tag > RadioBio
-
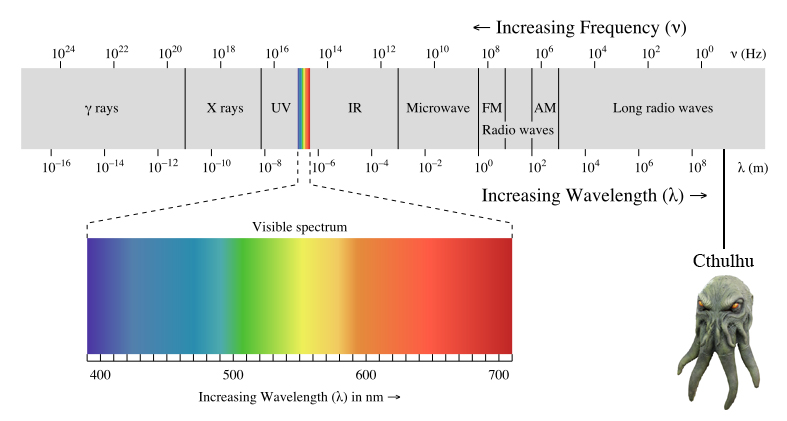
Frequencies of sound and average range of hearing
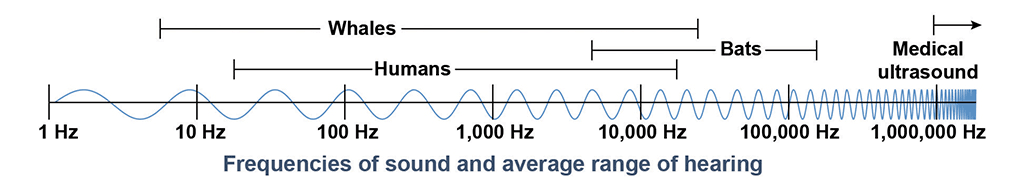
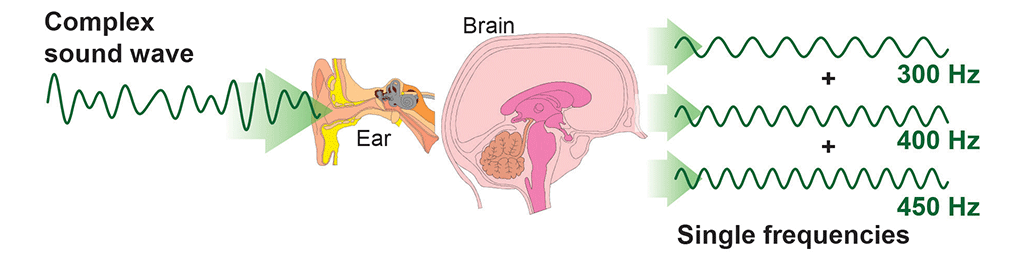
In physiology, sound is produced when an object’s vibrations move through a medium until they enter the human eardrum. In physics, sound is produced in the form of a pressure wave. When an object vibrates, it causes the surrounding air molecules to vibrate, initiating a chain reaction of sound wave vibrations throughout the medium.
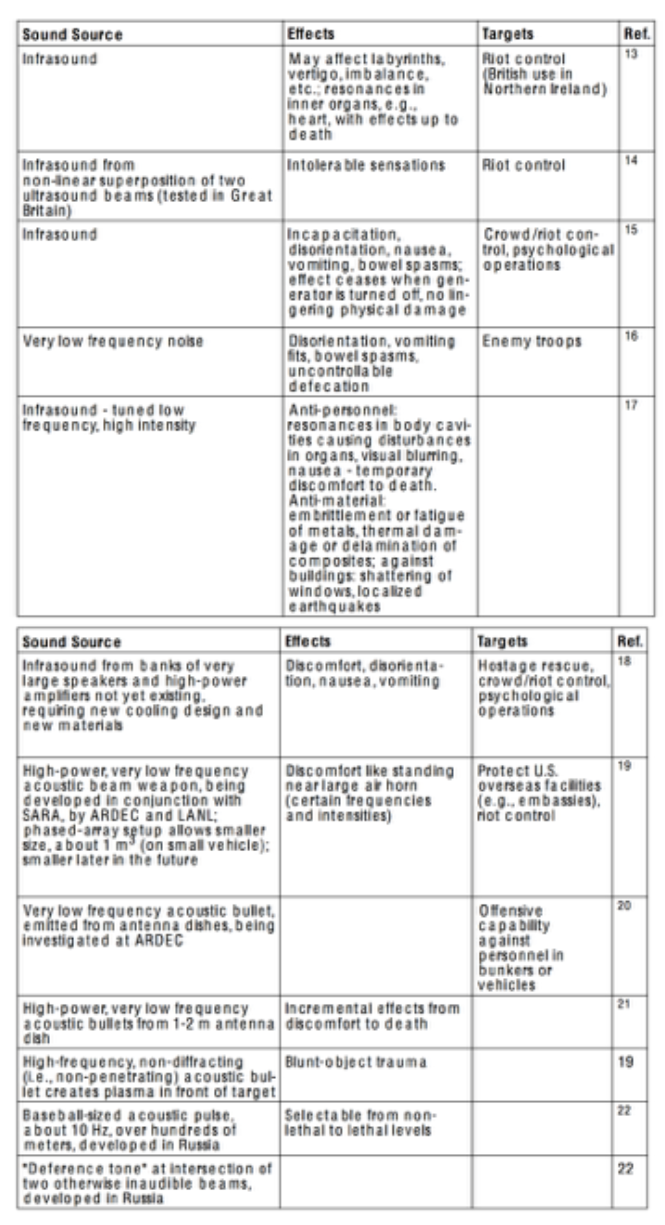
Infrasound - sound waves with a frequency below the lower limit of audibility (20 Hz)
"Animal communication: whales, elephants, hippopotamuses, rhinoceroses, giraffes, okapis, peacocks, and alligators are known to use infrasound to communicate over distances—up to hundreds of miles in the case of whales."
"One study has suggested that infrasound may cause feelings of awe or fear in humans. It has also been suggested that since it is not consciously perceived, it may make people feel vaguely that odd or supernatural events are taking place."
- Infrasound, human health, and adaptation: an integrative overview of recondite hazards in a complex environment - Research by Michael A. Persinger
- The psychoacoustic effect of infrasonic, sonic and ultrasonic frequencies within non-lethal military warfare techniques - Research by Littlefield
- Infrasonic Vibrations in Humans - Research by George Rajna
- Infrasound, human health, and adaptation: an integrative overview of recondite hazards in a complex environment - Research by Michael A. Persinger
-
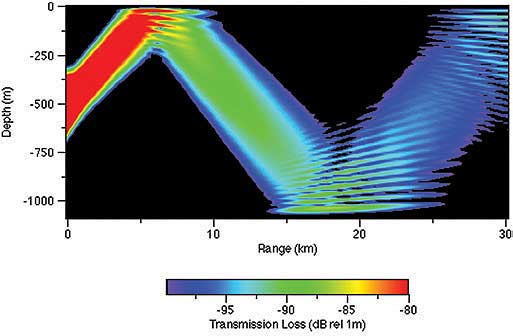
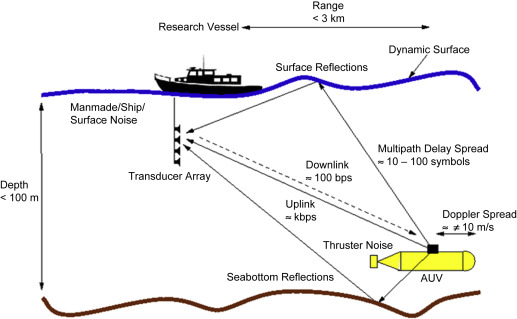
Underwater acoustics is the study of the propagation of sound in water and the interaction of the mechanical waves that constitute sound with the water, its contents and its boundaries.

-
Noveto develops biometric device to beam personal audio with no headphones
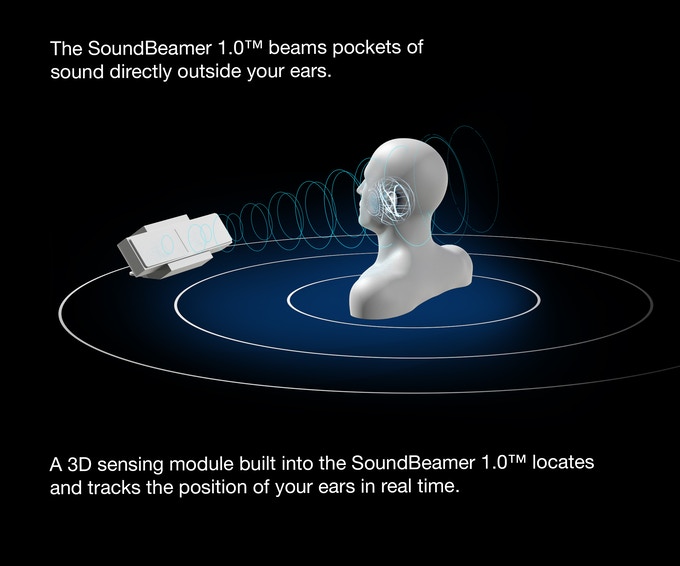
Noveto, an Israeli sound technology startup, is introducing the SoundBeamer 1.0, a compact desktop personal audio device embedded with multimodal biometrics and capable of beaming sound directly to a person’s ears without the use of headphones. A post to the Kickstarter crowdfunding platform says that SoundBeamer 1.0 creates a personal listening experience without disturbing others. A built-in 3D sensing module which helps locate and track the users’ ears in real-time enables the SoundBeamer to beam pockets of sound that only the intended listener can hear. Listeners are identified with face biometrics, and the device also includes voice and gesture recognition.
-
New AI Can Detect Emotion With Radio Waves (defenseone)
The paper from a team out of Queen Mary University of London and published in the online journal PLOS ONE, demonstrates how to apply a neural network to decipher emotions gathered with transmitting radio antenna. There are national security and privacy implications.
-

This report deals with an issue of which the importance cannot be overrated: the possible health effects of Radiofrequency Radiation (RfR) or electro magnetic fields (EMF); It deals more specifically with how the scientific debate has been hijacked by corporate interests from the Telecom industry.
-
Scientists Observe Live Cells Responding To Magnetic Fields For First Time (newatlas.com)
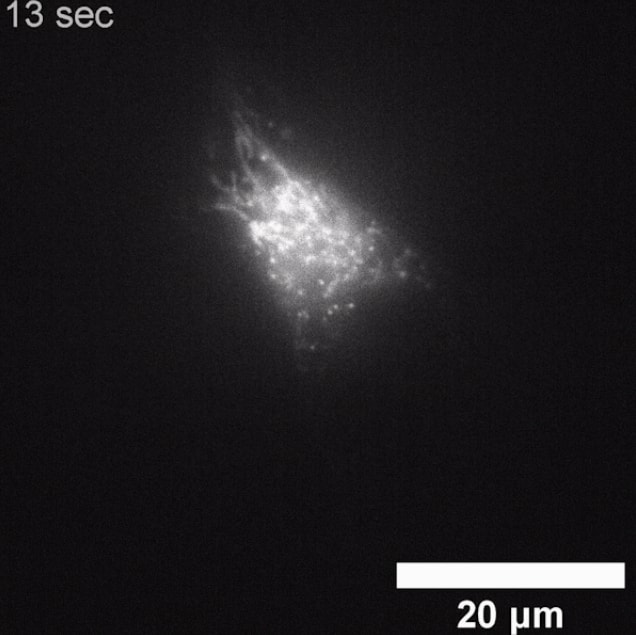

One of the most remarkable "sixth" senses in the animal kingdom is magnetoreception -- the ability to detect magnetic fields -- but exactly how it works remains a mystery. Now, researchers in Japan may have found a crucial piece of the puzzle, making the first observations of live, unaltered cells responding to magnetic fields. Many animals are known to navigate by sensing the Earth's magnetic field, including birds, bats, eels, whales and, according to some studies, perhaps even humans. However, the exact mechanism at play in vertebrates isn't well understood. One hypothesis suggests it's the result of a symbiotic relationship between the animals and magnetic field-sensing bacteria. But the leading hypothesis involves chemical reactions induced in cells through what's called the radical pair mechanism.
Essentially, if certain molecules are excited by light, electrons can jump between them to their neighbors. That can create pairs of molecules with a single electron each, known as a radical pair. If the electrons in those molecules have matching spin states, they will undergo chemical reactions slowly, and if they're opposites the reactions occur faster. Since magnetic fields can influence electron spin states, they could induce chemical reactions that change an animals' behavior. In the living cells of animals with magnetoreception, proteins called cryptochromes are thought to be the molecules that undergo this radical pair mechanism. And now, researchers at the University of Tokyo have observed cryptochromes responding to magnetic fields for the first time.
“We’ve not modified or added anything to these cells,” says Jonathan Woodward, co-lead author of the study. “We think we have extremely strong evidence that we’ve observed a purely quantum mechanical process affecting chemical activity at the cellular level.”
The research was published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
-
Effect of Electromagnetic Field Exposure on Mouse Brain Morphological and Histopathological Profiling (Journal of Veterinary Research)
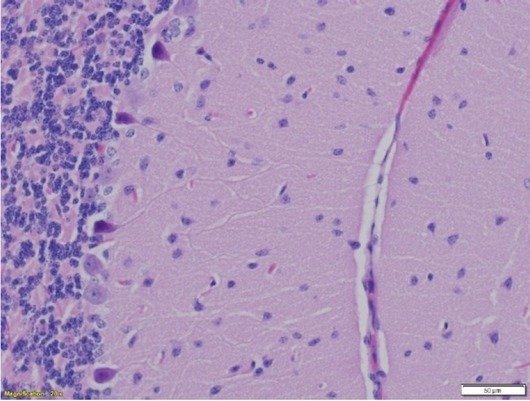
"In conclusion, different exposure levels of EMF from MP over 72 h affected mouse brains and had a negative influence on segmentation parameters of mouse brain structures. These findings suggested that EMF equipment operating at a 3 cm distance from the cage may induce appreciable morphological changes in the brain. "
-
Revisiting Burr and Northrop’s “The Electro-Dynamic Theory of Life” (1935)
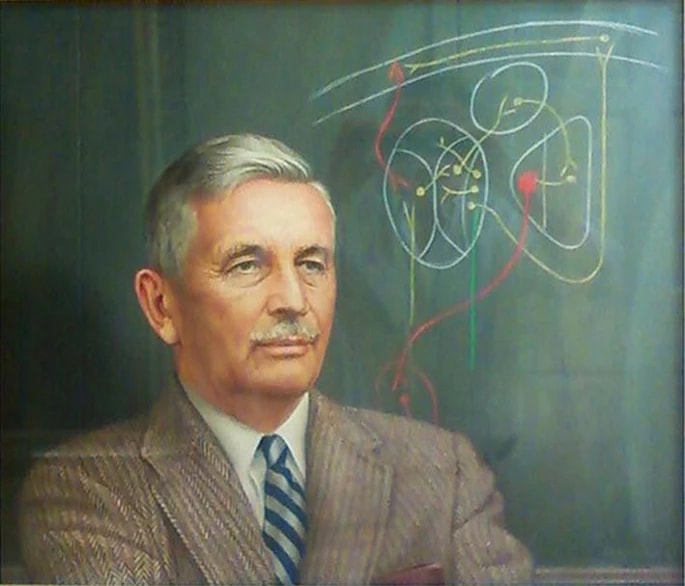
Abstract: Harold Saxton Burr was a biologist working throughout the 1930s–1950s on an important set of problems related to biological organization and the origin of complex living forms. He was a profound thinker, suggesting a complementary focus on field concepts in addition to the emphasis on particle models and integrating concepts from physics and philosophy in his work. He developed innovations in electrophysiological technique and used them to perform a wide experimental survey of bioelectricity in normal and pathological growth. Here, I briefly review his classic paper with philosopher F. S. C. Northrop, “The Electro-Dynamic Theory of Life,” in the context of advances in this field over the last few decades. Based on recent progress, it is now clear that Burr was a prescient and visionary thinker. His main hypothesis, that bioelectric gradients serve as prepatterns guiding morphogenesis, has been confirmed using modern molecular physiology, as have his ideas about the place of cancer and the nervous system in the question of biological organization. With limited technology but deep insight, he derived insights that anticipated many modern discoveries. Even more importantly, Burr’s view of bioelectricity as a convenient entry point for rigorous investigation of the broader question of self-organizing properties of life highlights a frontier of inquiry that awaits today’s researchers. Burr and Northrop’s “The Electro-Dynamic Theory of Life,” originally published in the Quarterly Review of Biology (10(3):322–333, 1935), is available as supplementary material in the online version of this essay.
Talent hits a target no one else can hit; genius hits a target no one else can see. —Arthur Schopenhauer
-
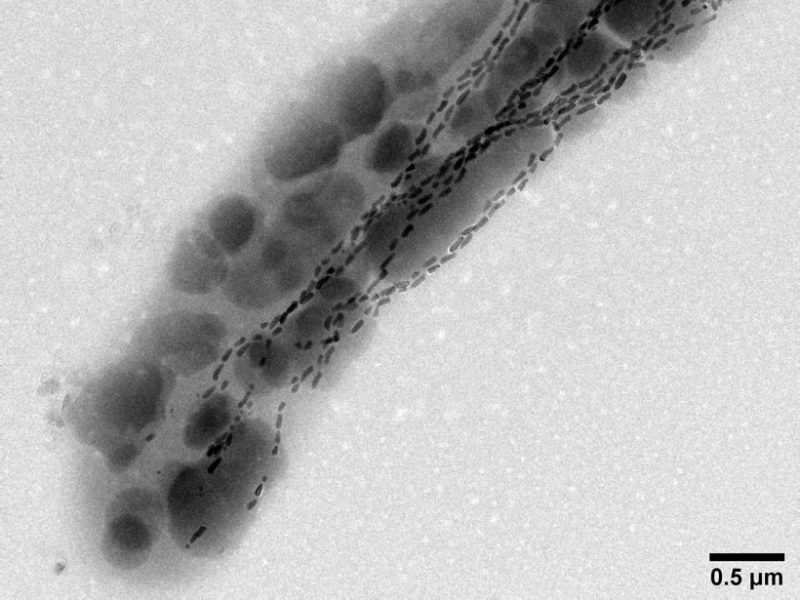
Chemical-Shuttling Bacteria Follow Earth’s Magnetic Field (eos.org)
Magnetotactic bacteria shunt sulfur, nitrogen, and other important elements between oxygen-poor and oxygen-rich waters.
-
Havana syndrome: 'directed' radio frequency likely cause of illness – report (Guardian)
First official explanation of illness that affected US diplomats in Cuba says ‘pulsed’ energy may have led to unexplained symptoms
Electromagnetic spectrum management tool coming next year (c4isrnet)
The electromagnetic spectrum has gained importance in recent years, with adversaries becoming more proficient in exploiting it to jam communications and geolocate units based solely on their electromagnetic signatures. As such, the Department of Defense has realized it needs to take a more holistic approach than just electronic warfare — the manipulation of signals — to planning & managing forces and systems within the spectrum.
-
A Protein Has Been Caught Conducting Electricity, And Scientists Are Really Excited
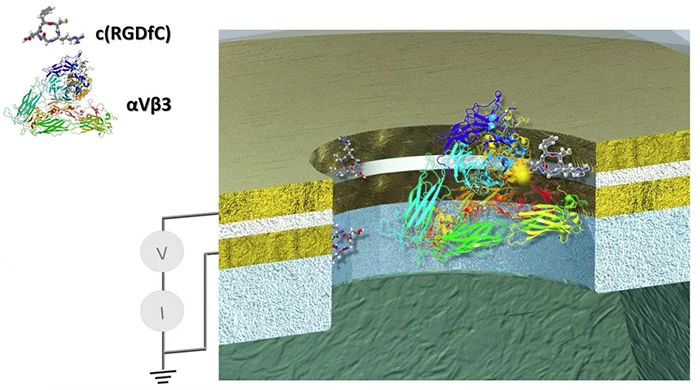
Proteins, the building blocks in every cell, have usually been thought of as blobs of inert organic matter. Now scientists have caught one particular protein doing something incredible: conducting electricity. The research has been published in Nano Futures.
-
Albert Szent-Györgyi on Water - from his book "Bioenergetics" (1957)

-
Public Shut Out of Global RF Health Briefing - Updates from NTP, Japan, Korea & WHO
An international briefing on RF health research, known as GLORE 2020, was held online, November 9-12, featuring updates on the second phase of the U.S. National Toxicology Program (NTP) project and the Japanese-Korean partial repeat. The WHO presented a status report on ten ongoing systematic reviews of RF health effects. Government and industry representatives from Australia, Canada, France, Japan, Korea, New Zealand and the U.S. participated, as did an assortment of academics. The public and the press were not invited. Everything about GLORE 2020 is being kept secret.



-
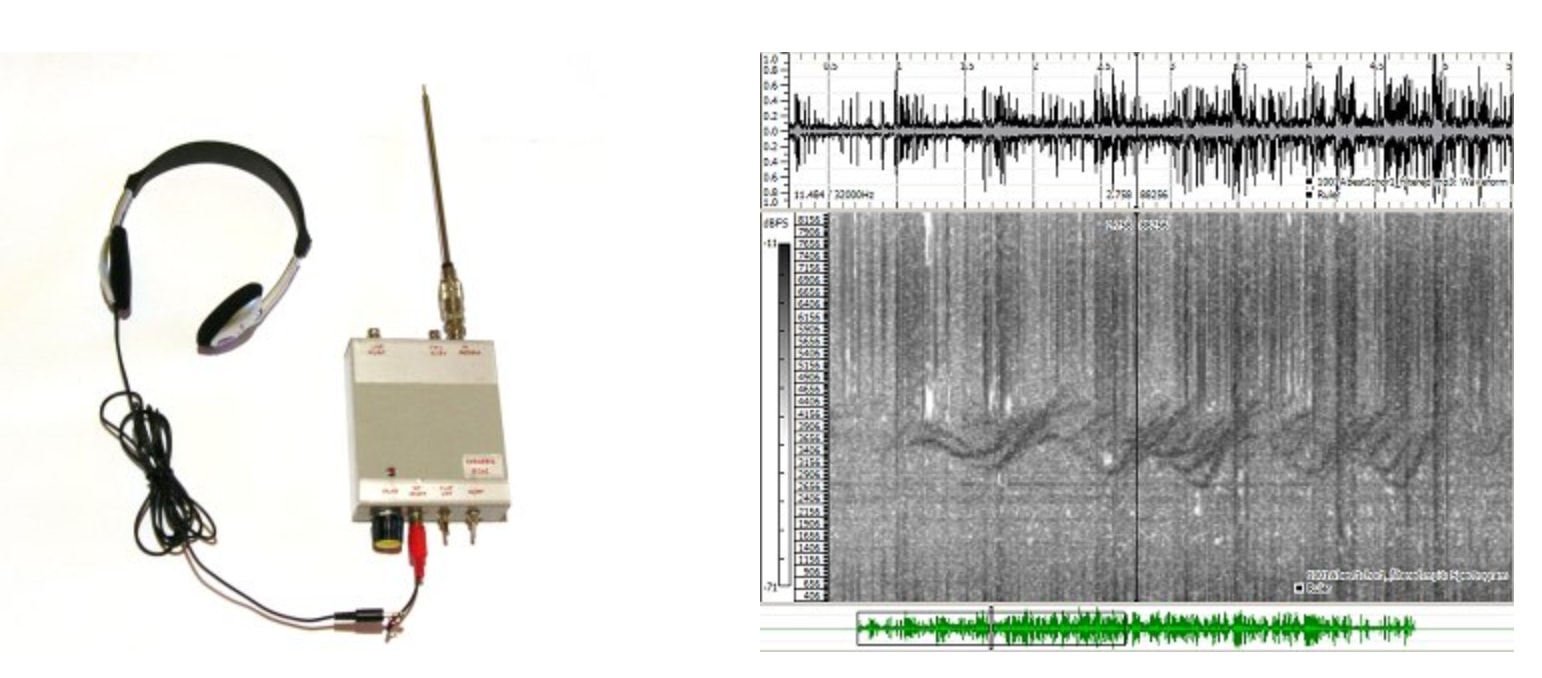
Want: A VLF Radio Receiver (less than 1kHz range) such as Explorer E-202 or WR-3 - A simple but effective portable device for natural radio signal reception.
-
Did China use microwave weapons on Indian soldiers?
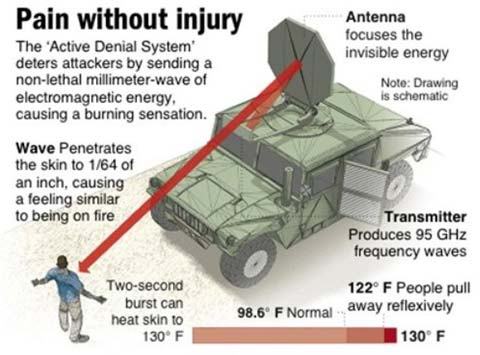
The electromagnetic weapon, which cooks the human tissue of enemy troops, 'turned the mountain tops into a microwave oven' ... While the US has also developed microwave-style weapons, China’s alleged use of them may be the first against enemy troops anywhere in the world. Also envisioned for use in crowd control, the sensation was once described in a medical journal as equivalent to touching a hot lightbulb.
-
Remote, brain region–specific control of choice behavior with ultrasonic waves

Abstract: The ability to modulate neural activity in specific brain circuits remotely and systematically could revolutionize studies of brain function and treatments of brain disorders. Sound waves of high frequencies (ultrasound) have shown promise in this respect, combining the ability to modulate neuronal activity with sharp spatial focus. Here, we show that the approach can have potent effects on choice behavior. Brief, low-intensity ultrasound pulses delivered noninvasively into specific brain regions of macaque monkeys influenced their decisions regarding which target to choose. The effects were substantial, leading to around a 2:1 bias in choices compared to the default balanced proportion. The effect presence and polarity was controlled by the specific target region. These results represent a critical step towards the ability to influence choice behavior noninvasively, enabling systematic investigations and treatments of brain circuits underlying disorders of choice.
-
The Global Brain Hive Mind Artificial Intelligence Control Grid
#Comment: It is a golden age for colourful conspiracy narratives which artfully mix bullshit and realshit in fun ways - and this video is a delicious example. Operation Mindfuck in full effect. What people who take such things very serious ("its real!" and "its not real!!") have not internalized yet (but some monks and other trippers might): The "conspiracy" governing reality is far more weird and bizarre. We - a domesticated monkey - are sitting on a round rock racing through infinite space, and left and right are infinite black-holes, where time/space collapses...
Closer to the mundane everyday life abstraction level, there is some truth to the following:

-
Integrating information in the brain’s EM field: the cemi field theory of consciousness - paper by Johnjoe McFadden #NeuroScience #RadioBio
-
U.S. Diplomats and Spies Battle Trump Administration Over Suspected Attacks (nytimes)
American officials in China, Cuba and Russia say U.S. agencies are concealing the true extent of the episodes, leaving colleagues vulnerable to hostile actions abroad.