tag > NeuroScience
-
The Magical Number Seven, Plus or Minus Two
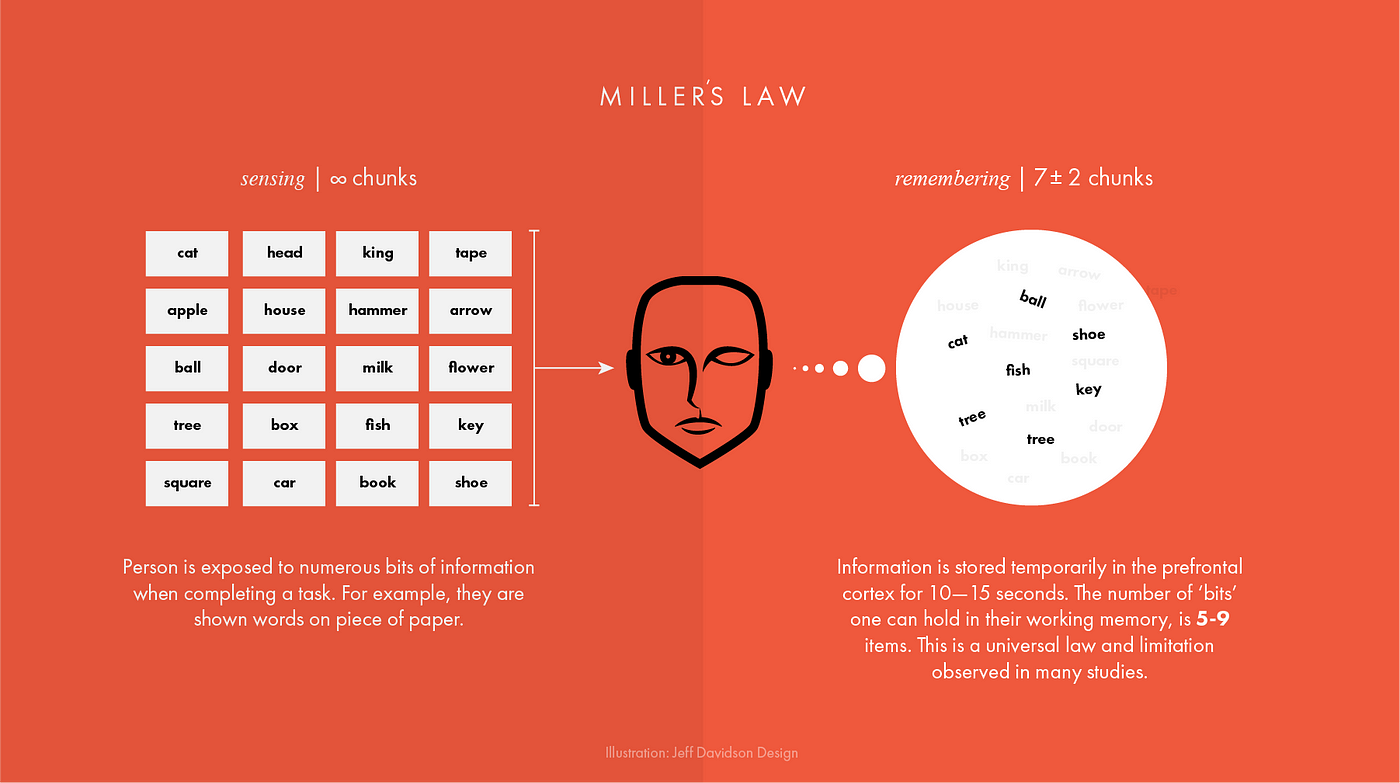
One of the most highly cited papers in psychology, written by the cognitive psychologist George A. Miller in 1956. It is often interpreted to argue that the number of objects an average human can hold in short-term memory is 7 ± 2.
-
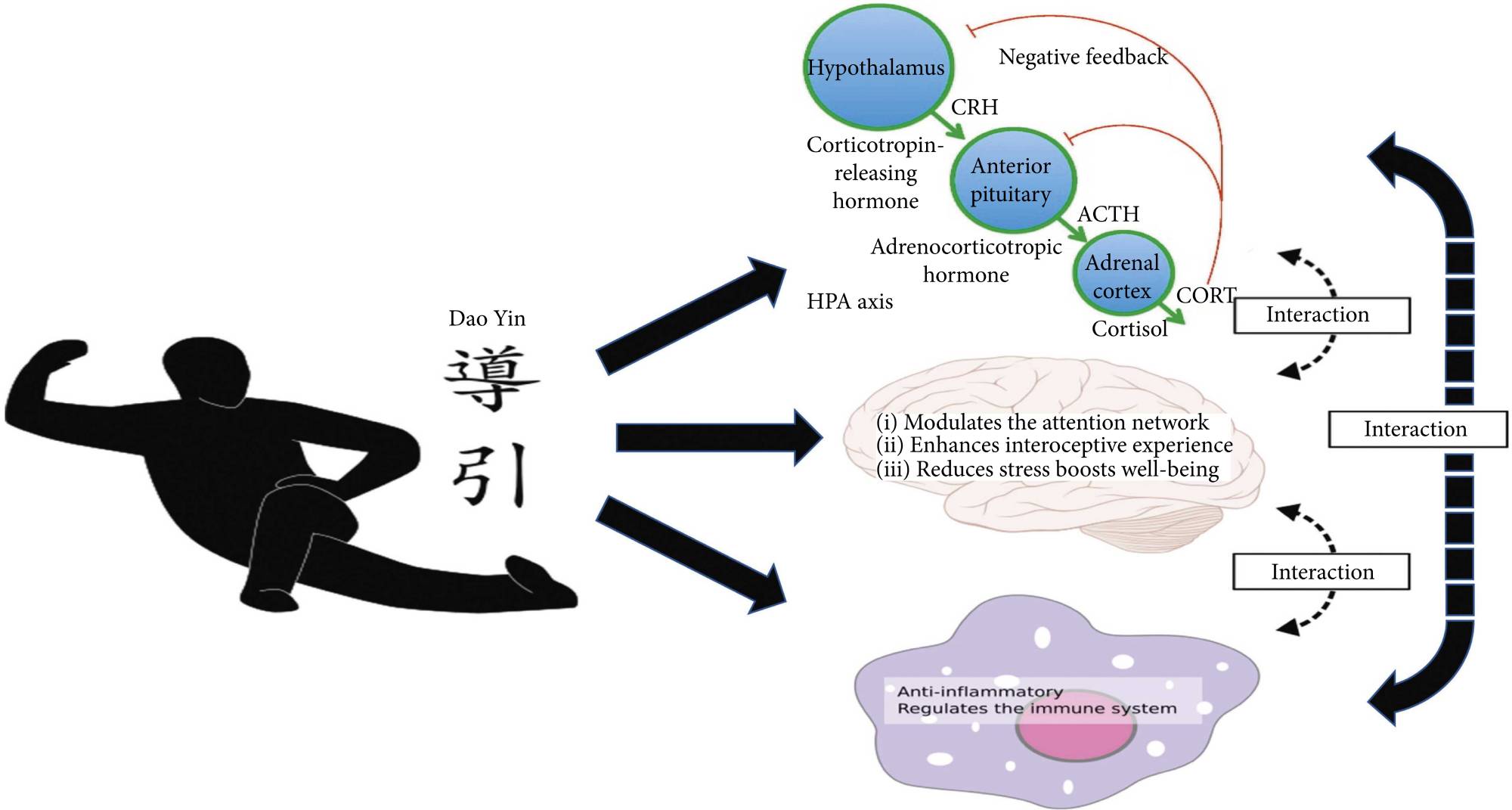
Diagram of the interaction of Dao Yin exercise with inflammatory markers & brain mechanisms.
-
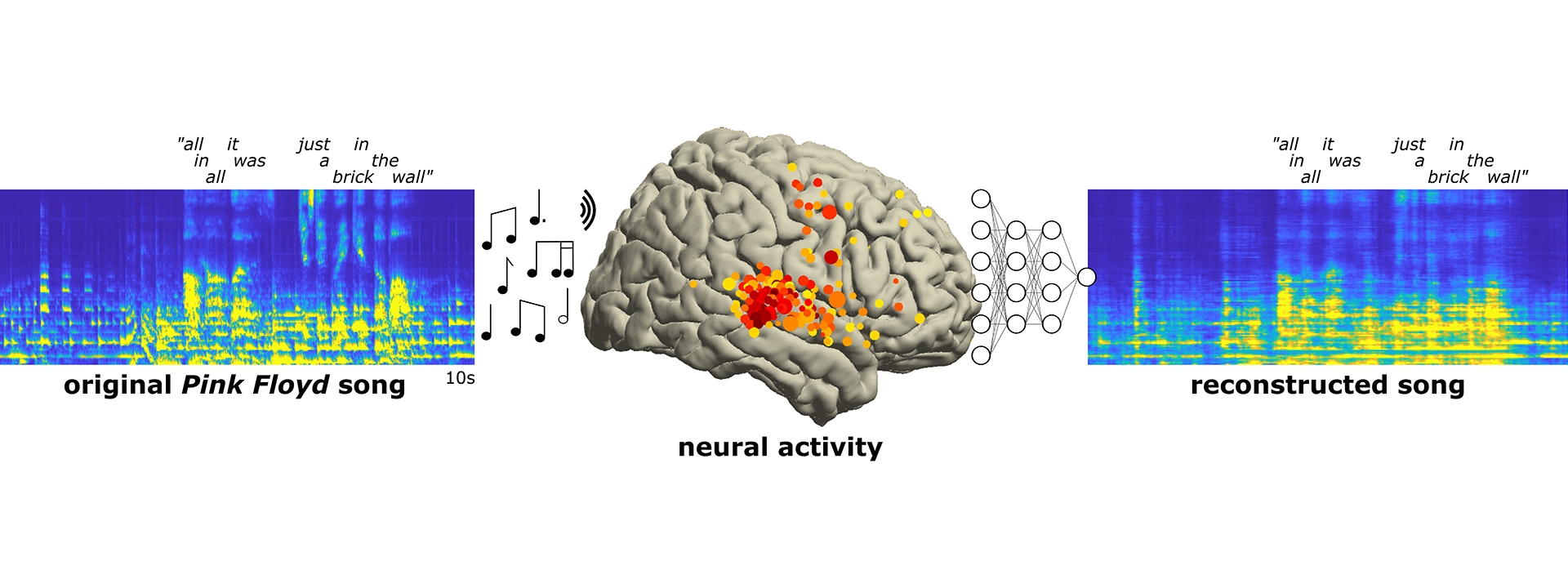
Brain recordings capture musicality of speech — with help from Pink Floyd - Neuroscientists decode song from brain recordings, revealing areas dealing with rhythm and vocals
-
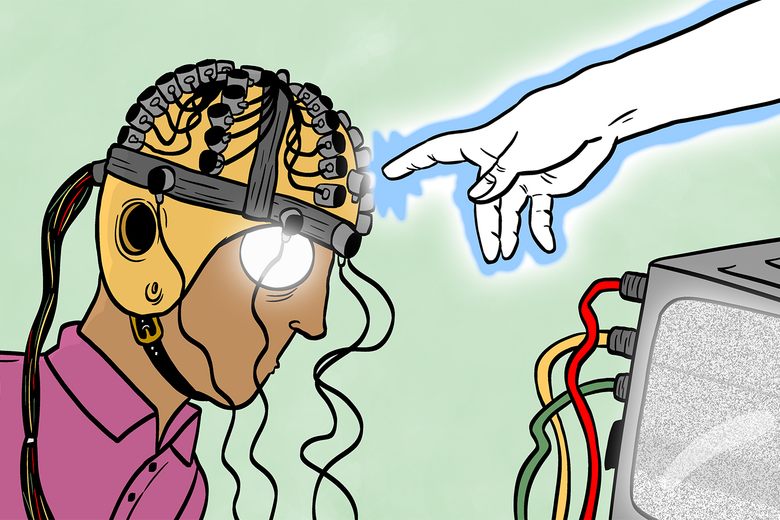
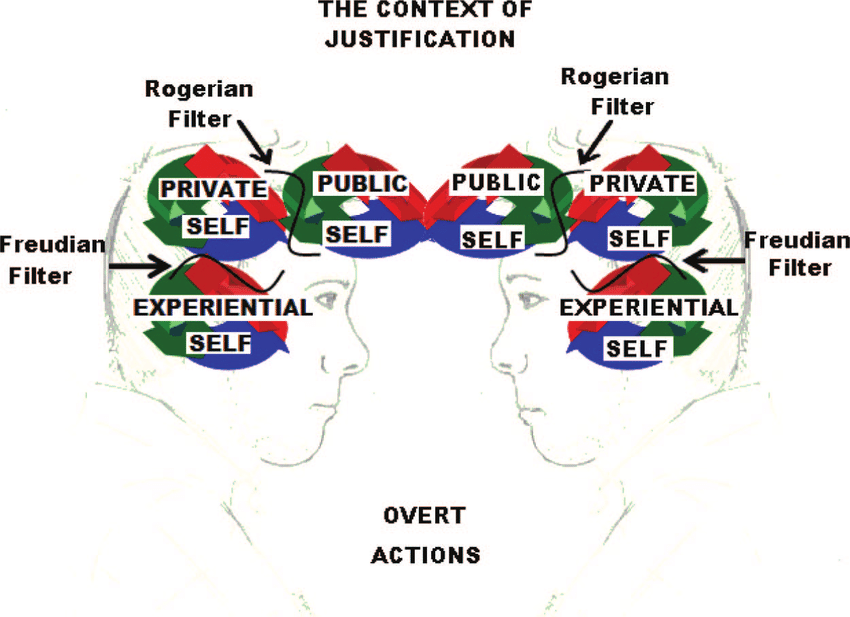
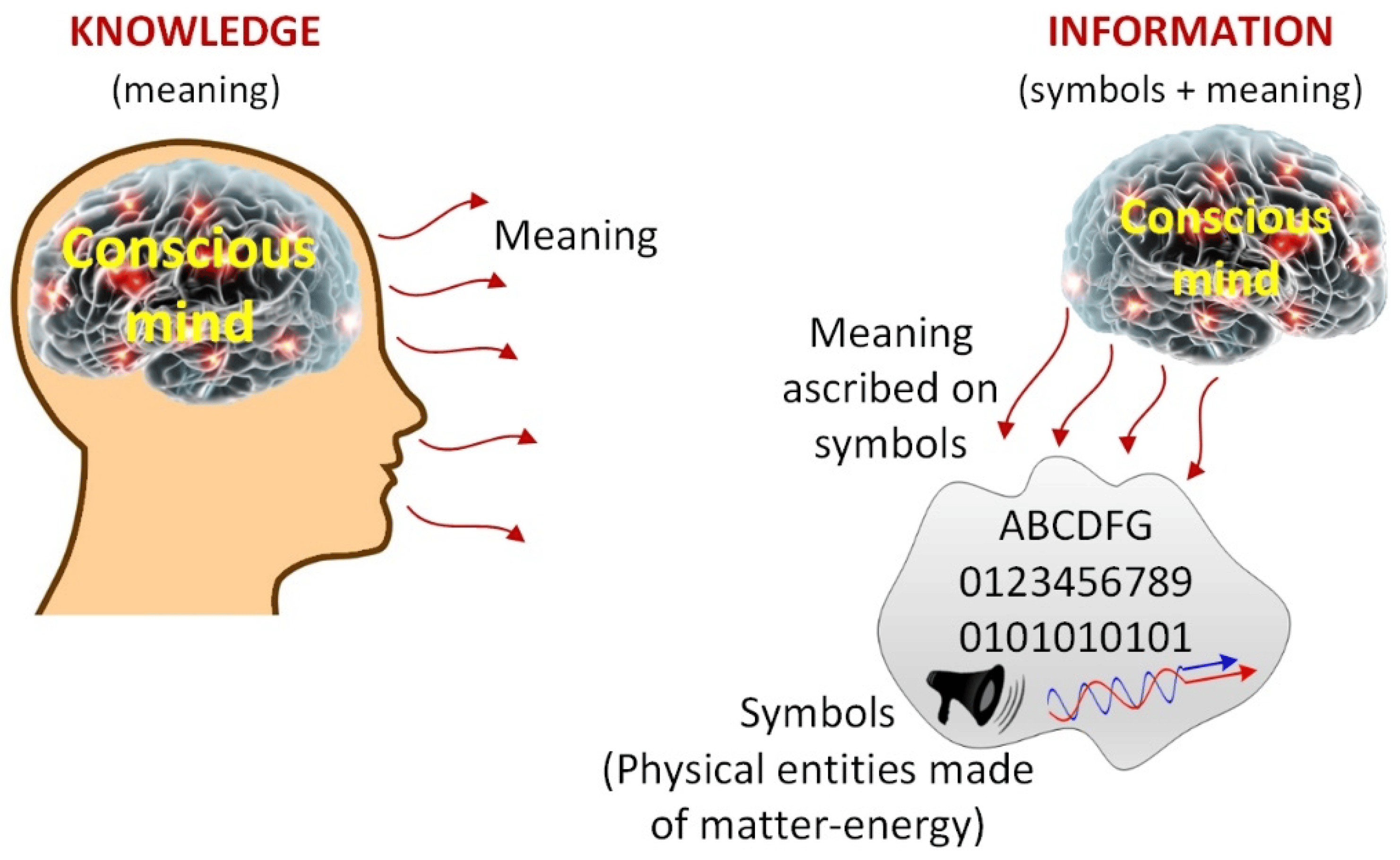
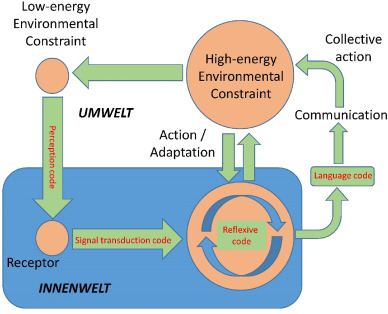
A core assumption of neuro- and computer science is that computation is local & independent - that the brain is effectively separated from the 'outside world' by a thin box of bones. In reality, every 'box' is highly leaky and everything is deeply intertwingled.
-
Macaque monkeys and humans sample temporal regularities in the acoustic environment
“The perception, if not the enjoyment, of musical cadences and of rhythm is probably common to all animals and no doubt depends on the common physiological nature of their nervous system” – Charles Darwin

-
Paradoxically, extremely stupid things are overwhelmingly done by extremely intelligent people throughout history.
The study of stupidity is a unexplored territory. It isn't merely the antithesis of intelligence, but a standalone phenomenon that permeates all strata of society, propelling evolution in peculiar ways. In our pursuit of AI, it's high time we also explore Artificial Stupidity.
Related: The Sixth Law of Stupidity: A Biophysical Interpretation of Carlo Cipolla’s Stupidity Laws
Related: Bonhoeffer’s Theory of Stupidity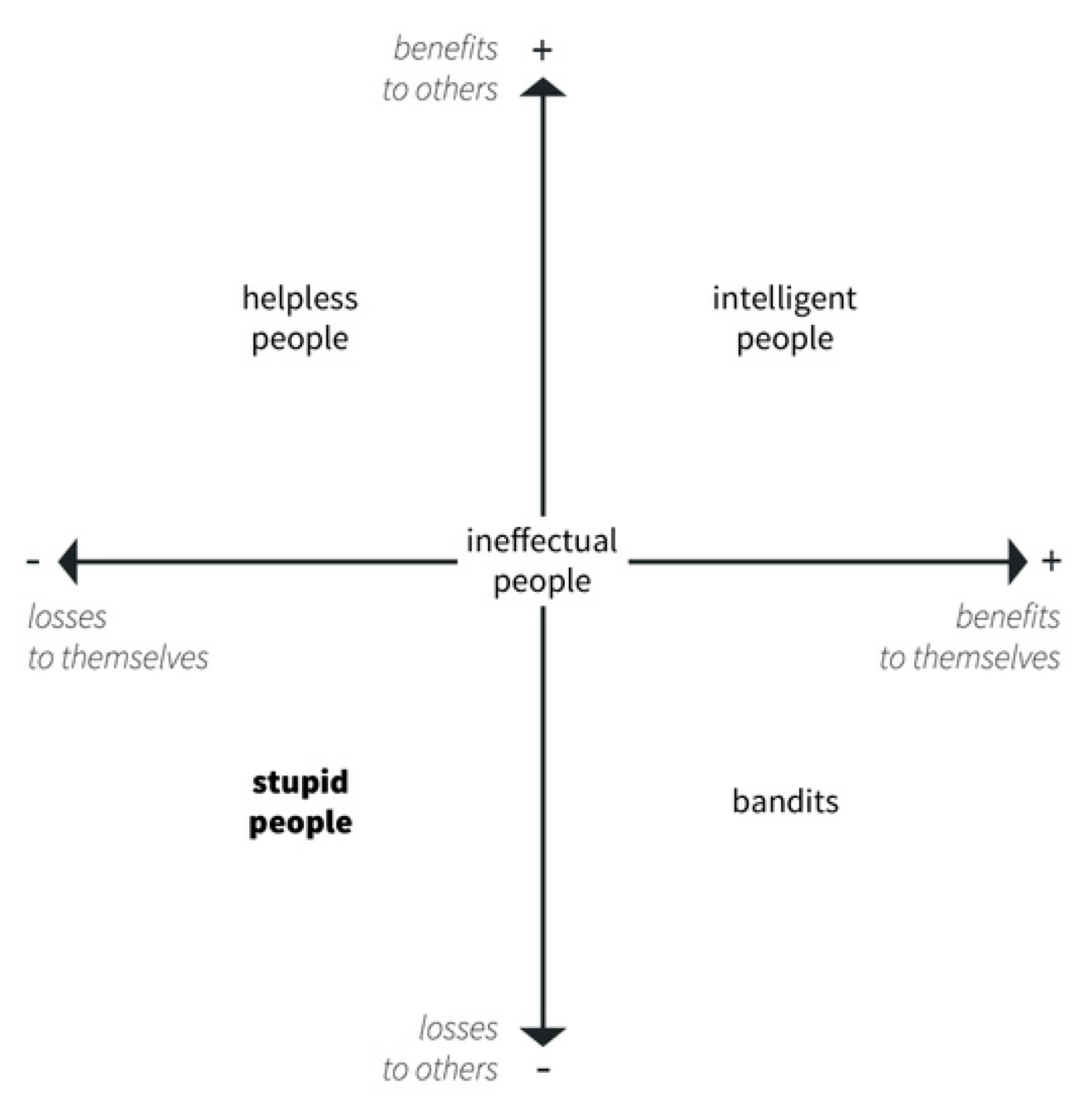
-
The geometry of your brain shapes its function: Brain activity may be more like "ripples in a pond" rather than signals sent on a telecommunications network.
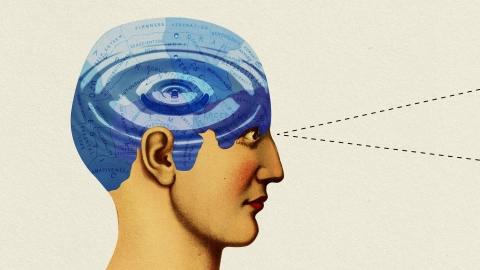
Researchers have challenged the conventional "connectomic" view of the brain, suggesting that brain function may be more akin to ripples in a pond than signals in a telecommunication network. They found that their wave model, which uses information about the brain's shape, predicted activation patterns more accurately than neuronal connectivity data. While the study suggests a paradigm shift in understanding brain function, critics argue that the study doesn't consider the local brain activity patterns evoked by simple stimuli.
-
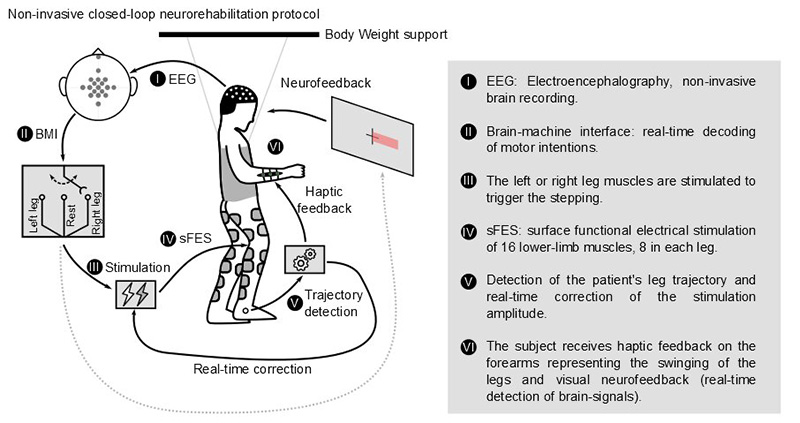
When using a computer, your brain and body performs a complex dance of cognitive processes, engaging attention, memory, and problem-solving skills to navigate the digital landscape.
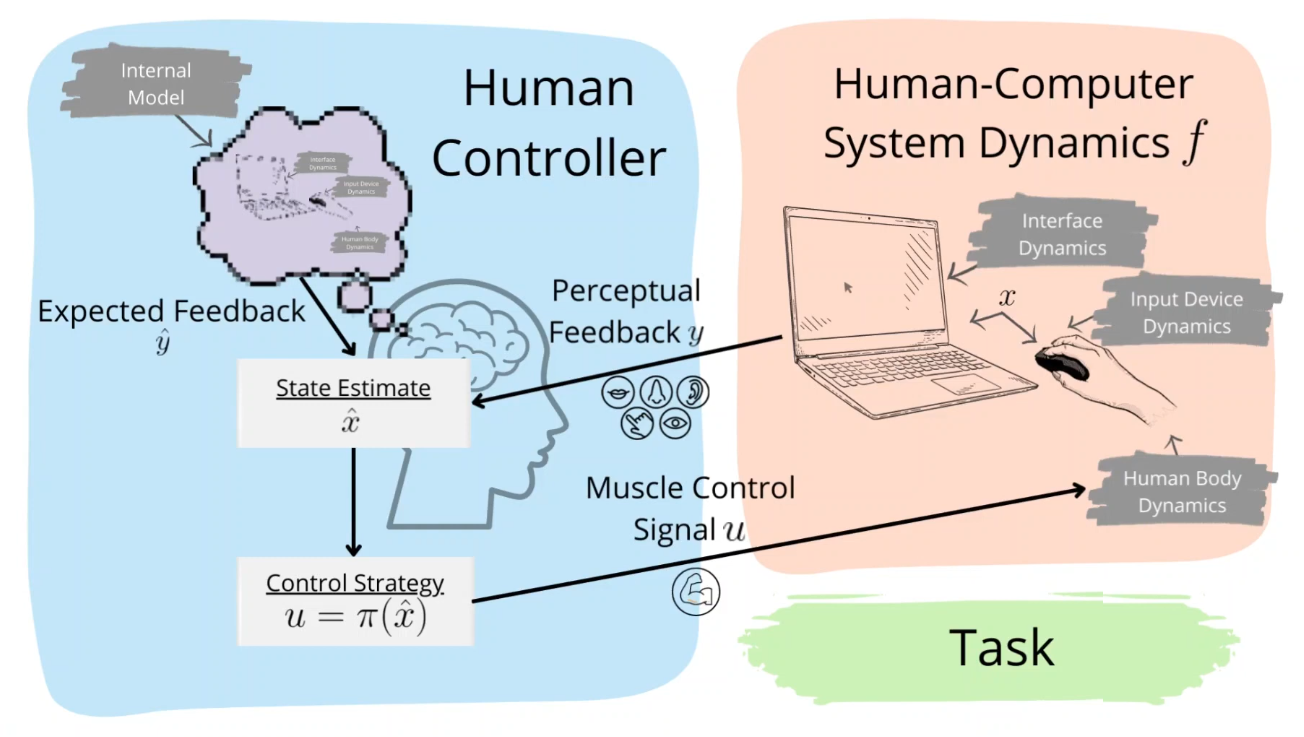
(from "Optimal Feedback Control for Modeling Human-Computer Interaction") #HCI #NeuroScience
-
The notion that "intelligence" and "life" is a "distinct thing" that is contained "in a box" is likely one of the most short-sighted dogmatisms in current AI & Neuroscience culture.