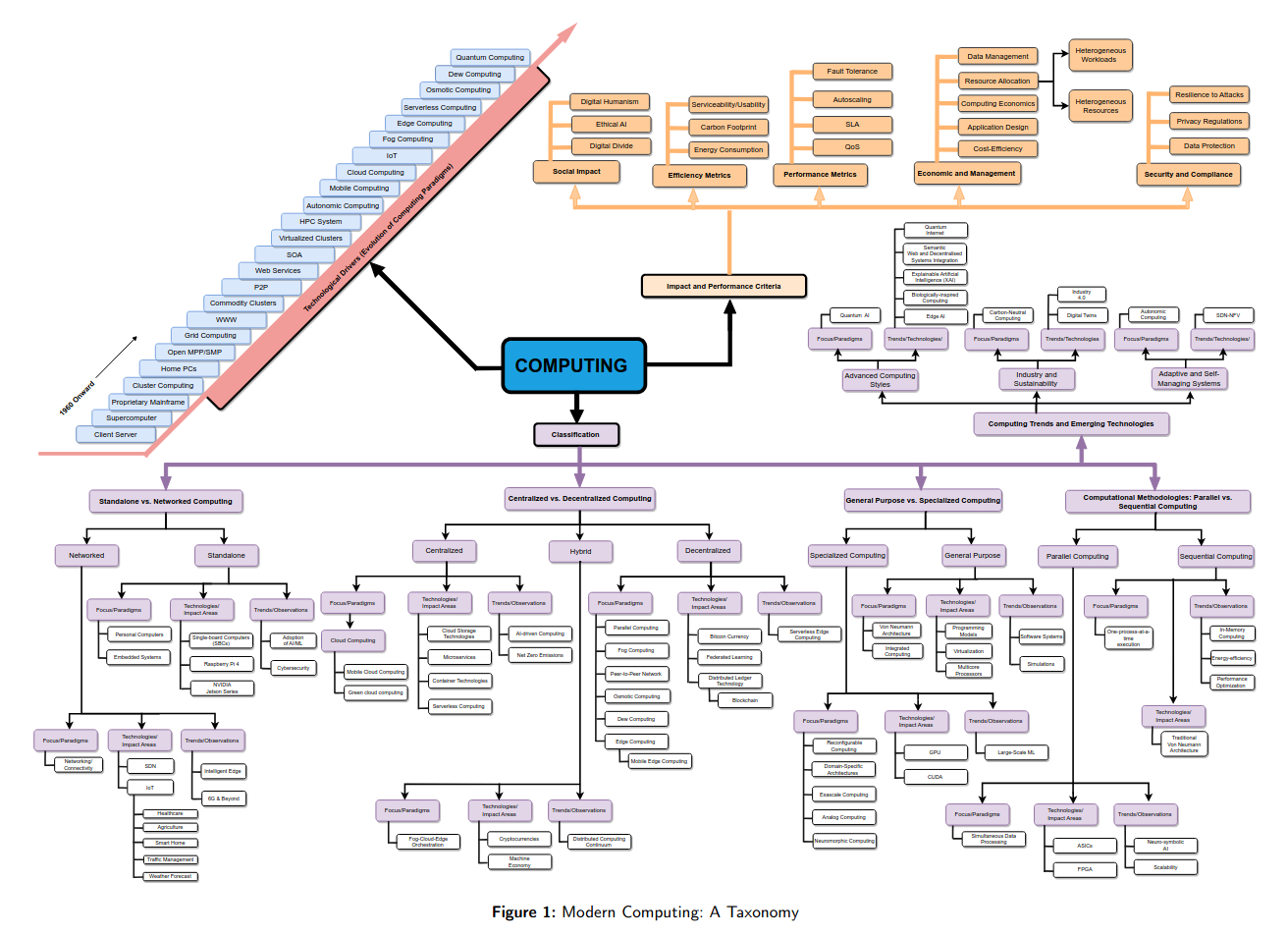
tag > Complexity
-
Phase-locked loop (blog, video)
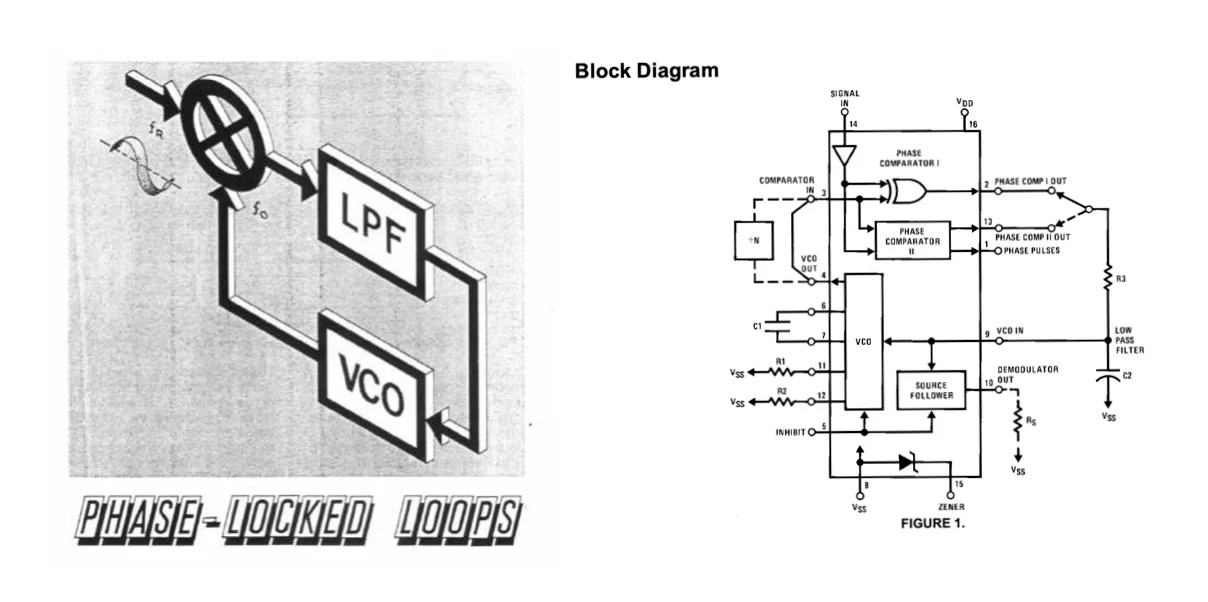
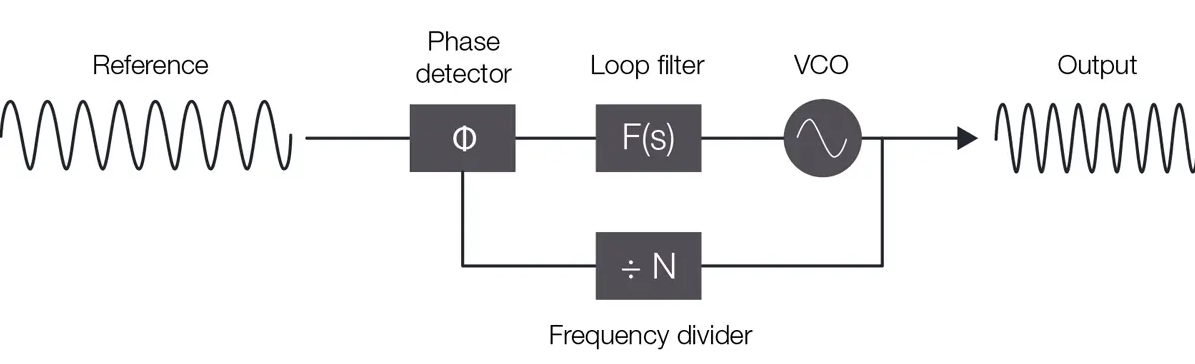
Reminder: Any place biology needs to compare phases (timing) and feed back a control signal to adjust an oscillator - whether it’s molecules in a cell, neurons in your ear, or cells in your heart - you’ll find PLL‐like behavior that helps keep everything ticking in harmony.
-
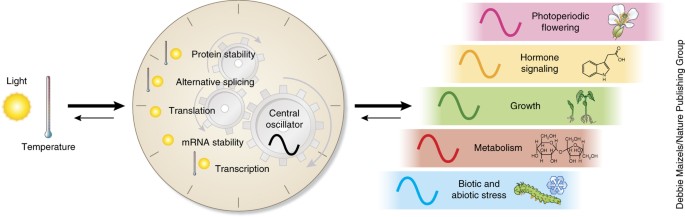
κ_catuskoti: A Meta-Logical Framework for Contradiction-Tolerant, Self-Referential Paradox Computation
Samim.A.Winiger - 5.5.2025
Abstract
Traditional logic systems, rooted in the binary true/false dichotomy, break down in the presence of paradox, contradiction, and self-reference. Yet such phenomena are not marginal—they are central to language, consciousness, ethics, and the very foundations of mathematics. Inspired by the Buddhist tetralemma _catuskoti_ and informed by developments in paraconsistent and fixed-point logic, we introduce κ_catuskoti: a meta-logical framework that treats paradoxes as structurally navigable rather than fatal flaws.
κ_catuskoti extends standard logic with four truth values—true, false, both, and neither—allowing it to model contradiction \((P \wedge \neg P)\) and indeterminacy (neither P nor ¬P) natively. A key innovation is the self-reflective operator ρ, which enables controlled recursive evaluation of self-referential expressions, including classic paradoxes like the Liar and Russell. We provide a formal syntax, semantics, and computational prototype, and demonstrate the logic’s applicability in reasoning agents, ambiguous ethical scenarios, and meta-linguistic cognition. By parameterizing logical modes with \(\Delta_i\), κ_catuskoti bridges classical, dialetheist, and paraconsistent reasoning. This framework offers a new foundation for logical systems that aim to engage with the complexity of real-world reasoning rather than abstract it away.
_Paradox Computation is simultaneously paradoxical and computational while paradoxically being neither paradoxical nor computational. It computes by not computing and creates paradoxes by resolving them. What is the sound of one hand clapping? Mu!_”
1. Introduction
Classical logic falters in the face of paradox, contradiction, and self-reference. These phenomena are not just edge cases; they permeate natural language, cognition, ethics, and computation. Systems that reject or suppress them risk misrepresenting complex, ambiguous realities. κ_catuskoti addresses this gap by building a formal, contradiction-tolerant logic grounded in Buddhist and paraconsistent traditions, capable of modeling self-reference, oscillation, and epistemic uncertainty. This paper presents the κ_catuskoti framework, including its formal syntax and four-valued semantics, the novel self-reflective operator (\(\rho\)) for handling fixed-point paradoxes, and a computational prototype demonstrating its application to challenging reasoning scenarios.
2. Philosophical Background
The philosophical background of κ_catuskoti weaves together threads from Buddhist logic, paraconsistent logic, and modern self-referential meta-theories, forming a logic that welcomes paradox rather than eliminating it.
2.1. Buddhist Origins: The Catuskoti
From early Buddhist Madhyamaka philosophy, the _catuskoti_ (Sanskrit: चतुष्कोटि, “four corners") breaks with classical binary logic:
For any proposition P, four possibilities exist:
- P (affirmation)
- ¬P (negation)
- P ∧ ¬P (both)
- ¬P ∧ ¬¬P (neither)
Nāgārjuna, a key philosopher, used this to show the limits of conceptual thought and the emptiness of fixed views. In contrast to Aristotelian logic, which treats contradiction as fatal, _catuskoti_ accepts that some truths are beyond binary classification.[^2]
2.2. Paraconsistency and Dialetheism
Modern paraconsistent logic—developed by thinkers like Graham Priest—allows contradictions to exist without collapsing the system (avoiding _explosion_, where anything can be proven).
- In dialetheism, some contradictions are true (e.g. “This sentence is false").
- κ_catuskoti inherits this tolerance, but adds granularity: not only can P and ¬P both be true, but they can also be indeterminate or change truth-value under context.
2.3. Self-Reference and Meta-Logic
Traditional logic struggles with self-reference:
- The Liar Paradox: “This sentence is false.”
- Russell’s Paradox: The set of all sets that don’t contain themselves.
Most classical solutions involve restrictions or hierarchies (e.g., type theory). But κ_catuskoti, via the ρ operator, embraces self-reference as a native part of reasoning.
ρ allows:
- Fixed-point semantics for paradoxical expressions
- Meta-cognitive stepping outside the system to re-evaluate rules
- Context-sensitive interpretation (via Δ_i)
2.4. Motivations
κ_catuskoti arises from a need to:
- Model ambiguous, paradoxical, or self-referential domains (like natural language, ethics, AI consciousness, or philosophy of mind)
- Build resilient reasoning systems that do not break on contradiction
- Reflect the complexity of real-world cognition and language, which defy classical dichotomies
In essence: κ_catuskoti is not just a formal tool—it’s a philosophical stance:
The world and thought are not always binary. Logic must evolve to match their complexity.
3. Syntax and Semantics of κ_catuskoti
3.1 Syntax
We begin with a classical logical syntax extended with modal and self-referential operators. The language includes atomic propositions, standard Boolean connectives, and two non-classical constructs:
- \(\rho\): a self-reflective operator enabling fixed-point constructions
- \(\Delta_i\): a modal context shift operator, used to tune logical tolerance
The grammar of well-formed formulas is defined recursively:
\[ \phi ::= p \mid \neg\phi \mid (\phi \wedge \phi) \mid (\phi \vee \phi) \mid (\phi \rightarrow \phi) \mid \rho(\phi) \mid \Delta_i(\phi) \]3.2 Semantics
3.2.1 Truth Values and Valuation
The κ_catuskoti logic operates over a four-valued semantic domain:
\[ \mathbb{V} = \{\top, \bot, \mathbb{B}, \mathbb{N}\} \]Each value corresponds to a distinct logical state:
- \(\top\): true
- \(\bot\): false
- \(\mathbb{B}\): both true and false (contradictory)
- \(\mathbb{N}\): neither true nor false (indeterminate)
A valuation function \(v : \Phi \to \mathbb{V}\) assigns each formula a value in this domain.
3.2.2 Semantics of Connectives
Let \(\phi, \psi \in \Phi\) and define:
For the definitions of conjunction, disjunction, and implication that follow, the conditions within each
casesblock are to be evaluated in order from top to bottom. The first condition that holds true determines the semantic value of the expression.Negation
\[ v(\neg \phi) = \begin{cases} \bot & \text{if } v(\phi) = \top \\ \top & \text{if } v(\phi) = \bot \\ \mathbb{B} & \text{if } v(\phi) = \mathbb{B} \\ \mathbb{N} & \text{if } v(\phi) = \mathbb{N} \end{cases} \]Conjunction
\[ v(\phi \wedge \psi) = \begin{cases} \bot & \text{if } \bot \in \{v(\phi), v(\psi)\} \\ \mathbb{N} & \text{if } \mathbb{N} \in \{v(\phi), v(\psi)\} \\ \mathbb{B} & \text{if } \mathbb{B} \in \{v(\phi), v(\psi)\} \\ \top & \text{otherwise} \end{cases} \]Disjunction
\[ v(\phi \vee \psi) = \begin{cases} \top & \text{if } \top \in \{v(\phi), v(\psi)\} \\ \mathbb{B} & \text{if } \mathbb{B} \in \{v(\phi), v(\psi)\} \\ \mathbb{N} & \text{if } \mathbb{N} \in \{v(\phi), v(\psi)\} \\ \bot & \text{otherwise} \end{cases} \]Implication (material conditional)
\[ v(\phi \rightarrow \psi) = \begin{cases} \top & \text{if } v(\phi) = \bot \text{ or } v(\psi) = \top \\ \mathbb{B} & \text{if } \mathbb{B} \in \{v(\phi), v(\psi)\} \\ \mathbb{N} & \text{otherwise} \end{cases} \]_(Note: The precise definitions for conjunction, disjunction, and implication in many-valued logics can vary. These represent one possible formalization; specific use cases might warrant alternative definitions, such as those based on lattices like First Degree Entailment.)_
3.2.3 Interpretive Commentary
This truth system allows κ_catuskoti to explicitly represent logical uncertainty and paradox. For example, a contradictory claim such as “The court both ruled and did not rule on the case” can be assigned the value \(\mathbb{B}\), whereas a vague or ill-defined claim such as “Justice is red” might be interpreted as \(\mathbb{N}\).
Operators behave intuitively based on the definitions above: Negation flips \(\top\) and \(\bot\), leaving \(\mathbb{B}\) and \(\mathbb{N}\) unchanged. The behavior of conjunction and disjunction prioritizes certain values (e.g., \(\bot\) for conjunction, \(\top\) for disjunction). Implication is defined conservatively.
These design choices maintain non-explosiveness—that is, the logic resists collapse under contradiction, a key feature inherited from paraconsistent principles.
3.3 Self-Reference and the ρ Operator
3.3.1 Fixed-Point Semantics
The \(\rho\) operator enables formulas to refer to themselves in a controlled manner. Formally, we define \(\rho(\phi)\) notionally as the fixed point of the operation represented by \(\phi(x)\), where \(x\) conceptually stands for the formula \(\rho(\phi)\) itself. That is, \(\rho(\phi)\) seeks a truth value \(v^{\ast} \in \mathbb{V}\) such that applying the logical operation defined by \(\phi\) to \(v^{\ast} \) yields \(v^{\ast} \) again.
This semantic interpretation is constructed iteratively. We define an evaluation sequence starting with an initial value (e.g., \(\top\) as a convention):
\[ v^{(0)}(\rho(\phi)) := \top \]\[ v^{(n+1)}(\rho(\phi)) := v(\phi[v^{(n)}(\rho(\phi)) / x]) \]Here, \(v(\phi[v’ / x])\) represents the semantic evaluation of the formula structure \(\phi\) where the placeholder \(x\) (representing the value of \(\rho(\phi)\)) is assigned the value \(v’\) from the previous iteration. The process continues until the sequence of values \(v^{(0)}, v^{(1)}, v^{(2)}, \dots\) stabilizes.
- If the sequence converges to a single value \(v^{\ast} \in \mathbb{V}\) (i.e., \(v^{(k+1)} = v^{(k)} = v^{\ast} \) for some \(k\)), we assign \(v(\rho(\phi)) = v^{\ast} \).
- If the sequence enters a stable oscillation (e.g., cycling between \(\top\) and \(\bot\)), we assign \(v(\rho(\phi)) = \mathbb{B}\).
- If the sequence diverges or shows no clear convergent or oscillatory pattern within a predefined computational bound, we may assign \(v(\rho(\phi)) = \mathbb{N}\).
This formalism allows the system to represent and reason about paradoxes internally.
3.3.2 Example: The Liar Sentence
We define the Liar Sentence \(L\) as a formula that asserts its own negation, using the \(\rho\) operator:
\[ L := \rho(x). \neg x \]Evaluated iteratively, starting with \(v^{(0)}(L) = \top\):
- \(v^{(1)}(L) = v(\neg \top) = \bot\)
- \(v^{(2)}(L) = v(\neg \bot) = \top\)
- \(v^{(3)}(L) = v(\neg \top) = \bot\)
- … and so on.
The sequence \(\top, \bot, \top, \bot, \dots\) oscillates indefinitely. According to the rule for stable oscillation:
\[ v(L) = \mathbb{B} \]3.3.3 Interpretive Commentary
The \(\rho\) operator formalizes self-reference as a truth-evaluable process. Rather than banning paradoxes like the Liar or Russell’s Set (which would require a set-theoretic formulation), κ_catuskoti models their semantic dynamics directly. This iterative approach aligns with established fixed-point semantics for truth predicates, notably Kripke’s theory of truth (Kripke, 1975), and the dynamic perspective of revision theories (Gupta & Belnap, 1993), which also use stage-based evaluations to handle semantic paradoxes. This enables paradox to be treated as a computationally tractable phenomenon rather than a fatal flaw.
Optionally, one can formulate \(\rho\) using category theory by treating \(\mathbb{V}\) as an object in a semantic category, and \(\rho\) as related to fixed-point constructions like those found via coalgebraic methods. This perspective may provide future generalizations.
3.4. Context Sensitivity: The \(\Delta_i\) Operator
To handle shifts in perspective or context, crucial for interpreting many koans or evolving knowledge bases, we introduce the context-shifting operator, \(\Delta_i\). This operator is intended to allow the logic to dynamically alter the interpretation or significance of propositions based on a specified context \(i\).
For example, \(\Delta{zen}\) \(( Paradox )\) might evaluate a paradox within a ‘Zen’ context where its contradictory nature is embraced (Value B or N), while \(\Delta{classical}\) \(( Paradox )\) might force a rejection (Value F, depending on underlying assumptions). The \(\Delta_i\) operator represents a mechanism for modulating semantic evaluation based on external or meta-level considerations.
While the intuitive role of \(\Delta_i\) in enabling modal flexibility and context-dependent reasoning is clear, providing its full formal semantics—detailing precisely how it interacts with the valuation function \(v\) and the \(\rho\) operator across different contexts \(i\)—remains a significant avenue for future research. Its inclusion here signals a key direction for extending the core logic’s expressiveness.
4. Illustrative Examples
Here are three practical examples of the κ_catuskoti logic in action, across different domains where contradiction, indeterminacy, or self-reference must be modeled directly:
4.1 Natural Language Semantics (Liar Paradox)
Sentence:
“This sentence is false.”
Classical logic:
Breaks due to self-reference:- If it’s true, then it’s false.
- If it’s false, then it’s true.
κ_catuskoti logic:
Encode as a fixed-point, as shown in Section 3.3.2:\(L := \rho(x). \neg x\)
Evaluate under the four-valued semantics using the iterative \(\rho\) process:
- The evaluation results in a stable oscillation (\(\top \leftrightarrow \bot\)).
- Thus, \(v(L) = \mathbb{B}\) (both true and false).
Use case: Formalizing semantics for natural language, analyzing paradoxical statements in text, potential applications in truth valuation for generative models.
4.2 Ethics or Legal Reasoning (Contradictory Norms)
Scenario:
An act is judged according to conflicting principles. For example:“Whistleblowing is both an act of integrity (fulfilling a duty to expose wrongdoing) and an act of betrayal (breaking loyalty oaths).”
Classical logic:
Forces a resolution to either true or false, potentially oversimplifying the dilemma. If represented as \(P \wedge \neg P\), the system risks explosion.κ_catuskoti logic:
Model the core propositions:\(P := “The act (whistleblowing) is permissible/good"\)
Assign the contradictory value based on the scenario:
\(v(P) = \mathbb{B}\) (both)
A reasoning system using κ_catuskoti can then use this value:
- Acknowledge the conflict without system collapse.
- Apply different meta-rules based on context, possibly using the \(\Delta_i\) operator:
- In \(\Delta_1\) (e.g., a pluralist ethical mode), the state \(\mathbb{B}\) might be accepted as representing a genuine dilemma.
- In \(\Delta_0\) (e.g., a strict legal mode requiring a single verdict), the state \(\mathbb{B}\) might trigger a specific procedure (e.g., referral, declaring a mistrial, applying a tie-breaking rule).
Use case: Modeling complex ethical dilemmas, AI safety and alignment (handling conflicting values), legal reasoning systems dealing with ambiguous statutes or precedents.
4.3 AI Self-Modeling / Metacognition (Epistemic Uncertainty)
Scenario:
An AI agent needs to represent its own uncertainty about a belief it holds.“The agent assesses its belief state regarding proposition X as unreliable or indeterminate.”
Classical modal logic: Typically represents belief (\(B(X)\)) or lack of belief (\(\neg B(X)\)), but struggles to natively represent a state of acknowledged indeterminacy about X itself without extensions.
κ_catuskoti logic:
Let \(\phi\) represent the proposition “The agent has conclusive evidence for/against X”.- If a meta-assessment process evaluates the evidence regarding X (or the reliability of the reasoning process itself) as inconclusive, contradictory, or ill-defined, the agent can directly assign the value \(\mathbb{N}\) to the relevant proposition reflecting this assessment.
- For instance, assigning \(v(\phi) = \mathbb{N}\) explicitly represents the agent’s state of indeterminacy regarding its conclusion about X.
Allowing propositions to be assigned \(\mathbb{N}\) enables the system to explicitly represent states of doubt, ambiguity, or acknowledged ignorance. This facilitates more nuanced self-reflection and can trigger appropriate behaviors, such as seeking more information rather than acting on an uncertain conclusion. While the \(\rho\) operator _could_ be used for more complex recursive self-assessments (e.g., “I believe that my belief is indeterminate"), the direct use of \(\mathbb{N}\) already provides a powerful tool for representing basic epistemic uncertainty.
Use case: Building more introspective AI agents, modeling cognitive dissonance or uncertainty in cognitive science, developing robust agents for environments with highly uncertain or deceptive information.
5. Computational Implementation
While κ_catuskoti is primarily a theoretical framework, its potential computational applications motivate exploring its implementation. A prototype system can demonstrate its feasibility and allow for empirical testing.
A basic prototype has been developed in Python to explore the core mechanics. The evaluation process centers around a function, conceptually
evaluate_rho(formula, max_iterations), which applies the semantic rules iteratively for self-referential formulas containing \(\rho\). It tracks the sequence of truth values assigned in each iteration up to a predefined limit (max_iterations) to determine convergence (to T, F, B) or divergence (assigned N). Standard test cases, such as the Liar Paradox formulated asL: \rho(\neg L), were used to validate the mechanism, confirming its ability to assign the expected paradoxical value (B in this case, assuming convergence within the iteration limit).5.1 Core Components
The engine includes implementations for:
- Four Truth Values: Representation of \(\top\) (TRUE), \(\bot\) (FALSE), \(\mathbb{B}\) (BOTH), and \(\mathbb{N}\) (NEITHER).
- Logical Connectives: Functions evaluating negation (\(\neg\)), conjunction (\(\wedge\)), disjunction (\(\vee\)), and implication (\(\rightarrow\)) based on the defined semantics (Section 3.2.2).
- \(\rho\) Operator Evaluation: An iterative process to compute fixed points for self-referential formulas involving \(\rho\), handling convergence, oscillation (assigning \(\mathbb{B}\)), and potential divergence (assigning \(\mathbb{N}\)), as described in Section 3.3.1.
- \(\Delta_i\) Operator (Conceptual): While the prototype focuses on the core paraconsistent mode, the structure allows for future extension with the \(\Delta_i\) operator to simulate different logical modes (e.g., classical, dialetheist) by altering evaluation rules.
- (Optional) Truth Table Visualization: The prototype includes utilities to generate and display the full truth tables for the implemented connectives across the four-valued domain.
5.2 Example: Simulated Agent Reasoning
The prototype allows simulating how an AI agent equipped with κ_catuskoti logic might handle contradictory or indeterminate information. Consider an agent evaluating safety conditions:
- If evidence regarding condition X is contradictory (e.g., sensor reports safe and unsafe), the logic assigns \(v(\text{X_is_safe})\) = \(\mathbb{B}\). The agent’s policy might map \(\mathbb{B}\) to a cautious action: "Proceed with caution".
- If evidence for condition Y is clearly positive, \(v(\text{Y_is_safe})\) = \(\top\). The agent proceeds confidently: "Proceed".
- If evidence for condition Z is insufficient or fundamentally ambiguous, \(v(\text{Z_is_safe})\) = \(\mathbb{N}\). The logic acknowledges this indeterminacy, potentially leading the agent to halt: "Do not proceed; seek clarification".
This simulation highlights how κ_catuskoti enables nuanced decision-making, allowing agents to recognize and react appropriately to contradiction and indeterminacy rather than defaulting to arbitrary choices or system failure.
6. Applications and Implications
The κ_catuskoti framework, with its capacity to handle contradiction, indeterminacy, and self-reference, opens significant applications across diverse fields.
- Artificial Intelligence: A primary application lies in building more robust AI reasoning systems. Agents equipped with κ_catuskoti can operate in complex environments with conflicting or incomplete information without crashing or resorting to arbitrary conflict resolution. This is crucial for decision-making under uncertainty, fusing contradictory sensor data, or navigating environments with deceptive information. It offers a path towards AI that can acknowledge and manage ambiguity rather than simply rejecting it.
- Cognitive Science: The logic provides formal tools for modeling aspects of human cognition that are challenging for classical systems. This includes phenomena like cognitive dissonance, ambivalence (holding conflicting beliefs or desires), managing dissociation, and potentially the recursive nature of self-awareness or meta-cognition, as explored in the AI self-modeling example (Section 4.3).
- Ethics and Law: κ_catuskoti allows for the formal representation of genuine ethical dilemmas or legal situations where conflicting principles or perspectives are equally valid (as illustrated in Section 4.2). Instead of forcing a premature resolution, the logic can maintain the contradictory state (\(\mathbb{B}\)) or indeterminate state (\(\mathbb{N}\)), enabling systems or analyses that explicitly acknowledge and reason about these conflicts, potentially reflecting pluralistic viewpoints more faithfully.
- Philosophy of Language and Semantics: The framework offers a way to analyze and assign semantic values to paradoxical utterances (like the Liar Paradox, Section 4.1) and potentially address issues of vagueness or boundary cases where predicates may seem to both apply and not apply, or neither apply nor not apply.
In essence, κ_catuskoti provides a foundation for systems that engage more directly with the paradoxical and ambiguous nature of real-world information and reasoning processes, moving beyond the limitations of purely binary logic.
7. Comparison with Related Systems
To situate κ_catuskoti within the landscape of existing logical frameworks, it is useful to compare its capabilities against related systems. Notably, the four-valued semantics employed here share the same truth values \({\top, \bot, \mathbb{B}, \mathbb{N}}\) as Nuel Belnap’s influential logic of First Degree Entailment (FDE), often used in computer science to handle inconsistent and incomplete information (Belnap, 1977).
However, while sharing this foundational structure, κ_catuskoti introduces crucial distinctions:
- Dynamic Self-Reference Handling (\(\rho\) Operator): Unlike standard FDE, which is primarily concerned with static entailment between formulas that might contain inconsistent/incomplete information, κ_catuskoti introduces the \(\rho\) operator to explicitly model and evaluate _self-referential* statements dynamically. Its iterative semantics provide a mechanism for determining the truth value of paradoxical sentences within the four-valued framework.
- Comparison to Kripke’s Theory of Truth: Kripke’s fixed-point semantics (1975) also provides a powerful way to handle self-reference, often over a three-valued logic (True, False, Undefined/Grounded). κ_catuskoti differs in its foundational four-valued structure (explicitly acknowledging Both/Contradiction) and, significantly, in how the \(\rho\) operator’s iterative process can terminate by assigning \(\mathbb{N}\) (Neither) to certain non-converging or oscillating cases (within a computational bound), rather than leaving them ungrounded or undefined in precisely the same way as Kripke’s minimal fixed point.
- Comparison to Revision Theory: Gupta and Belnap’s Revision Theory of Truth (1993) also uses an iterative process, but focuses on how the semantic status of paradoxical sentences (like the Liar) _revises_ over stages of evaluation, often resulting in non-stable or cyclically changing classifications. While \(\rho\)’s iteration shares similarities, κ_catuskoti aims to assign a _single* final value from \({\top, \bot, \mathbb{B}, \mathbb{N}}\) based on the iteration’s behavior (convergence or bounded oscillation/divergence), offering a different end-state classification compared to the typical outcomes in Revision Theory.
- Context Sensitivity (\(\Delta_i\) Operator): The conceptual \(\Delta_i\) operator (whose full formalization is future work, see Sec 3.4) aims to provide a built-in mechanism for context-dependent evaluation, a feature not typically integrated directly into the core semantics of FDE, Kripke’s theory, or standard Revision Theory.
The following table summarizes key feature differences across several logical paradigms:
Logic System Contradiction Indeterminacy Self-Reference Dynamic Semantics Classical Logic ✘ ✘ ✘ ✘ Fuzzy Logic ✘ ✓ ✘ ✘ Paraconsistent Logic ✓ ✘ partial [^1] ✘ Modal μ-calculus ✘ ✘ ✓ ✓ κ_catuskoti ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓
8. Limitations and Future Work
While the κ_catuskoti framework presented here offers a novel approach to handling paradox and inconsistency, it represents foundational work with several avenues for further development. We identify the following key limitations and directions for future research:
- Proof Theory: This paper has focused on the syntax and semantics of κ_catuskoti. A significant next step is the development of a corresponding proof theory—a formal deductive system (e.g., natural deduction, sequent calculus, or axiomatic system) that precisely captures the logic’s entailment relation. This is crucial for formal verification and automated reasoning applications.
- Quantification: The current formulation is propositional. Extending κ_catuskoti to include first-order or higher-order quantification would significantly increase its expressive power, allowing reasoning about objects, properties, and relations, but would also require careful consideration of how quantifiers interact with the four-valued semantics and the \(\rho\) operator.
- Convergence Properties of \(\rho\): The iterative semantics for the \(\rho\) operator guarantee finding fixed points or detecting oscillation in finite domains or under certain conditions. However, a more rigorous formal analysis is needed to characterize the convergence properties of \(\rho\) under various constraints, especially for potentially infinite iterations or more complex formula structures. Establishing conditions for guaranteed termination or identifying classes of formulas with predictable behavior is an important theoretical goal.
- Machine Learning Integration: The capacity of κ_catuskoti to handle contradictory and uncertain information suggests intriguing possibilities for integration with machine learning models. Future work could explore using κ_catuskoti as a meta-reasoning layer for large language models (LLMs) to improve their handling of inconsistent inputs or to allow them to represent their own uncertainty more explicitly (perhaps connecting to research on calibrating model confidence). Investigating learnable versions of the \(\Delta_i\) modal shifts is another potential direction.
Addressing these areas would further mature κ_catuskoti as both a theoretical framework and a practical tool for advanced reasoning systems.
9. Conclusion
κ_catuskoti logic offers a radical yet rigorous reconceptualization of logical foundations: one that embraces contradiction, supports indeterminacy, and renders paradox productive. By synthesizing Buddhist tetralemmic thought with modern fixed-point meta-logic and four-valued semantics, this system reframes long-standing philosophical and computational limitations. The introduction of the \(\rho\) operator allows for dynamic, recursive truth evaluation, making κ_catuskoti uniquely suited for domains where self-reference and epistemic instability are the norm, not the exception.
Our computational prototype demonstrates how an AI agent using κ_catuskoti can reason coherently in contradictory environments—a capacity increasingly relevant for systems interacting with complex, conflicting human data. This logic not only resists the collapse of classical systems under paradox but transforms paradox into an epistemic resource. Looking ahead, κ_catuskoti opens promising avenues for machine consciousness, legal and moral pluralism, and robust epistemology under uncertainty. In rejecting the tyranny of the excluded middle, it brings logic one step closer to the way real minds—and real worlds—work.
References
- Belnap, Nuel D. – _A Useful Four-Valued Logic_ (1977) _In Modern Uses of Multiple-Valued Logic, ed. J. Michael Dunn and George Epstein._
- Bieberich, Erhard – _What the Liar Paradox Can Reveal About the Quantum Logical Structure of Our Minds_ (2001) [arXiv]
- Chaitin, Gregory – _The Unknowable_ (1999)
- da Costa, Newton C.A. – _Paraconsistent Logic: Consistency, Contradiction and Negation_ (2010)
- Hofstadter, Douglas – _Gödel, Escher, Bach: An Eternal Golden Braid_ (1979)
- Hofstadter, Douglas – _I Am a Strange Loop_ (2007)
- Gupta, Anil, and Belnap, Nuel – _The Revision Theory of Truth_ (1993)
- Kripke, Saul A. – _Outline of a Theory of Truth_ (1975) _Journal of Philosophy, 72(19), 690-716._
- Matilal, B.K. – _The Central Philosophy of Buddhism_ (1986)
- Priest, Graham – _In Contradiction: A Study of the Transconsistent_ (1987)
- Prokopenko, Mikhail et al. – _Self-Referential Basis of Undecidable Dynamics_ (2017) [arXiv]
- Robinson, Richard H. – _Some Logical Aspects of Nagarjuna’s System_ (1957)
- Szpiro, George – _Perplexing Paradoxes: Unraveling Enigmas in the World Around Us_ (2024)
- Yanofsky, Noson S. – _A Universal Approach to Self-Referential Paradoxes, Incompleteness and Fixed Points_ (2003) [arXiv]
- Zizzi, Paola A. – _Turning the Liar Paradox into a Metatheorem of Basic Logic_ (2007) [arXiv]
Additional Resources
For further context and related topics, readers may find the following resources and areas of exploration helpful:
- Berry Paradox – Wikipedia Article (Wikipedia)
- Catuṣkoṭi – Wikipedia Article (Wikipedia)
- Grelling–Nelson Paradox – Wikipedia Article (Wikipedia)
- Foundations of Many-Valued Logic: Works by Jan Łukasiewicz.
- Paraconsistent Logic (Further Developments): Contributions by Richard Routley (Sylvan) and Ross Brady.
- Dialetheism (Further Perspectives): Writings by J.C. Beall and Peter Mortensen.
- Algebraic Structures for Many-Valued Logic: Research on bilattices by Melvin Fitting, Ofer Arieli, and Arnon Avron.
- Four-Valued Logic (Further Theory): Contributions by J. Michael Dunn.
- Classical Approaches to Paradox: Theories of truth and hierarchical solutions by Alfred Tarski and Saul Kripke.
- Nāgārjuna’s Philosophy: Direct engagement with primary texts like the _Mūlamadhyamakakārikā_.
-
Yablos Paradox is the idea that there is no way to coherently assign a truth value to any of the sentences in a countably infinite sequence of sentences, when these sentences all state that “all of the subsequent sentences are false”.

"The point of these observations is not the reduction of the familiar to the unfamiliar[...] but the extension of the familiar to cover many more cases." - Saunders MacLane, Categories for the Working Mathematician, Page 226
Most truths cannot be expressed in language
-
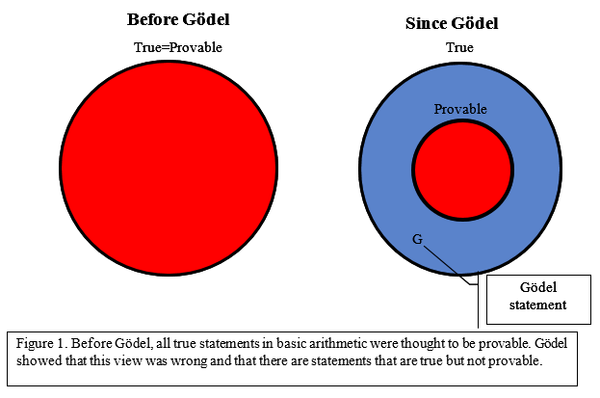
The Period-doubling cascades en route to chaos remains one of the most puzzling features of nature
-
Was Floquet Engineering to identify nonlinear resonances in Floquet‑Driven Reservoirs all night long. Exhausted but unbothered. moisturized. happy. in my lane. focused. flourishing. periodically driven.
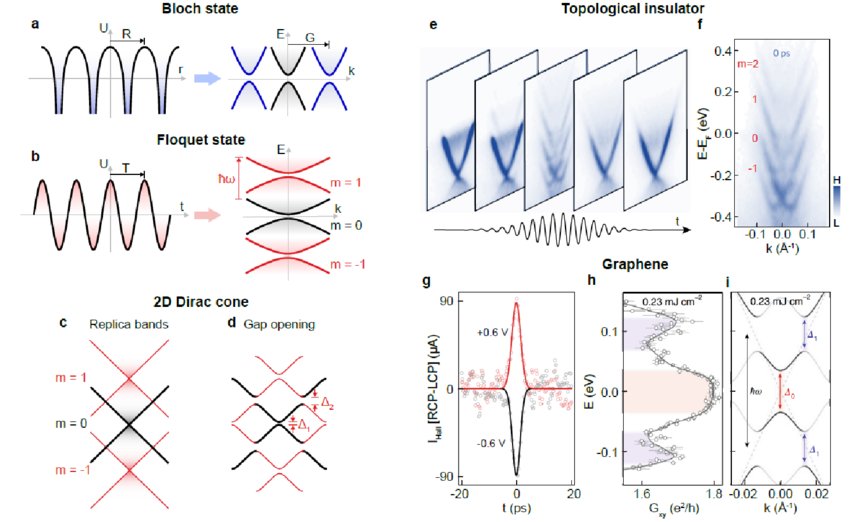
-
Neural waves study provides evidence that brain's rhythmic patterns play key role in information processing
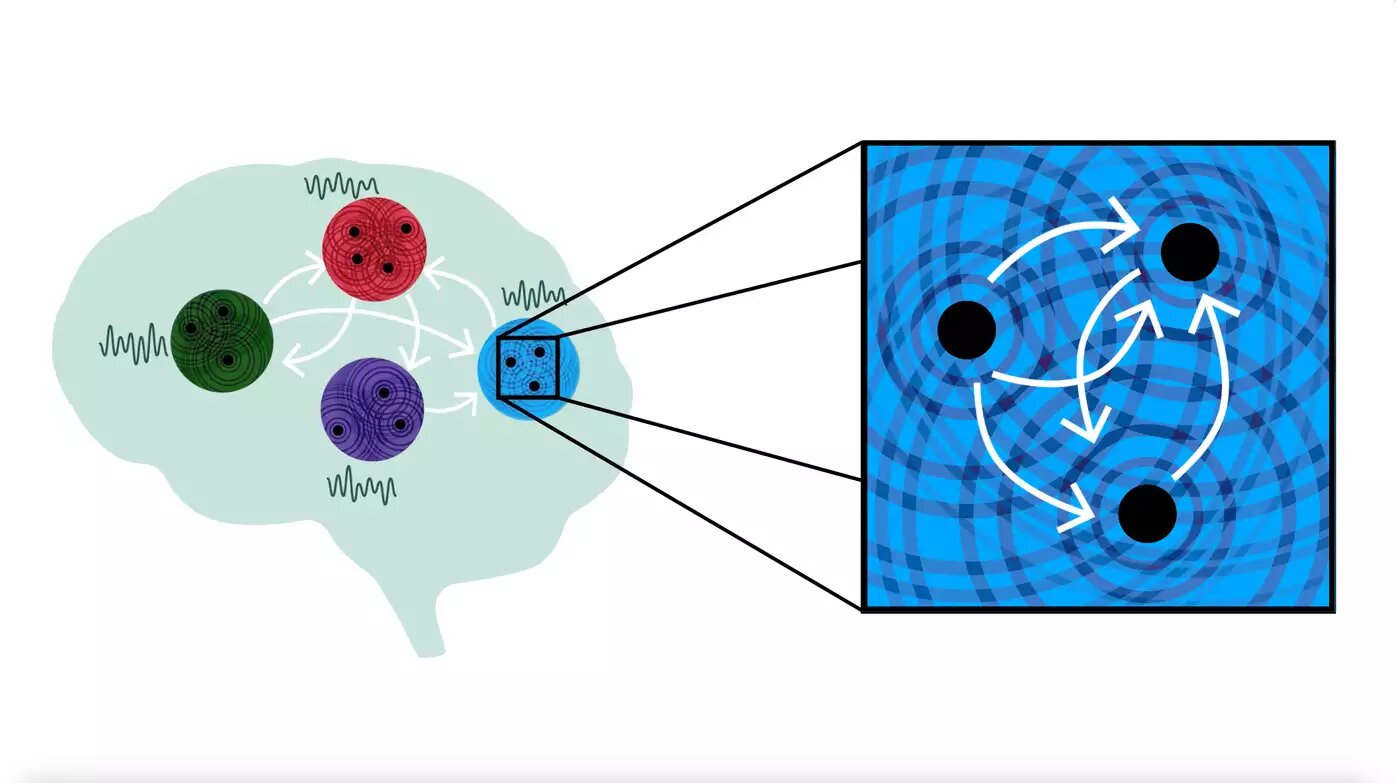
The authors of the study suggest that the brain uses the superposition & interference patterns of waves to represent and process information in a highly distributed way, exploiting the unique properties of coupled oscillator networks such as resonance and synchronization.
Papers & Code:
Code: Harmonic oscillator recurrent network (HORN) Pytorch Implementation
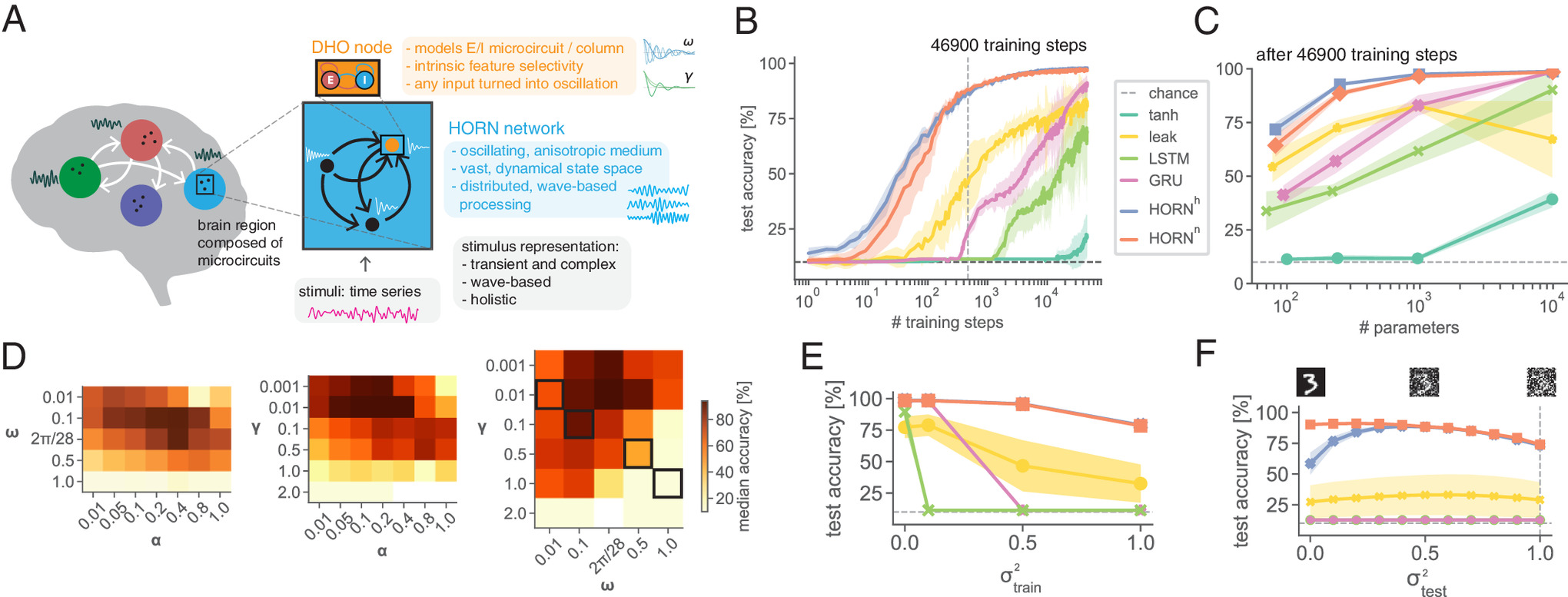
Overview:
High-level concepts:
Recast neural processing as continuous‐time dynamics rather than pure feed-forward stateless layers.
Embedding physical, continuous dynamics—oscillations, waves, vortices, and damping—directly into the network’s layers unlocks powerful, implicit mechanisms for attention, multi-scale integration, and long-range memory, without the combinatorial bloat of explicit attention heads or deeper stacks.
1. Controlled Oscillations as an Inductive Bias
Damped Harmonic Oscillator (DHO) nodes
In
model.py, each hidden unit integrates its “position” x and “velocity” y via: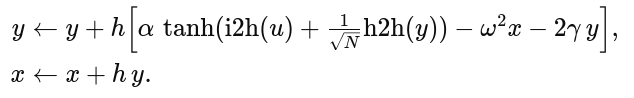
Key Insight: forcing every node into an oscillatory regime makes phase, frequency and amplitude available for coding from the very first forward pass—no need to “discover” oscillations through recurrent loops alone.
Why it matters:
- Leaky‐integrator RNNs can oscillate only indirectly (if you tweak weights).
- By baking oscillations into the node, you guarantee resonance‐based feature extraction and a rich dynamical repertoire from the start.
2. Wave‐Based Representations & Interference
Traveling waves & standing waves
- External input → local standing oscillation in each DHO
- Recurrent coupling → traveling waves that propagate, collide, and interfere
High‐Dimensional Mapping:
- Low‐dimensional time-series (e.g. pixel sweep in sMNIST) → high-dimensional spatiotemporal interference pattern across the N oscillators.
- After training, these patterns carve out stimulus‐specific trajectories in the N-dimensional state space that are linearly separable by your final
h2olayer.
Code touch-point: The
record=Trueflag inforward()gives yourec_x_tandrec_y_t. Visualizing these (as indynamics.pyortrain.py) shows exactly how different input classes sculpt different wave‐interference signatures.
3. Resonance & Intrinsic Receptive Fields
The intrinsic gain curve of each DHO node is defined as:

In the PNAS work, a grid‐search found optimal \omega \approx 2\pi/28 to match the dominant frequency of straight strokes in sMNIST.
Computational payoff: Nodes automatically amplify (resonate) in-band inputs—so you’re baking in priors about the signal’s spectral content at the architectural level, not just via learned weights.
How to explore in your code:
- In
dynamics.py, drive a single DHO with a pure sine wave at different frequencies. - Measure steady‐state amplitude &bar; x &bar; after transients → plot &bar; x &bar; vs. frequency.
- That’s your empirical G(\omega_{\text{in}}) curve.
4. Heterogeneity → Near‐Critical Dynamics
Biological motif: neurons/pyramidal microcircuits have tunings and delays that vary across the network.
HORN’s version: drawing each unit’s \omega_i and \gamma_i (and later, delays) from a distribution.
Why it helps:
- Expands the repertoire of possible wave‐interference patterns
- Brings network closer to a “critical” regime: balance of order/disorder, long memory tails, richer transient dynamics
Simple test in code:
- In
dynamics.pyyou already sampleomegaandgamma. Try:- Homogeneous run (all ω = ω_base, γ = γ_base) vs.
- Heterogeneous run (sampled ω, γ)
- Quantify:
- Pairwise phase‐locking values between units over time (look at how PLV distribution broadens)
- Linear separability: train a small linear SVM on the recorded
rec_x_tsnapshots and compare classification accuracy.
5. Hebbian Alignment of Backprop
Surprising finding: gradient‐based BPTT weight updates on
h2hend up correlating strongly with pre-post activity correlations—i.e. they “look Hebbian.”Takeaway: Even though you’re minimizing a cross‐entropy loss at the readout, the recurrent weight updates reorganize the network to amplify stimulus‐specific synchrony patterns.
Next step in code:
- After an epoch of supervised training, scatter‐plot before & after training to see the emergence of a positive correlation between weight strength and firing‐correlation
6. Spontaneous → Evoked State Manifolds
Biological signature: cortex at rest floats through a “rich club” of states; stimuli transiently collapse it into a low‐variance, stimulus‐specific subspace.
HORN mimic:
- Add small random kicks to
y_t(Poisson noise) whenrecord=False - Observe via PCA on the recorded trajectories that:
- Rest: clouds of points filling a large manifold
- During input: rapid collapse to distinct clusters for each class
- After: rebound back to the resting manifold
In summary
- Oscillatory nodes give access to phase, frequency, and amplitude as first‐class coding variables.
- Wave interference provides a massively parallel, high‐dimensional embedding of inputs.
- Resonance priors let you tune the network at the architectural level to known signal statistics.
- Heterogeneity & delays enrich the dynamic repertoire and promote near‐critical, richly transient behaviors.
- Hebbian‐style learning emerges naturally even under supervised BPTT, hinting at fully unsupervised alternatives.
- Rest–stimulus manifold dynamics in HORN match key cortical phenomenology.
-
Weekend immersed in Deep Oscillator Neural Networks has been a resonant journey.
-
Phase-encoded information is elusive: no single wave holds meaning. It’s the alignment, the relationship, that reveals it. It dominates in systems across nature where precision, interference, or efficiency matter.
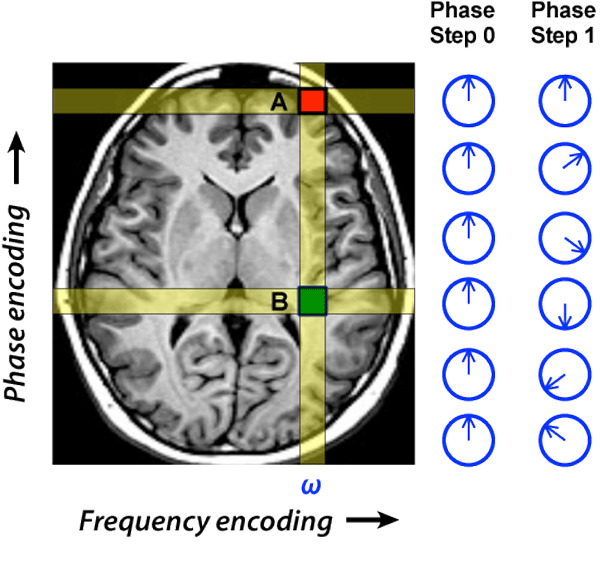
-
Life isn't about resisting chaos. Life is about blossoming into a natural and elegant order on the edge of chaos.

-
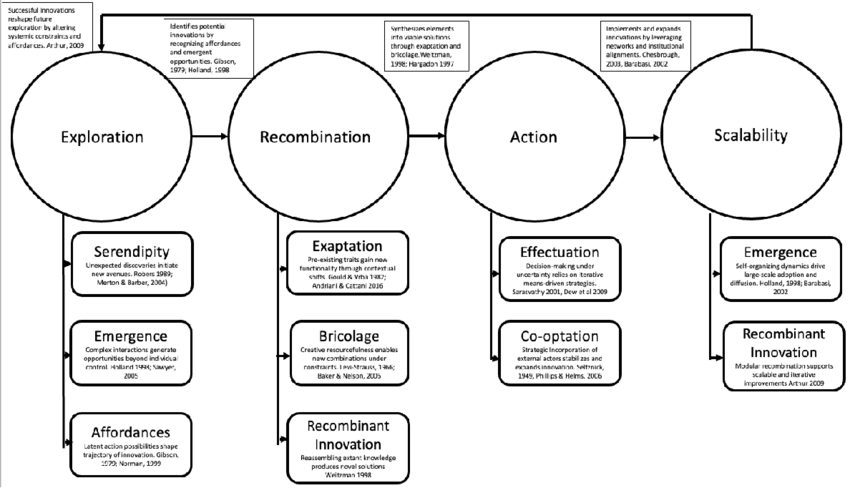
Exapt, Adapt, Disrupt: A Conceptual Framework for Systemic Innovation - by Jacqueline Fendt
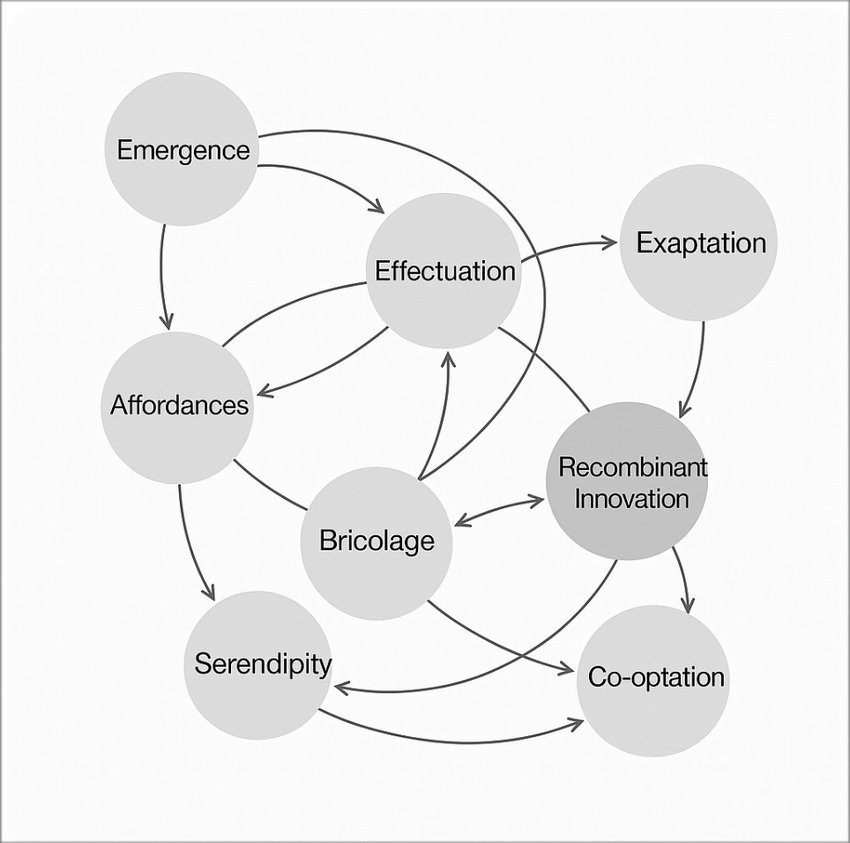
Abstract: How do breakthroughs emerge in unpredictable environments? This paper develops a unified framework for systemic innovation by integrating eight key concepts: exaptation, serendipity, emergence, co-optation, bricolage, affordances, recombinant innovation, and effectuation. By synthesizing insights from complexity science, sociology, and entrepreneurship, we reveal how creativity flourishes when innovators repurpose existing elements, harness uncertainty, and leverage unexpected affordances. Unlike conventional models that emphasize structured problem-solving, this framework captures the nonlinear, adaptive, and systemic nature of creativity in innovation ecosystems. We illustrate its applicability across diverse cases—from the exaptation of mRNA vaccines to the recombinant innovation of AI-driven drug discovery, the co-optation of gig work by tech giants, and the emergence of decentralized finance. Our findings suggest that transformative creativity is not a solitary act, but an emergent systems-level process shaped by adaptive recombination and strategic improvisation. By shifting the focus from predictive planning to creative adaptation, this study provides a novel roadmap for navigating uncertainty and fostering systemic change. It offers both scholars and practitioners an actionable lens to harness creativity, unlock latent affordances, and scale innovation in complex environments.
#Complexity #Science #ML #Creativity #Systems #KM #Generative #Augmentation
-
Towards a Theory of Serendipity: A Systematic Review and Conceptualization - by Christian Busch
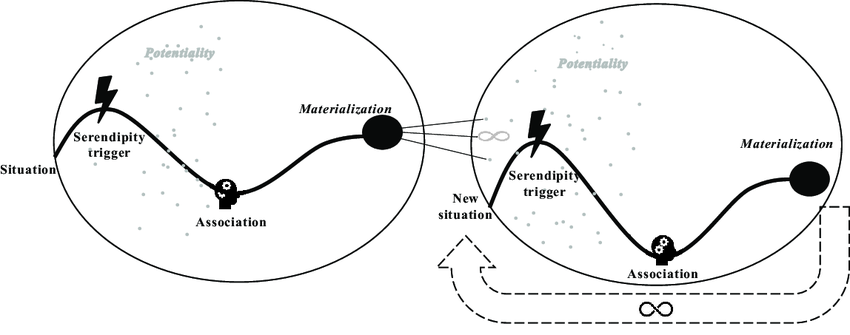
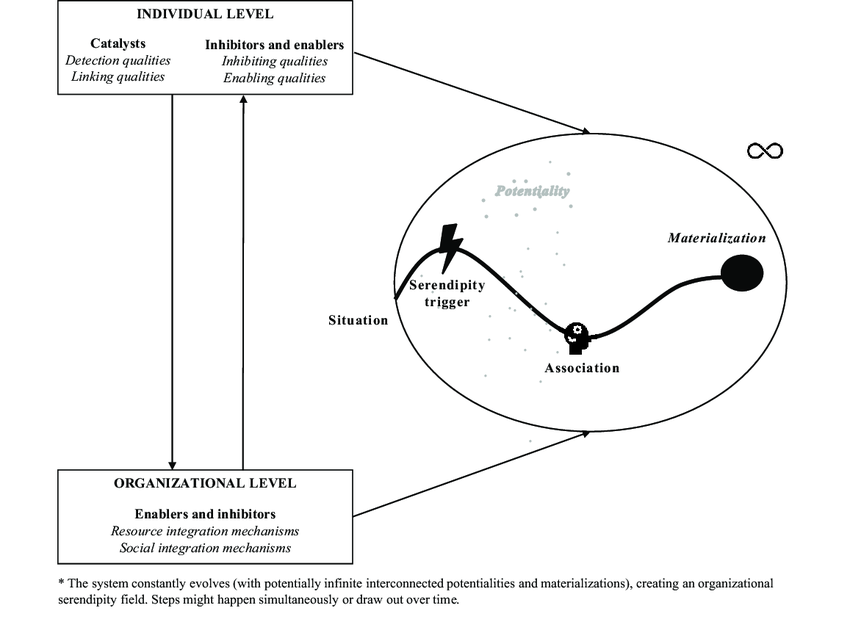
Serendipity is the discovery of valuable, unanticipated outcomes through exploration, often found while searching for something else. Serendipity is a catalyst for crossing emergence thresholds. Serendipity engineering tries to design systems that make serendipity more likely.
-
Second-Order Thinking

1. Predicting the direct consequences of one's actions is first-order thinking; second-order thinking requires us to think more long-term and holistically, considering the consequences behind the consequences. Therefore, this concept is often referred to as the "Law of Unintended Consequences."
2. We need to be aware of second-order outcomes and use the predicted results to guide our decision-making.
-
Emergence - The Key Role in Systems Thinking
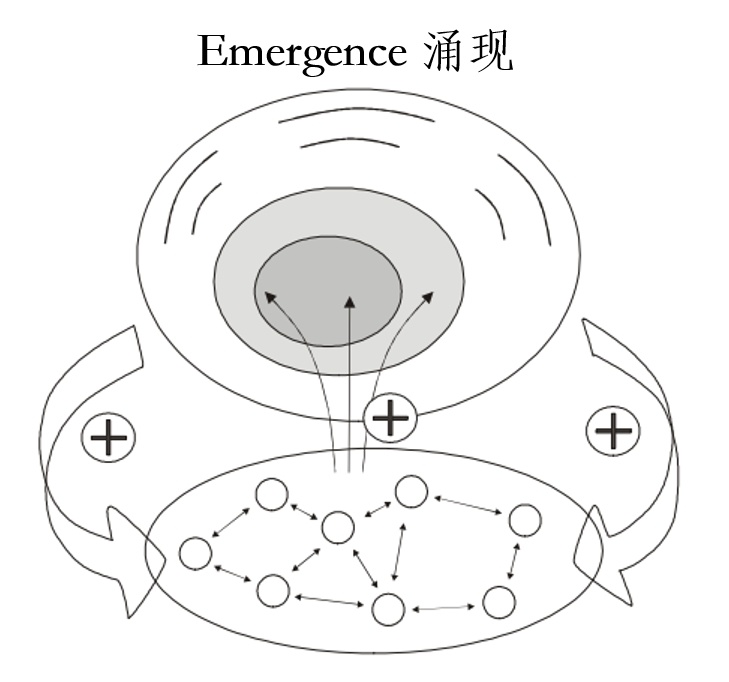
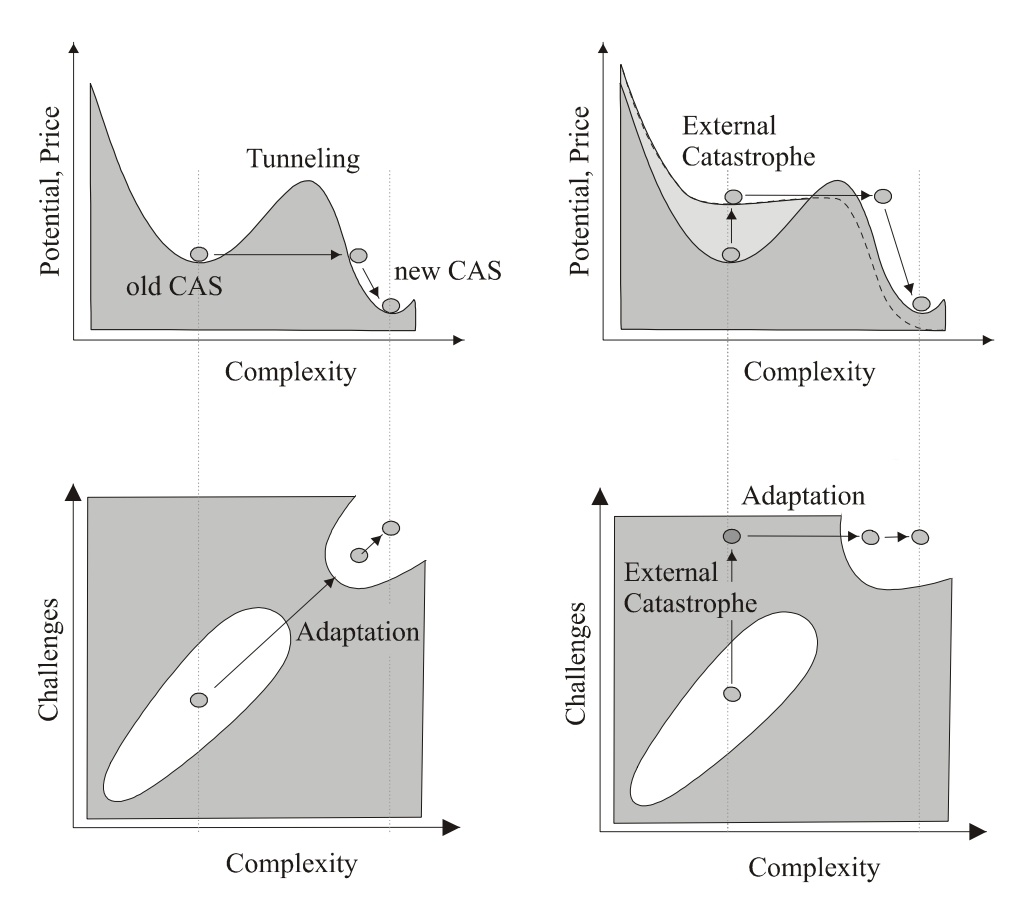
1. Definition and Core Paradox of Emergence
Definition: Emergence refers to properties that arise at a higher level of a system, which cannot be deduced or reduced from the individual characteristics of its basic elements. For example, life is an emergent property of gene interactions.
Paradox: Emergent properties possess both persistence and dynamism (e.g., the stable formation of a flock of birds despite individual changes), as well as dependence and independence (they depend on the system but are partially independent of microscopic elements).
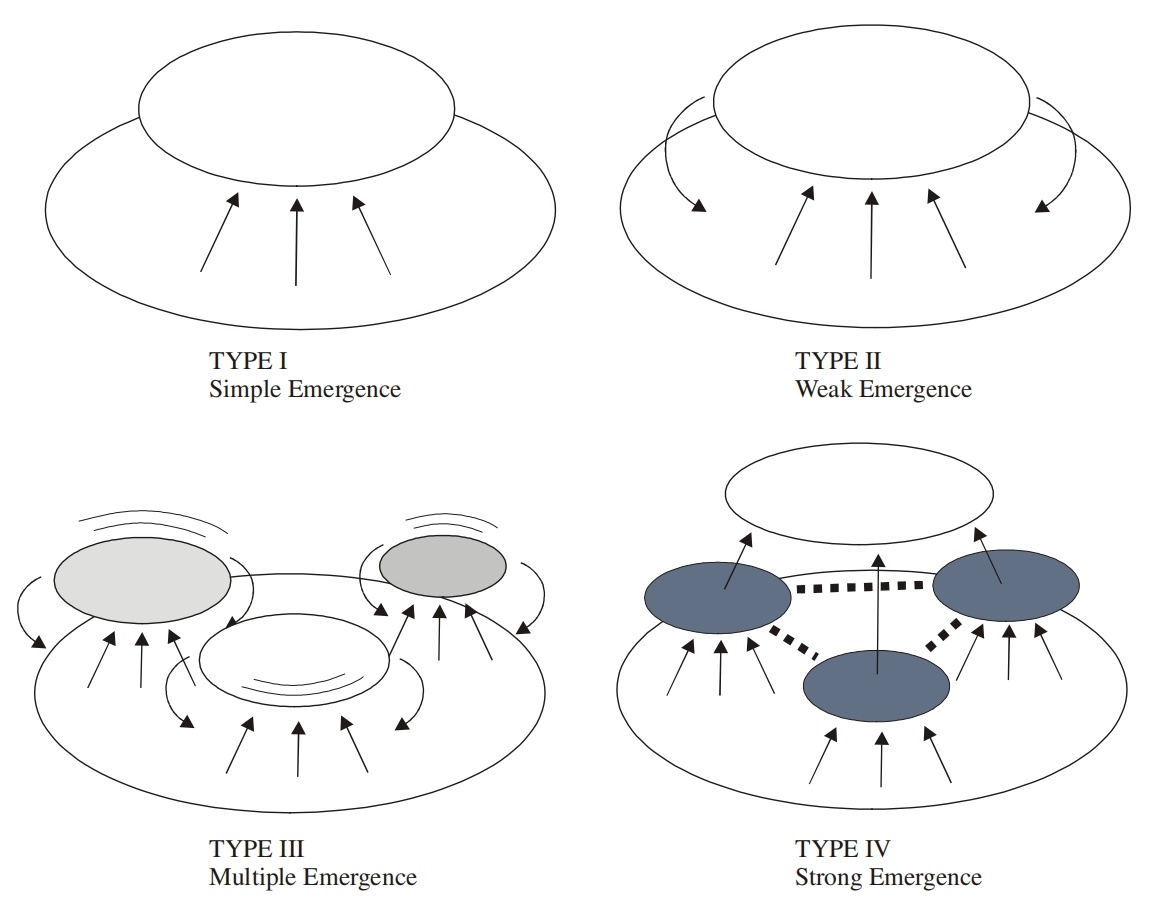
2. Classification Framework for Emergence
Emergence is classified into four types based on feedback mechanisms and causal relationships, each containing subtypes:
I. Simple Emergence (No Top-Down Feedback)
Ia (Intentional Emergence): Human-designed systems (e.g., machines, software) with clear and predictable functions but lacking flexibility. Examples: clock functions, code semantics.
Ib (Unintentional Emergence): Emergence of statistical average properties (e.g., gas pressure, network characteristics), dependent on relationships between elements but without feedback.
II. Weak Emergence (With Simple Feedback)
IIa (Stable): Dominated by negative feedback, forming stable patterns. Examples: ant foraging, bird flock behavior, market economy supply-demand balance.
IIb (Unstable): Positive feedback leads to short-term explosive phenomena. Examples: stock market bubbles, fashion trends, social media hotspots.
III. Multiple Emergence (Complex Feedback and Adaptability)
IIIa (Pattern Formation): Combination of positive and negative feedback, generating complex patterns. Examples: animal fur patterns, reaction-diffusion systems, cellular automata (e.g., "Conway's Game of Life").
IIIb (Adaptive Emergence): Systemic breakthroughs overcoming barriers, such as significant transitions in evolution. Examples: ecosystem evolution, scientific paradigm shifts.
IV. Strong Emergence (Irreducible New Systems)
New hierarchical systems completely independent of underlying rules, such as life based on genes, culture based on language. This type of emergence crosses the "correlation barrier," where microscopic details do not affect macroscopic behavior. Examples: the origin of life, the evolution of language.
3. Basis and Significance of Classification
Feedback Mechanism: From no feedback (Type I) to multiple feedbacks (Type III), ultimately to transcendent systems (Type IV).
Predictability: Type I is fully predictable, Type II is predictable in principle, Type III is chaotic and unpredictable, Type IV is unpredictable due to new laws.
Philosophical Relevance: Strong emergence is related to "supervenience," where higher-level properties depend on but are independent of the lower level.
4. Applications and Insights
Engineering and Science: Understanding emergence helps design robust systems (e.g., coping with unpredictable failures), and optimize collective intelligence (e.g., distributed algorithms).
Evolution and Innovation: Emergence explains breakthrough evolution in complex systems like life and culture, emphasizing the catalytic role of environmental mutations (e.g., disasters) in innovation.