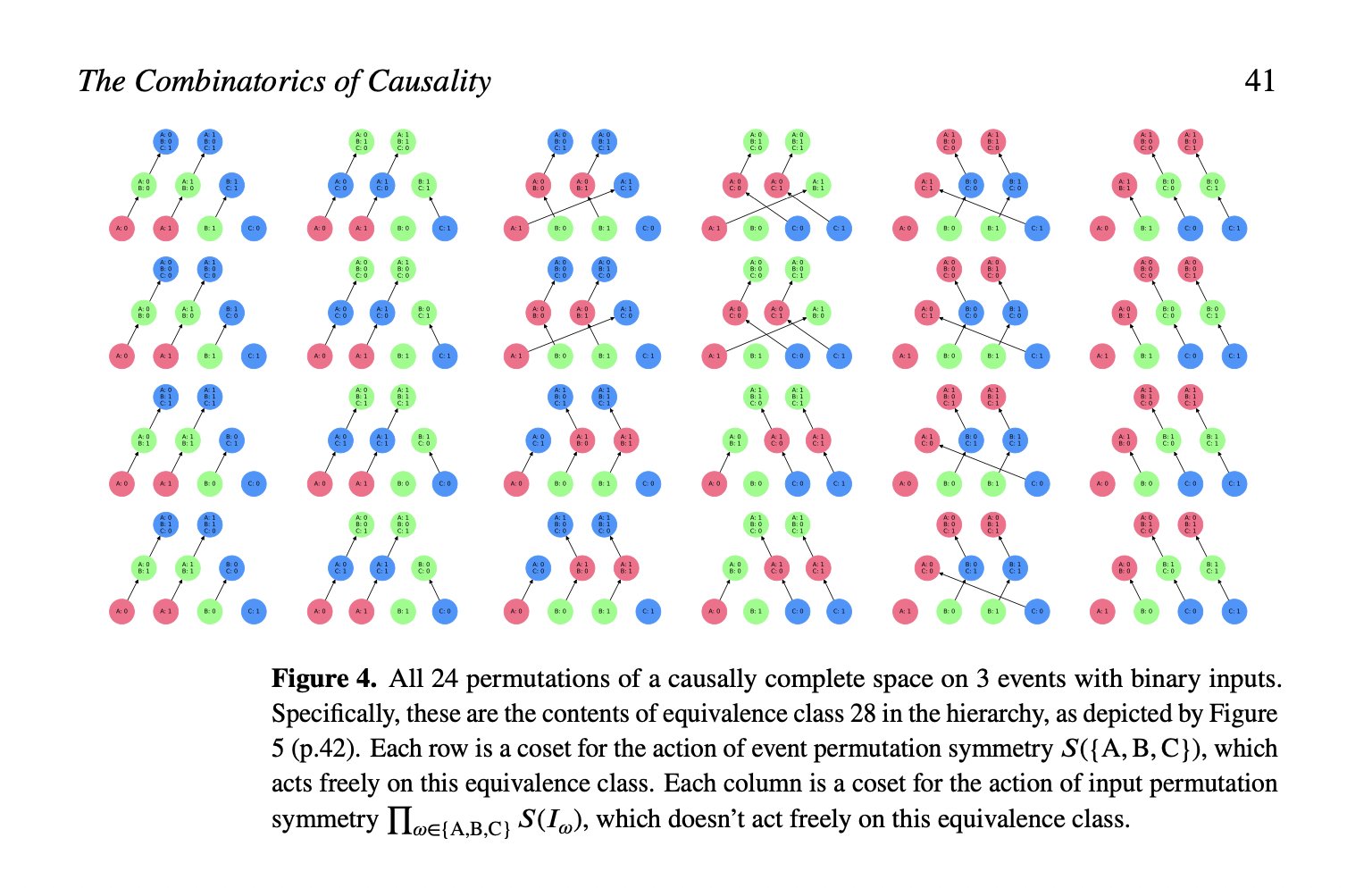
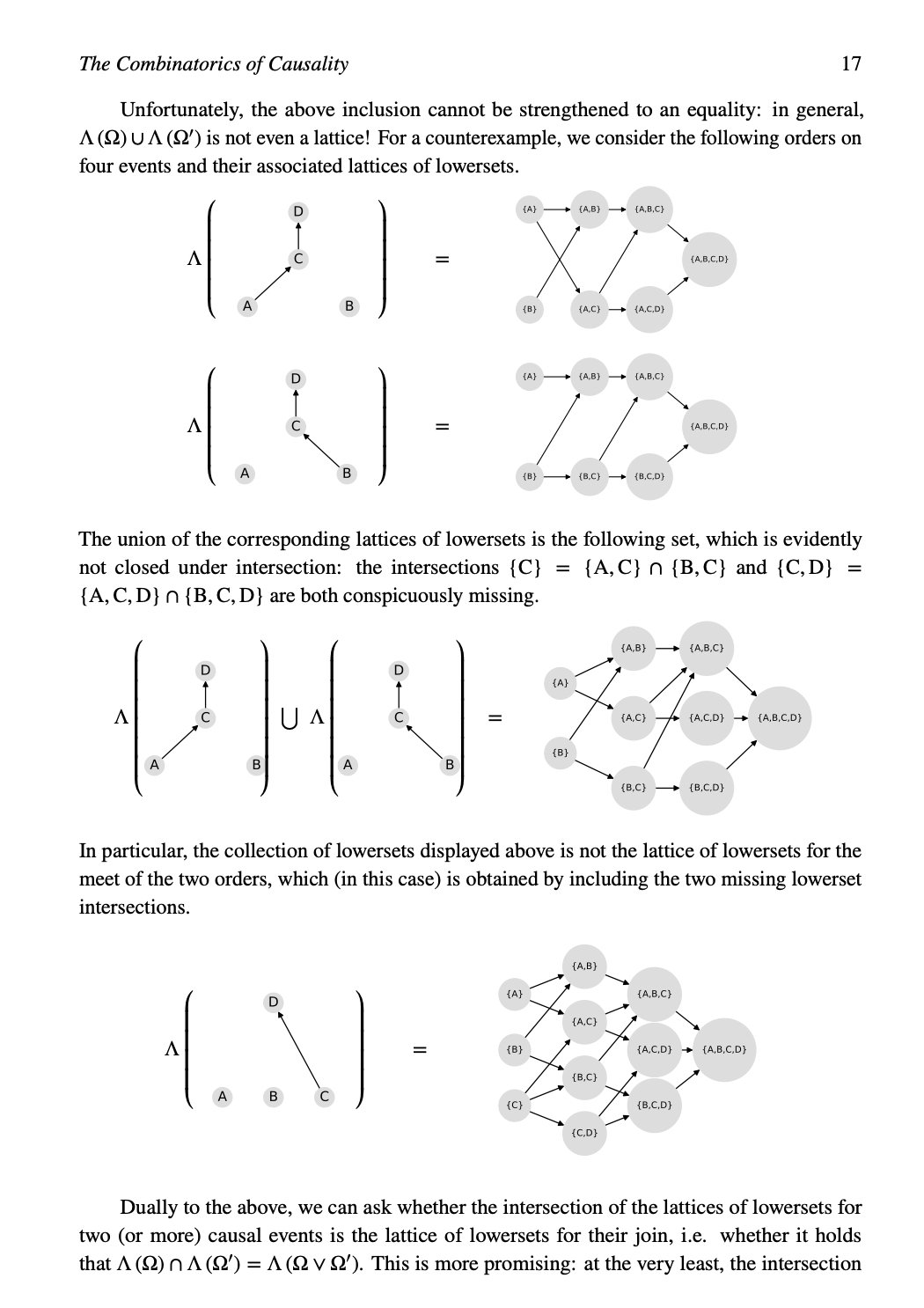
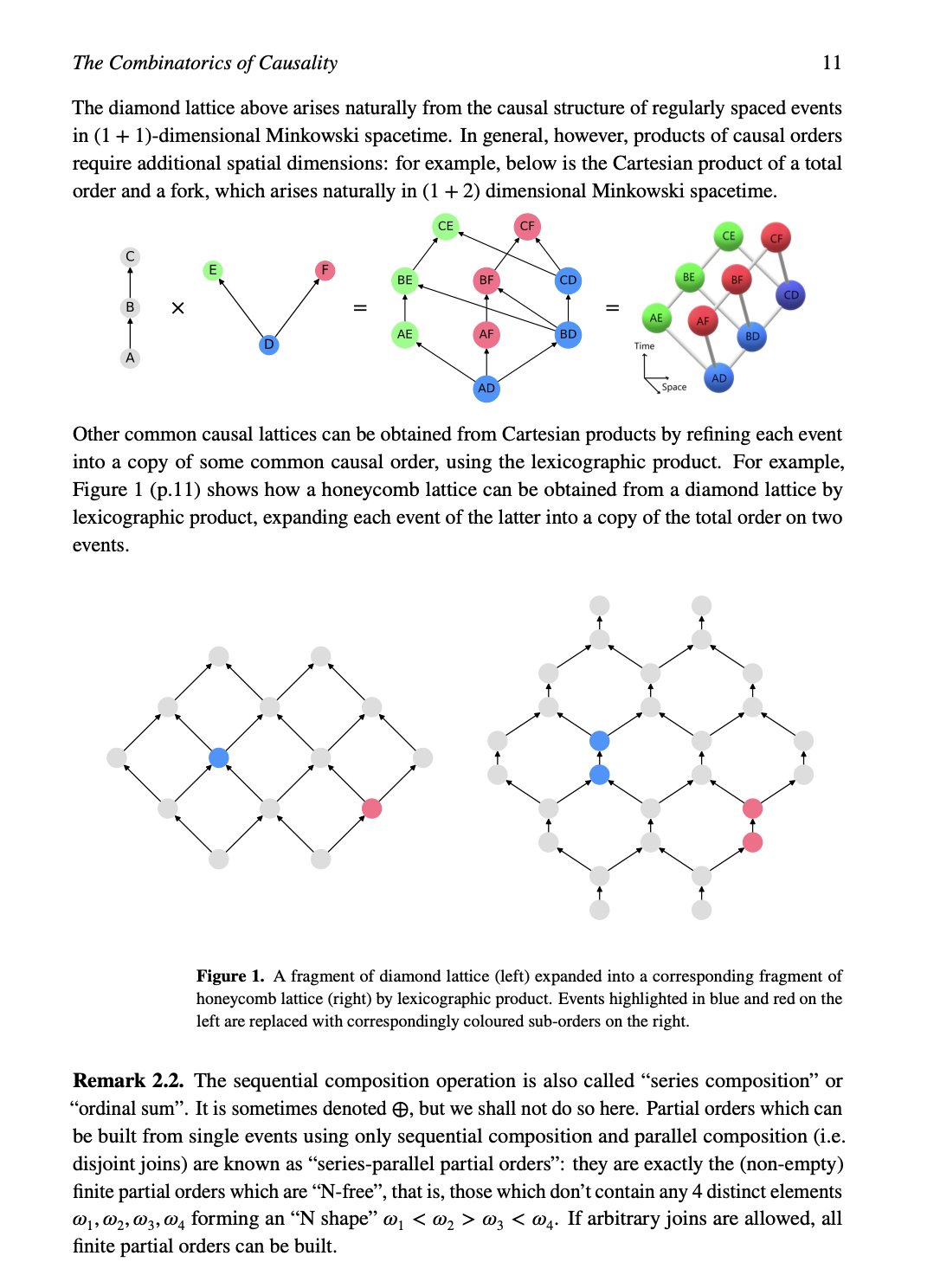
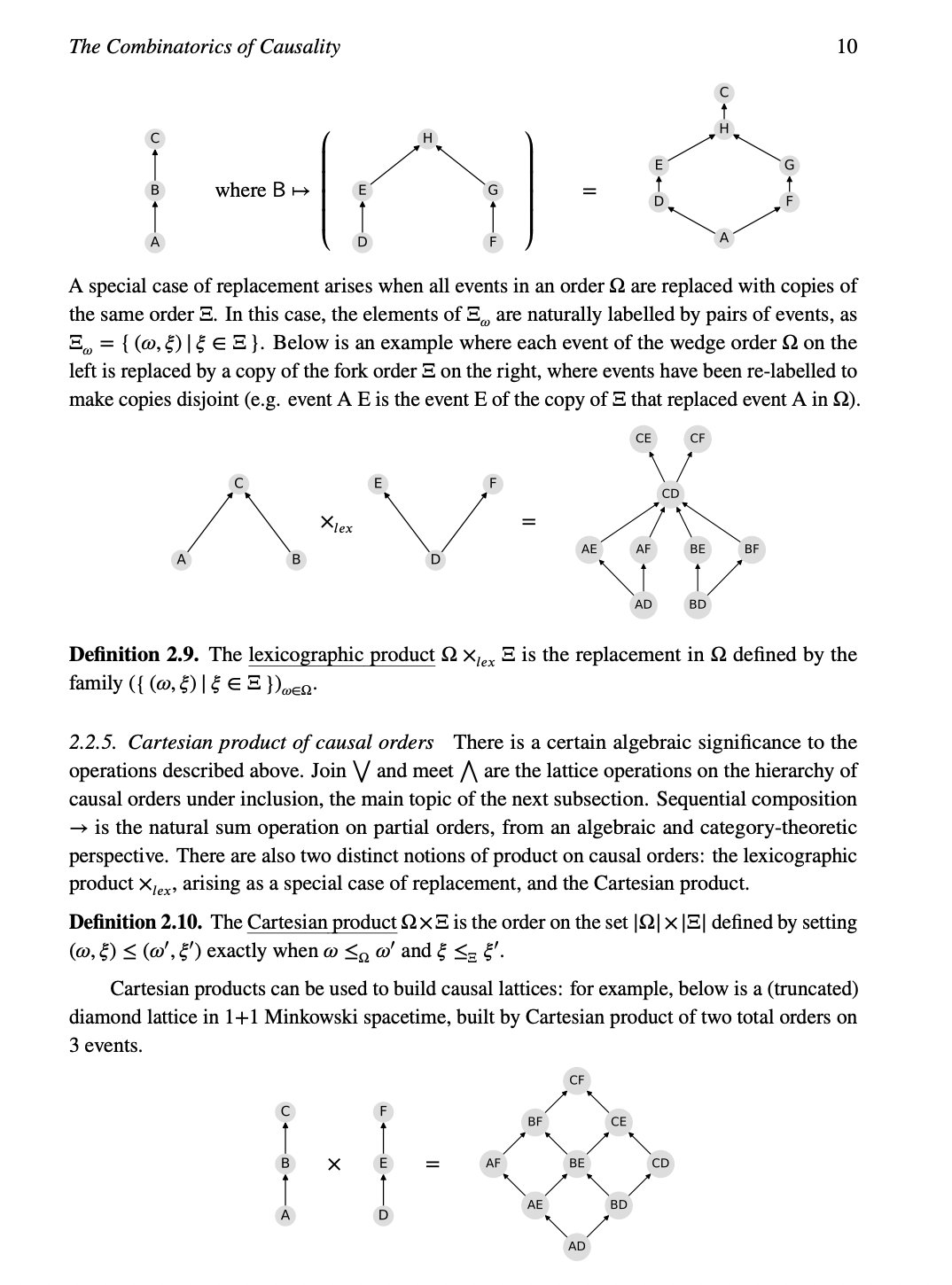
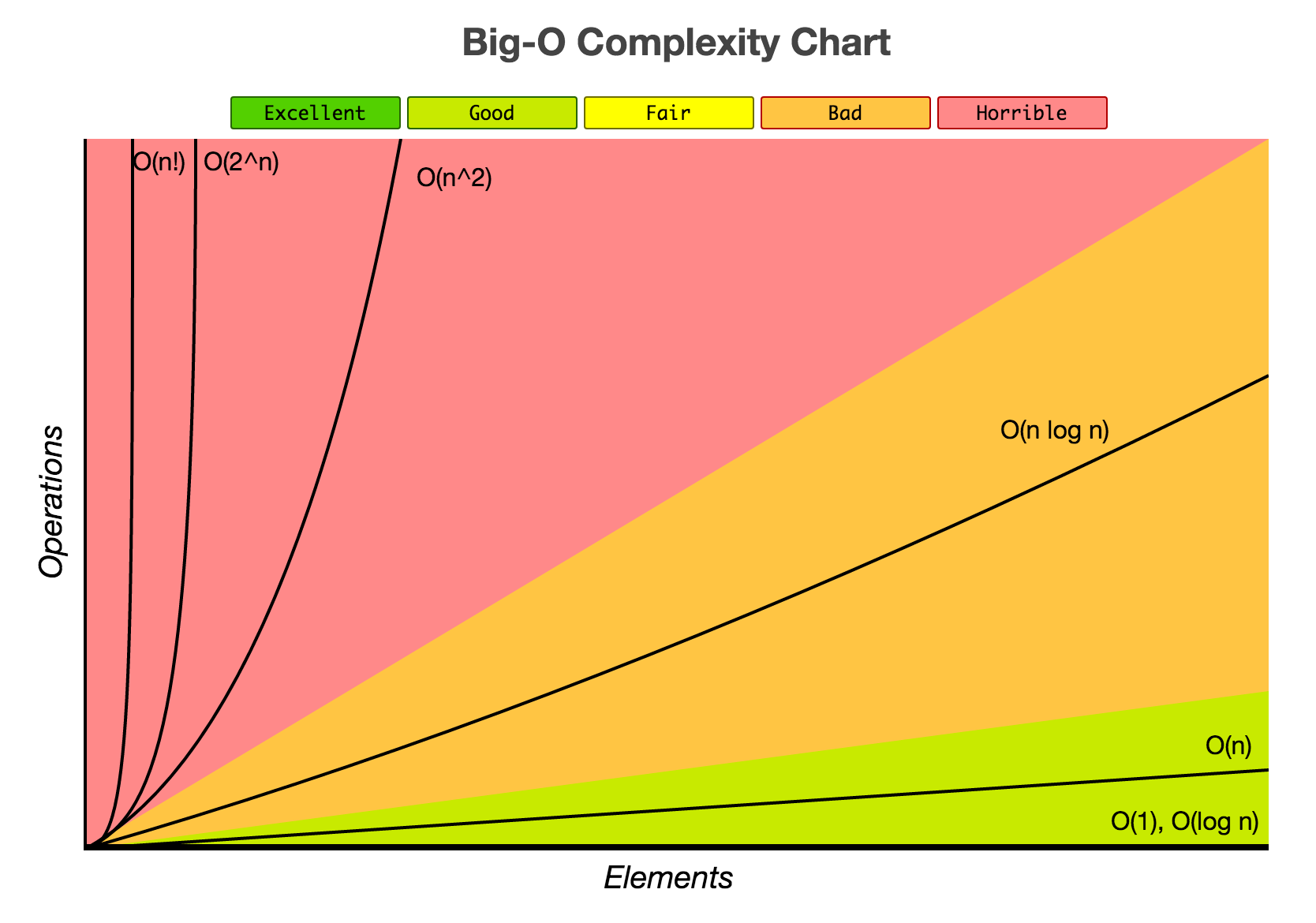
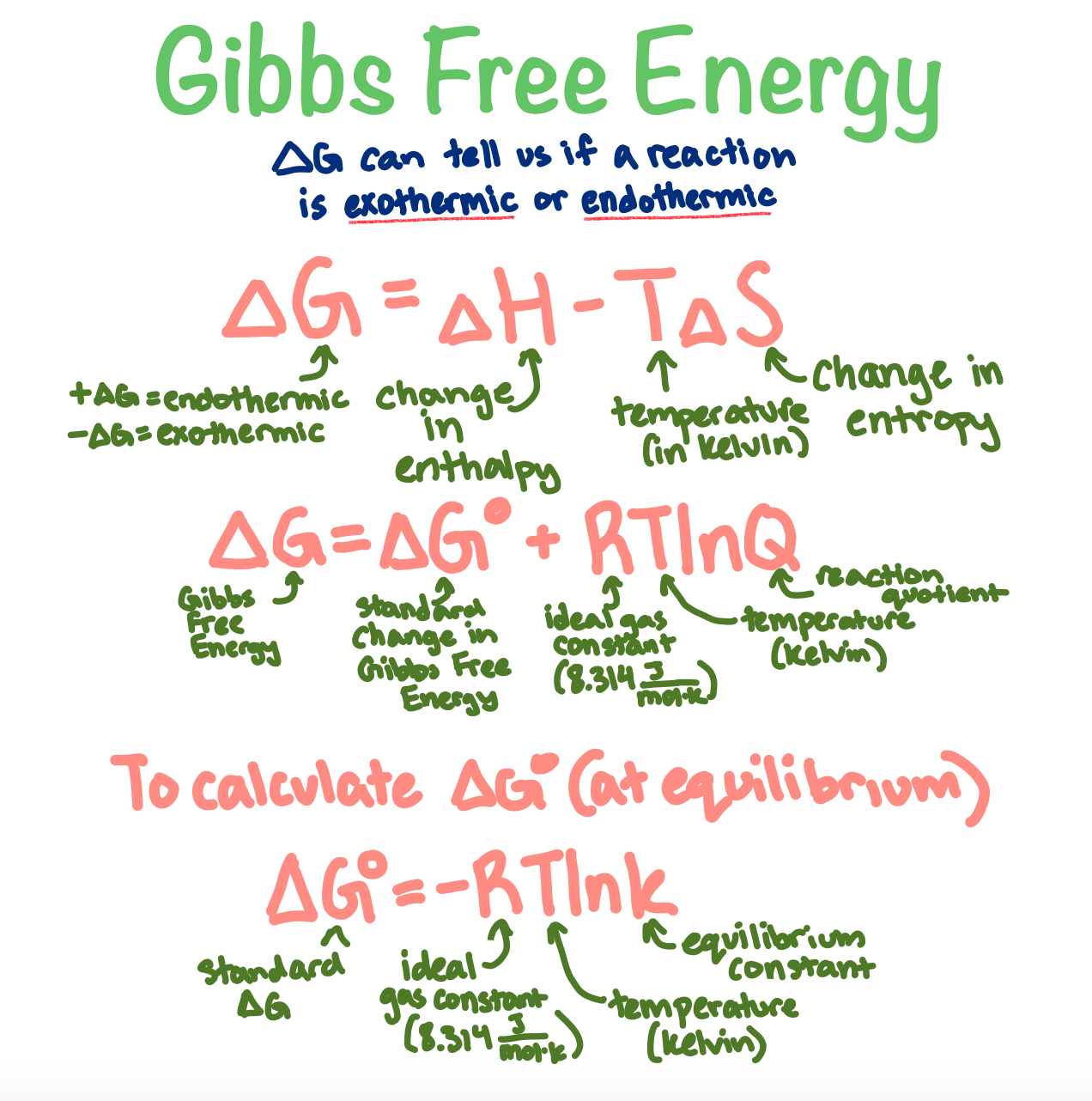
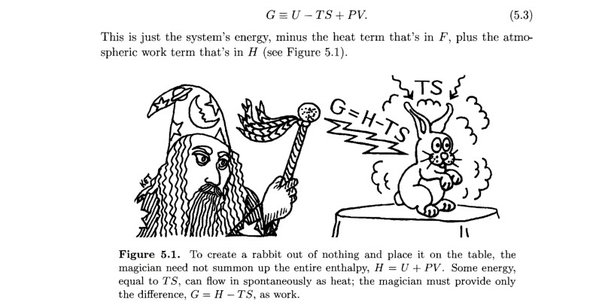
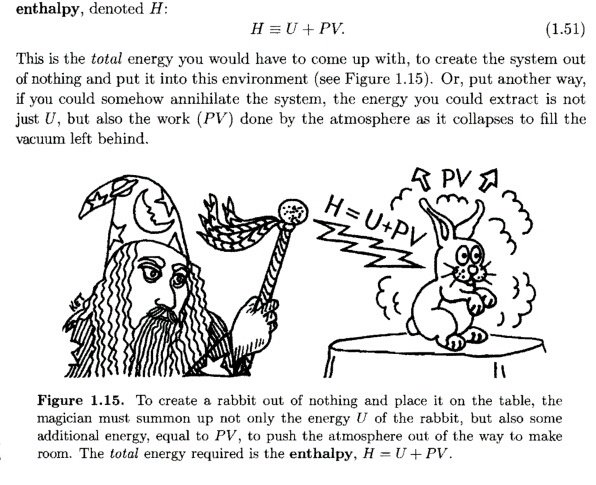
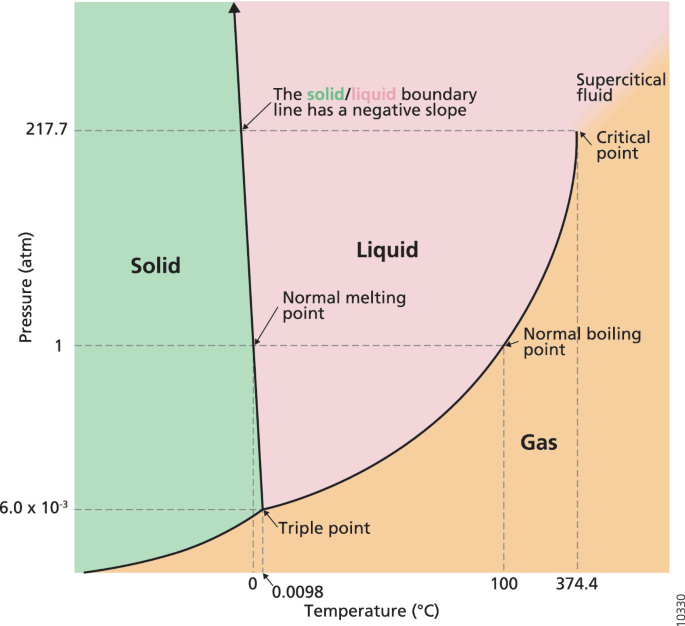
tag > Complexity
-
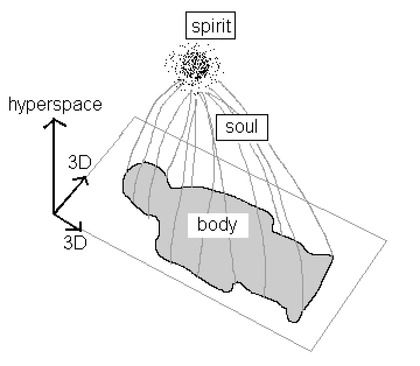
The human body completely changes the matter it is made of roughly every 8 weeks, through metabolism, replication and repair. Yet, you're still you --with all your memories, your personality... If science insists on chasing particles, they will follow them right through an organism and miss the organism entirely. — Robert Rosen (1934 - 1998)
-
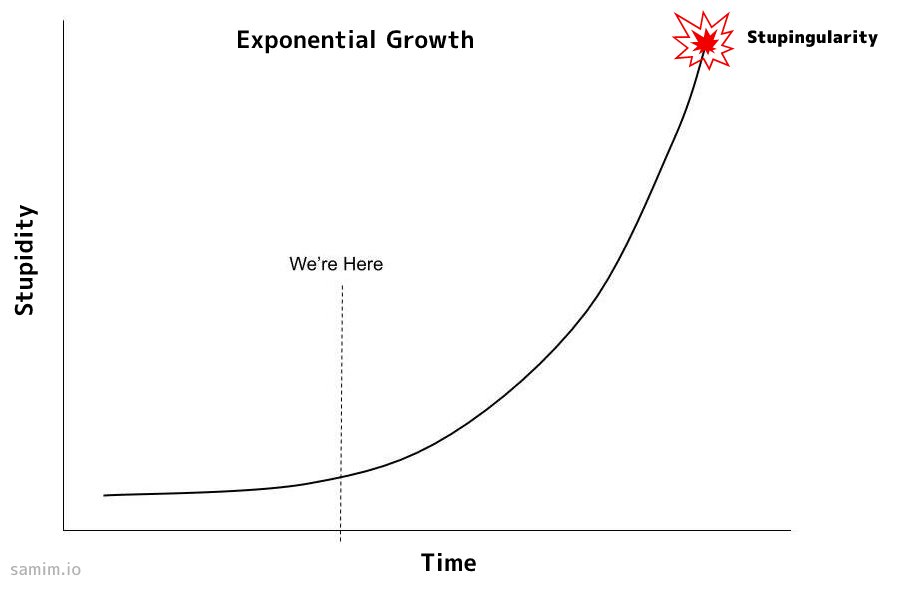
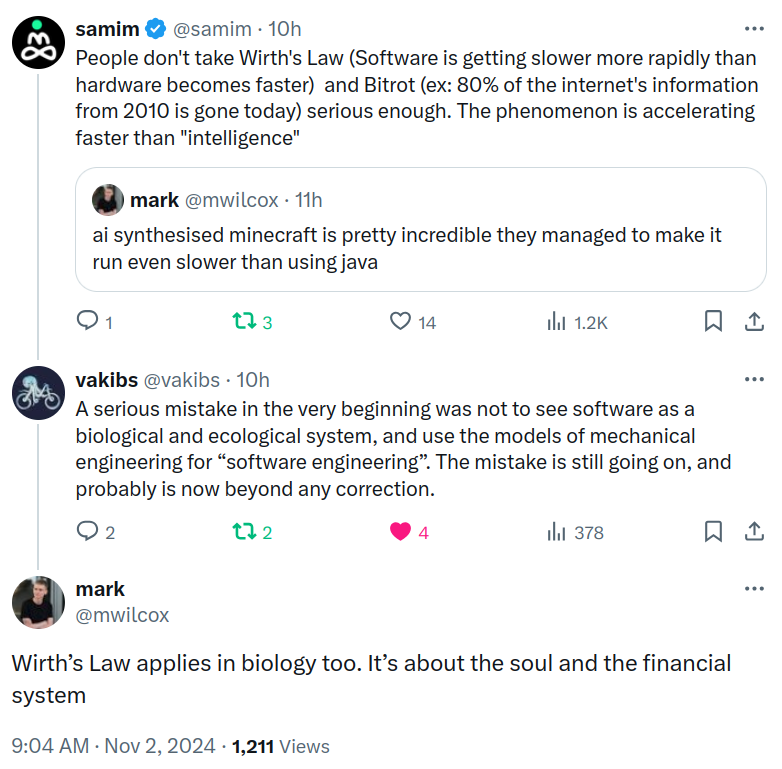
People don't take Wirth's Law (Software is getting slower more rapidly than hardware becomes faster) and Bitrot (ex: 80% of the internet's information from 2010 is gone today) serious enough. The phenomenon is accelerating faster than "intelligence". Niklaus Wirth, who was in intense exchanges with the Gnomes of Zürich, realized the spiritual dimension of software engineering early on.
-
Nuel Belnap (1930 - 2024) explored many interesting ideas during his long career


An analysis of Nuel Belnap's key philosophical contributions, particularly focusing on his work in logic and the philosophy of action.
Nuel Belnap is best known for several major contributions:
1. Four-Valued Logic
One of Belnap's most significant contributions is his four-valued relevance logic, developed with Alan Anderson. This logic system includes the traditional true and false values, but adds two more:
- Both (true and false)
- Neither (neither true nor false)
This was particularly influential in computer science and information systems, as it provides a framework for handling inconsistent or incomplete information.
2. Branching Time Theory
Belnap developed a sophisticated theory of branching time (also known as branching space-time), which is crucial for understanding:
- The nature of indeterminism
- The relationship between time and possibility
- How future contingents should be evaluated
3. The Theory of Agency and Action
His work with Michael Perloff and Ming Xu on the "stit" theory (seeing-to-it-that) is fundamental to understanding:
- How agents bring about changes in the world
- The logical structure of agency and action
- The relationship between choice, time, and causation
4. Knowledge Representation
His contributions to epistemic logic and belief revision include:
- How to represent and reason about knowledge states
- How to handle contradictory information
- The logic of questions and answers
5. Interrogative Logic (erotetic logic)
With Thomas Steel, Belnap developed important work on the logic of questions, including:
- The formal structure of questions and answers
- How to represent different types of questions
- The relationship between questions and knowledge
The philosophical significance of Belnap's work lies in several key insights:
1. Logic isn't limited to binary truth values - sometimes we need more sophisticated ways to represent information states.
2. Time and possibility are intimately connected, but their relationship is more complex than simple linear progression.
3. Agency and causation require careful formal analysis to understand properly.
4. Questions are as logically important as statements and deserve formal analysis.
More on Belnap's Theory of Agency and Action, particularly his influential "stit" (seeing-to-it-that) theory.
The "stit" theory is one of the most sophisticated logical analyses of agency and action ever developed. Here are its key components:
1. Core Concept of "Seeing-to-it-that"
- Instead of treating actions as primitive entities, Belnap analyzes them in terms of agents "seeing to it that" certain states of affairs come about
- The basic form is: [α stit: A] - which reads as "agent α sees to it that A"
- This shifts focus from actions themselves to their results/outcomes
2. Choice and Moments
Belnap's theory introduces several crucial elements:
- Moments: Points in time where choices can be made
- Choice cells: Sets of possible futures available at each moment
- Histories: Complete possible paths through time
- Agents have different choices available at different moments
3. Key Properties of Agency
The theory identifies several essential features of agency:
- Positive condition: The agent must make a difference
- Negative condition: The outcome shouldn't be inevitable
- Independence of agents: Different agents' choices are independent
- No backwards causation: Choices can only affect the future
4. Types of "stit" Operators
Belnap developed different versions of the stit operator:
- Achievement stit: Focusing on bringing about immediate results
- Deliberative stit: Involving conscious choice
- Strategic stit: Concerning long-term planning and strategy
5. Philosophical Implications
a) On Free Will:
- The theory provides a formal framework for understanding free will
- Shows how genuine choice can exist in a causally structured world
- Demonstrates how multiple agents can have real choices simultaneously
b) On Responsibility:
- Helps clarify when an agent is truly responsible for an outcome
- Distinguishes between direct and indirect responsibility
- Shows how responsibility relates to available choices
c) On Causation:
- Provides a sophisticated account of agent causation
- Shows how individual agency relates to broader causal structures
- Distinguishes between different types of causal influence
6. Applications
The theory has been applied to:
- Legal reasoning about responsibility
- Computer science (especially in multi-agent systems)
- Ethics (particularly in analyzing moral responsibility)
- Game theory
- Decision theory
7. Key Insights
a) Agency is Relational:
- Being an agent isn't just about having properties
- It's about standing in certain relations to outcomes
- These relations are temporally structured
b) Choice is Fundamental:
- Agency can't be reduced to mere causation
- Real choice requires genuine alternatives
- Choices must be effective but not guaranteed
c) Time and Agency are Interlinked:
- Agency only makes sense in a branching time structure
- Present choices affect which futures are possible
- Past choices constrain but don't determine future ones
8. Extensions and Developments
The theory has been extended to handle:
- Group agency
- Institutional action
- Probabilistic outcomes
- Normative concepts (obligations, permissions)
9. Current Relevance
The theory remains particularly relevant for:
- AI ethics (understanding artificial agency)
- Social robotics
- Collective responsibility
- Digital ethics and accountability
Belnap's theory of agency stands out for its mathematical rigor combined with philosophical depth. It shows how formal logical methods can illuminate fundamental questions about human action and responsibility. The theory continues to influence discussions in philosophy of action, ethics, and computer science.
-
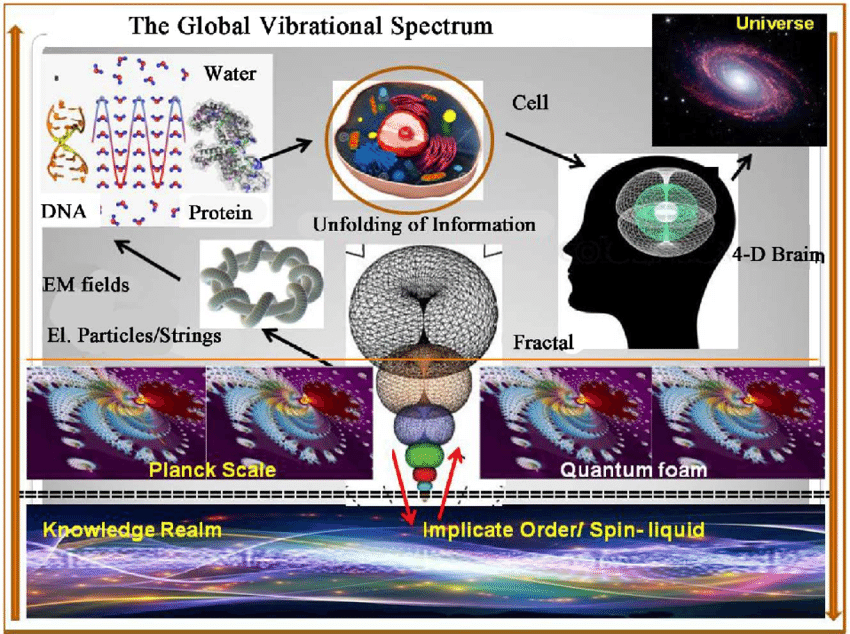
In complex, self-organizing systems like animals, plasmas, and crystals, filtering and composting abundant information is far more crucial than creating new information.

-
Complexity is not the problem. Ambiguity is. Simplicity does not solve ambiguity. Clarity does.

-
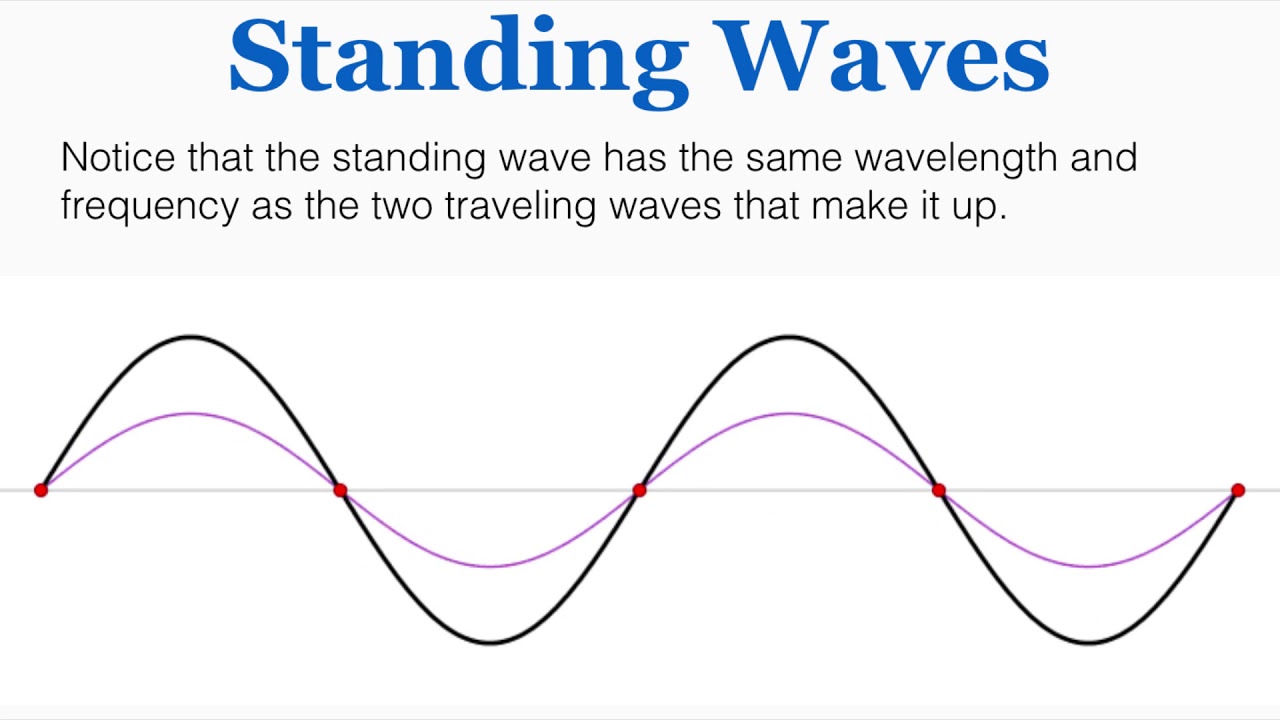
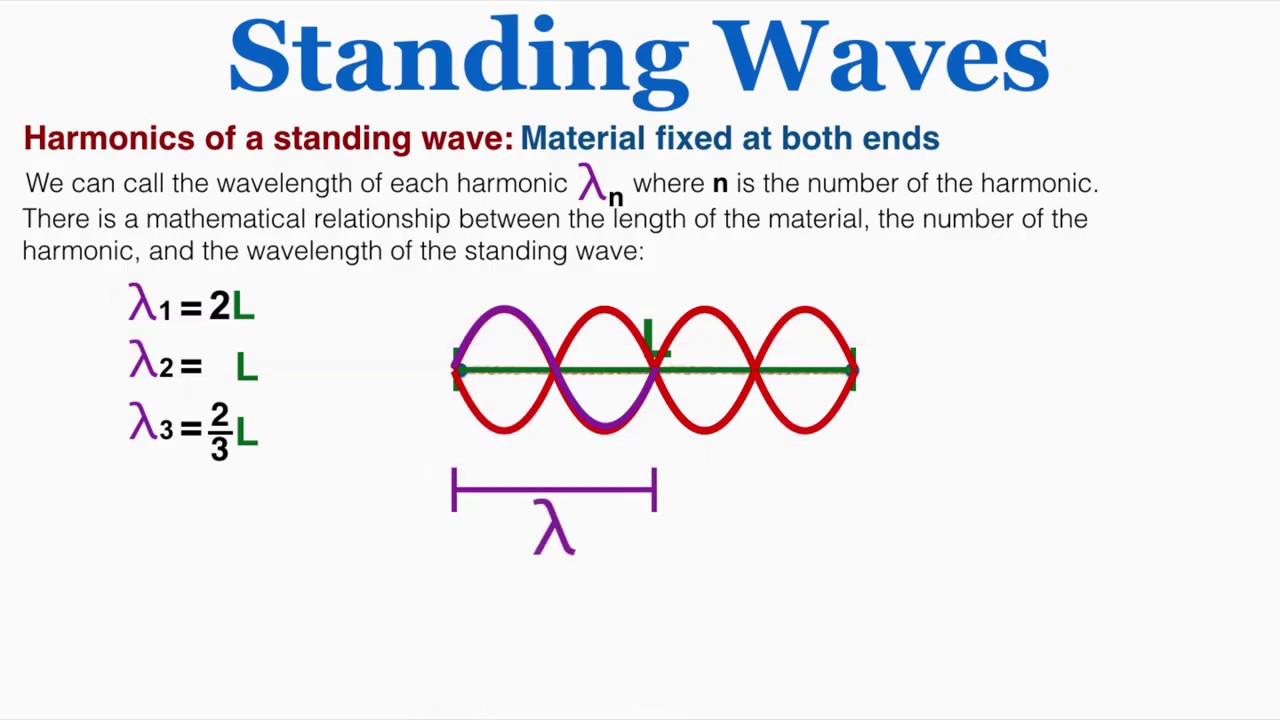
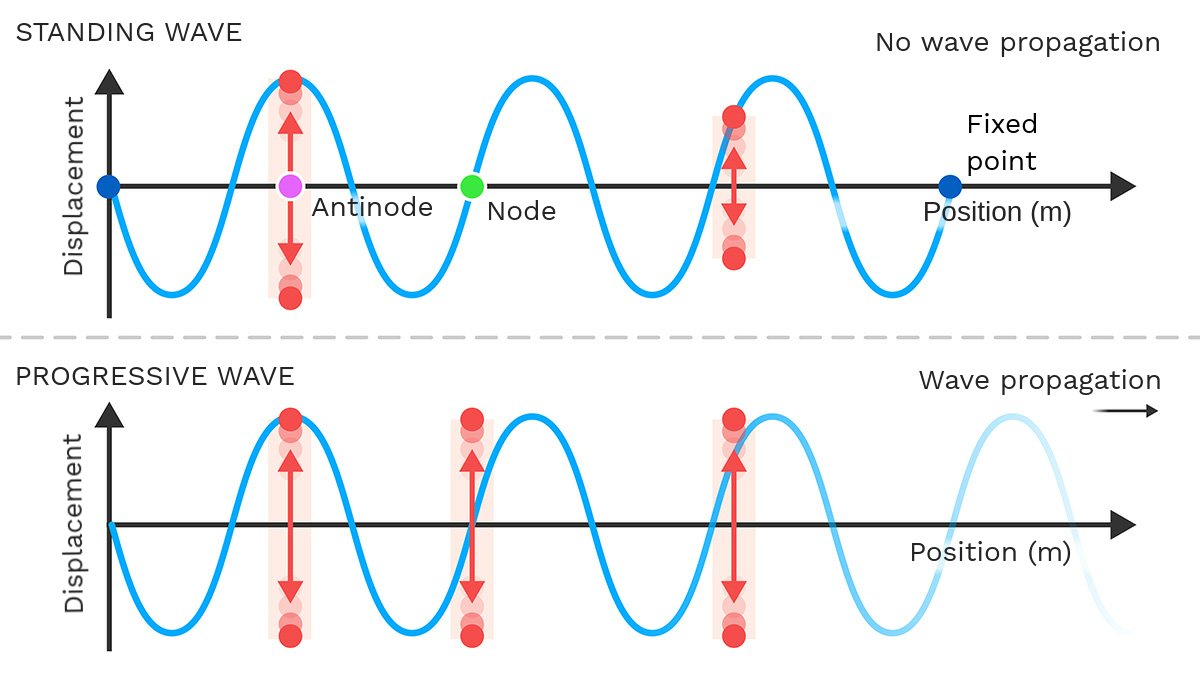
Standing waves is a wave that oscillates in time but whose peak amplitude profile does not move in space. They are formed by the superposition of two travelling waves of the same frequency travelling in opposite directions.
With 60% of the human body made up of water, it’s surprising how little we’ve explored standing waves and resonance effects within the body. This field seems to be in its infancy.
-
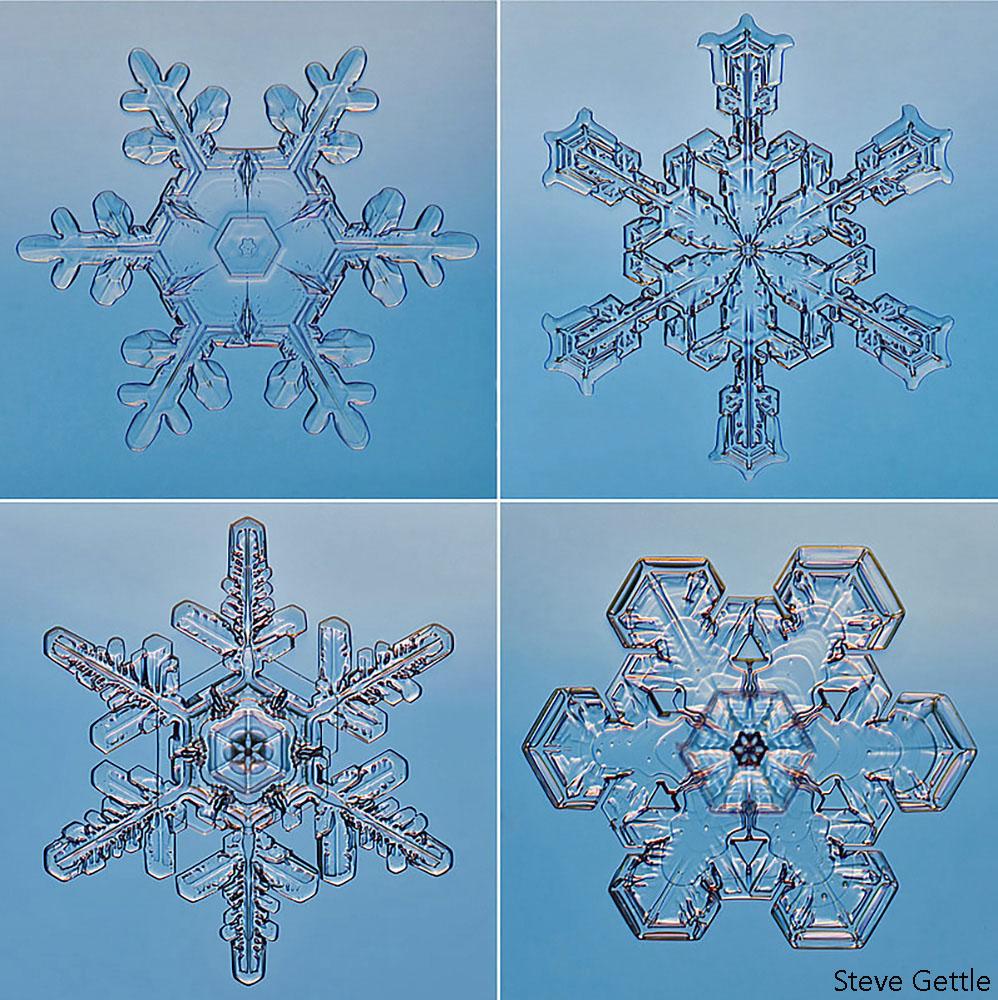
To the attentive mind, snowflake observation sparks deep questions about the nature of life & reality.

-
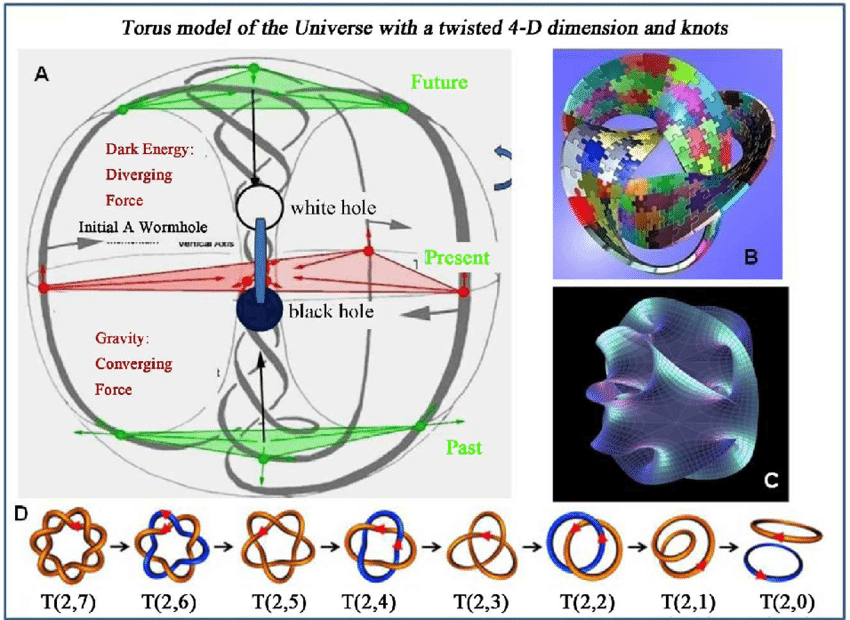
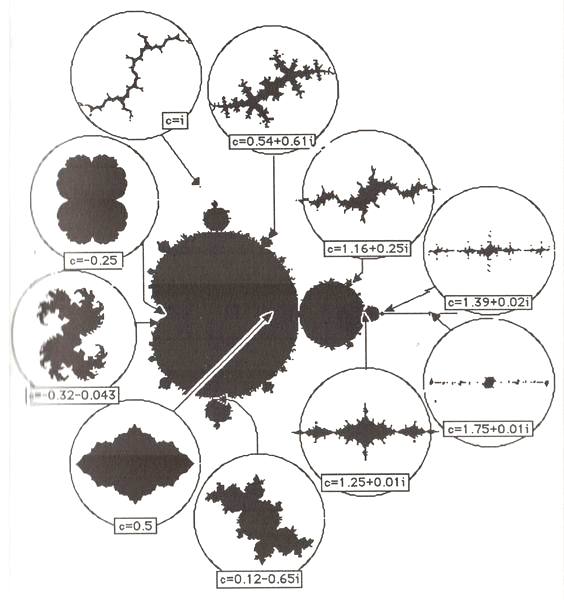
In the decades ahead, scientists will acknowledge that at the center of the decentralized hologram we call reality is a paradoxical, none-computational black hole, transforming everything into nothing and back again.

-
The study of self-organizing systems that exhibit intelligent behavior is too heavily focused on linear-time-bound causal cases. The real mystery lies in timeless, acausal phenomena like time crystals. Next gen post-computation systems embrace the eternal paradox at their core.
-
Viktor Shauberger observed implosive (collapse inward) energy of water, as opposed to explosive (collapse outward) energy. Life grows through a series of controlled implosive principles. Ancients mastered the way of water, ie the way of implosion.


-
"The Wi-Fi password is written on the back of the router." - möbius strip edition.
-
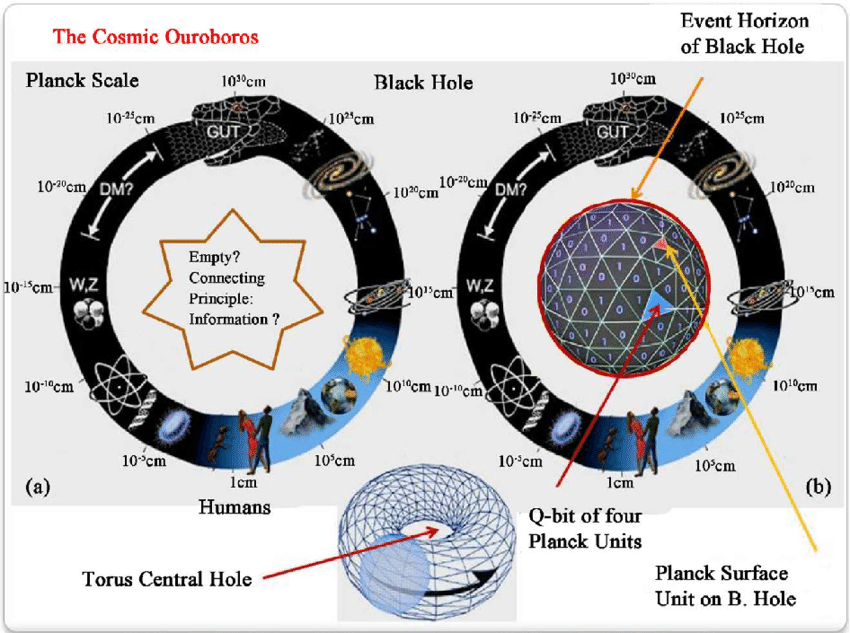
High-dimensional phenomena bend our intuition like spacetime bends light. Yet, they're mere ripples in the cosmic Ouroboros. In this reality, the counterintuitive is the appetizer; paradox is the main course.