tag > Systems
-
AI in the Wild - Sustainability in the Age of Artificial Intelligence - by Peter Dauvergne

Illustration by Christophe Vorlet This book analyzes the complex relationship between AI and sustainability. Using analytical tools from environmental politics, it describes the potential for AI to restore balance to earth systems — like its use in wildlife monitoring and improving efficiency of the electricity grid — but also emphasizes its capacity to reinforce economic and political structures, like resource extraction and suppression of activists, that have resulted in modern environmental crisis.
Machine learning for geographically differentiated climate change mitigation in urban areas - Nikola Milojevic Dupon & Felix Creutzig
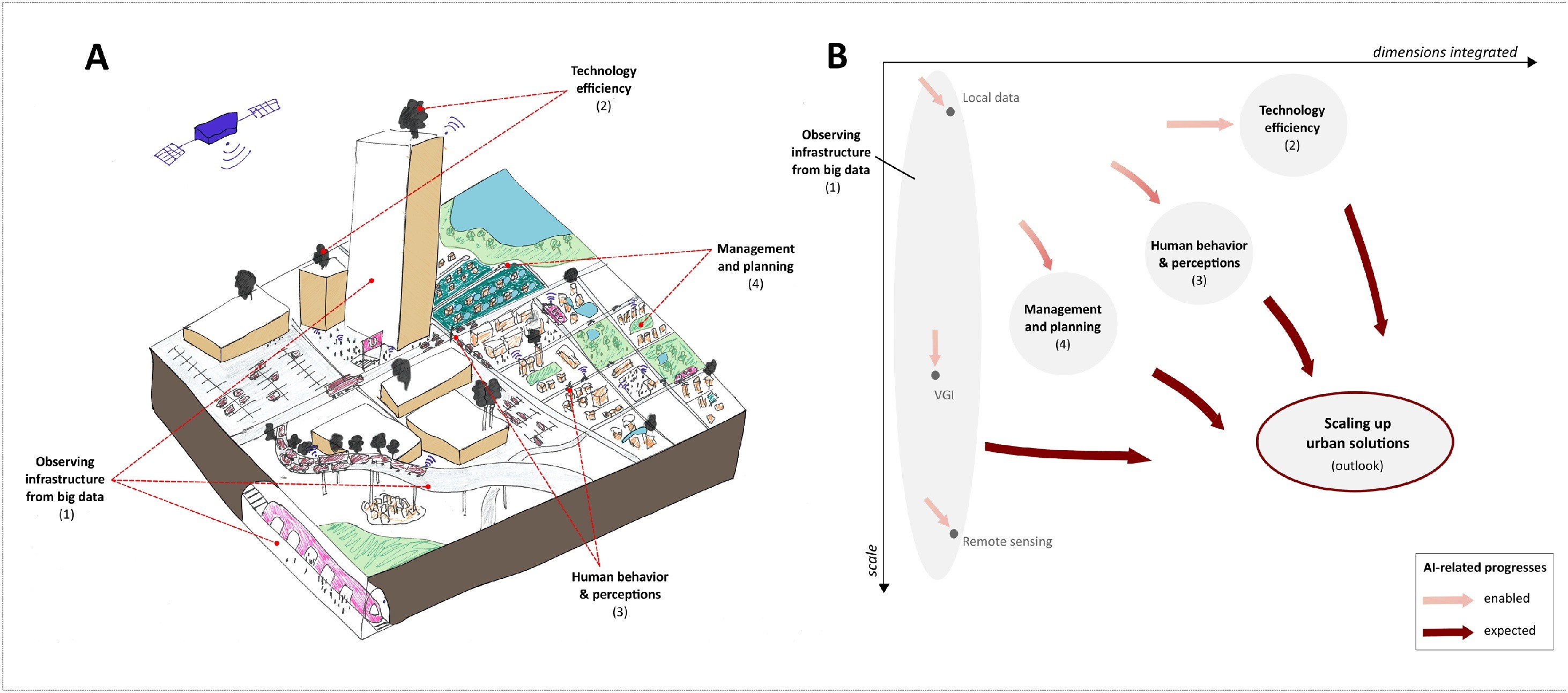
Traditionally, mitigation policies have been guided by coarse-scale scenario analysis. However, more and more data are available that can be used to characterize the carbon emissions of cities, from building footprints to mobility patterns. More than simply guiding efficiency improvements, the authors advocate that these data inform decarbonization via urban planning and policy recommendations, through a meta-algorithm they call Machine Learning for low-carbon Urban Planning.
Advancing AI for Earth Science: A Data Systems Perspective - by Manil Maskey, Hamed Alemohammad, Kevin J. Murphy, and Rahul Ramachandran
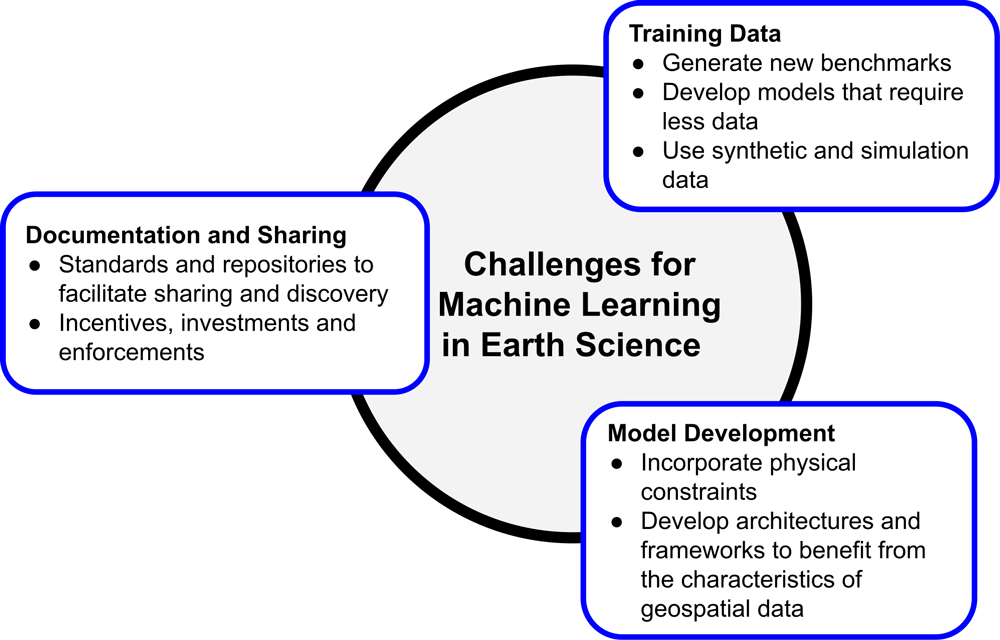
Tackling data challenges and incorporating physics into machine learning models will help unlock the potential of artificial intelligence to answer Earth science questions.
Continuing the conversation - Climate Change, Machine Learning, and the Power Grid
-
How Systems Collapse
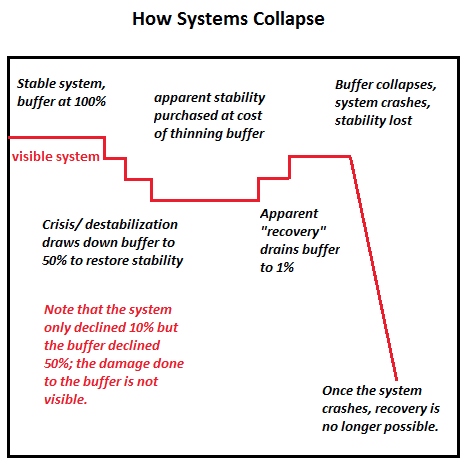
Societal collapse is the fall of a complex human society. Such a disintegration may be relatively abrupt, as in the case of Maya civilization, or gradual, as in the case of the fall of the Western Roman Empire. The subject of societal collapse is of interest in such fields as history, anthropology, sociology, political science, and, more recently, cliodynamics and complex-systems science. Common contributing factors are economical, environmental, social and cultural, and disruptions in one domain sometimes cascade into another. In some cases a natural disaster may precipitate a collapse.
-
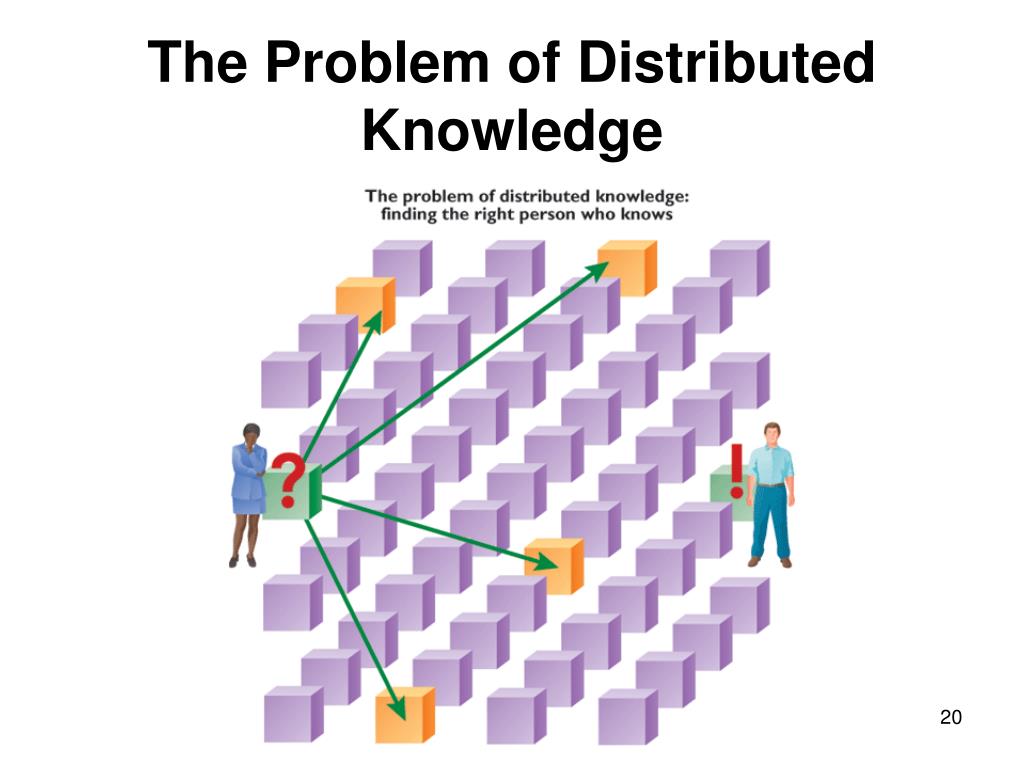
Distributed knowledge is the union of all the knowledge of individuals in a community. Distributed knowledge is approximately what "a wise man knows" or what someone who has complete knowledge of what each member of the community knows knows. Distributed knowledge might also be called the aggregate knowledge of a community, as it represents all the knowledge that a community might bring to bear to solve a problem.
-
Grey relational analysis (wikipedia)
Grey relational analysis (GRA), also called Deng's Grey Incidence Analysis model, was developed by a Chinese Professor Julong Deng of Huazhong University of Science and Technology. It is one of the most widely used models of Grey system theory. GRA uses a specific concept of information. It defines situations with no information as black, and those with perfect information as white. However, neither of these idealized situations ever occurs in real world problems. In fact, situations between these extremes, which contain Dispersed knowledge (partial information), are described as being grey, hazy or fuzzy. A variant of GRA model, Taguchi-based GRA model, is very popular in engineering.
Introduction to Grey System Theory - by Deng Julong (PDF)
Grey System theory was initiated in 1982 [7]. As far as information is concerned, the systems which lack information, such as structure message, operation mechanism and behaviour document, are referred to as Grey Systems. For example, the human body, agriculture, economy, etc., are Grey Systems. Usually, on the grounds of existing grey relations, grey elements, grey numbers (denoted by 8 ) one can identify which Grey System is, where "grey" means poor, incomplete, uncertain, etc. The goal of Grey System and its applications is to bridge the gap existing between social science and natural science. Thus, one can say that the Grey System theory is inter- disciplinary, cutting across a variety of specialized fields, and it is evident that Grey System theory stands the test of time since 1982. As the case stands, the development of the Grey System-as well as theoretical topic-is coupled with clear applications of the theory in assorted fields.
-
Critical infrastructure is a term used by governments to describe assets that are essential for the functioning of a society and economy – the infrastructure.
-
Simulation model as a decision support tool
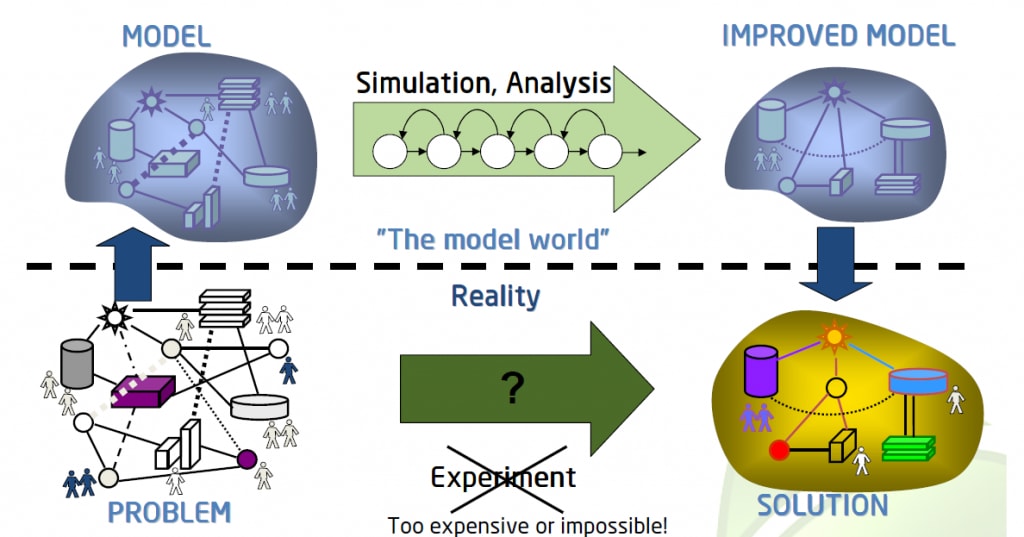
The simulation model does not give optimal decisions, unlike analytical solvers used for classical optimization tasks. The main advantage of this model is that it allows experts to answer the question of “What if?” using computational experiments. In the last decade, a lot of work was done to apply simulation to an opposite task: “What is need for?” This may also be called simulation-based optimization.
-
#Comment: In times of crisis, the true extent of hypocrisy and lunacy in a system becomes evident: Lawrence Gostin, who specializes in global health policy at Georgetown University Law Center, just called the policies of the Chinese government against the coronavirus “astounding, unprecedented, and medieval”. In the meantime, the EU is heavily debating if its worth emulating the Chinese measures, calling them "highly effective" yet simultaneously screaming "but don't forget, china is a evil dictatorship!". All while the coronavirus is rapidly spreading in the EU and US, where the responds of officials and public is progressively looking like a mix of ignorance and incompetence. The "west" has developed a curios mix of extreme arrogance coupled with systemic stupidity, which clearly has to yield catastrophic outcomes sooner or later...
-
Evolving the Visual Programming Environment with React - talk by Jonas Gebhardt (2016)
-
Blockly Developer Summit 2019: MakeCode Block Design - talk by Jacqueline Russell & Shannon Kao (2019)
Blockly: Using Block Based Coding in your App
-
Outbreak analytics: a developing data science for informing the response to emerging pathogens (2019)
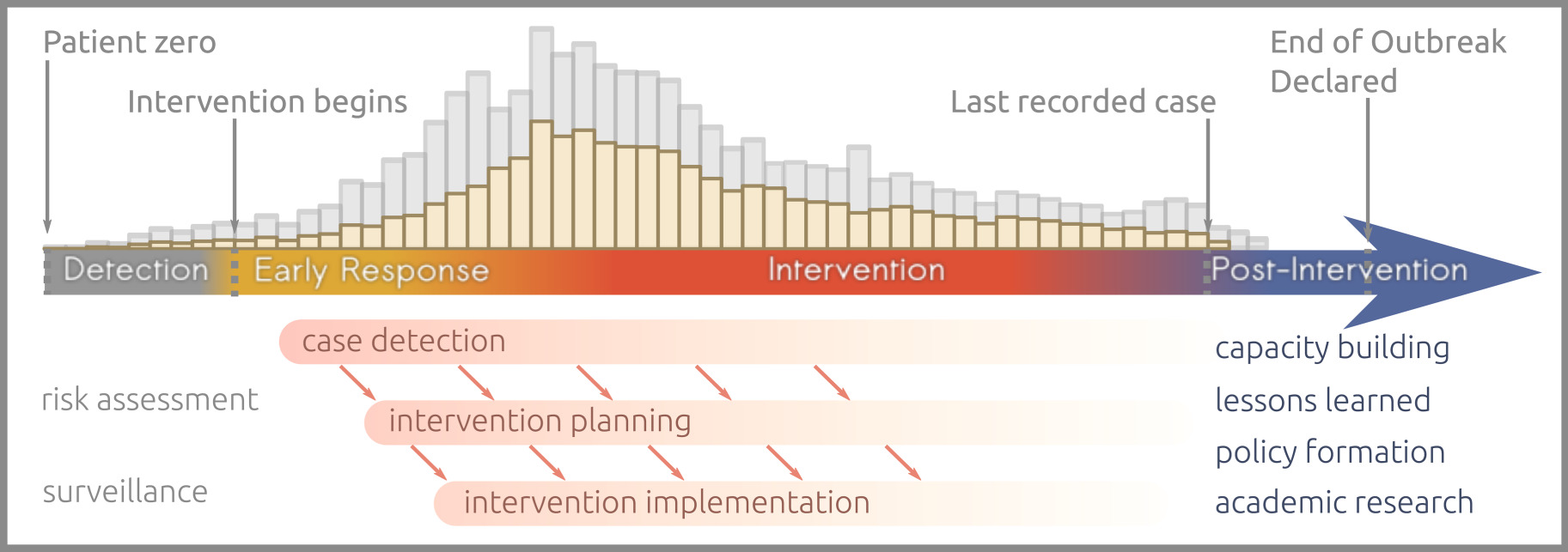
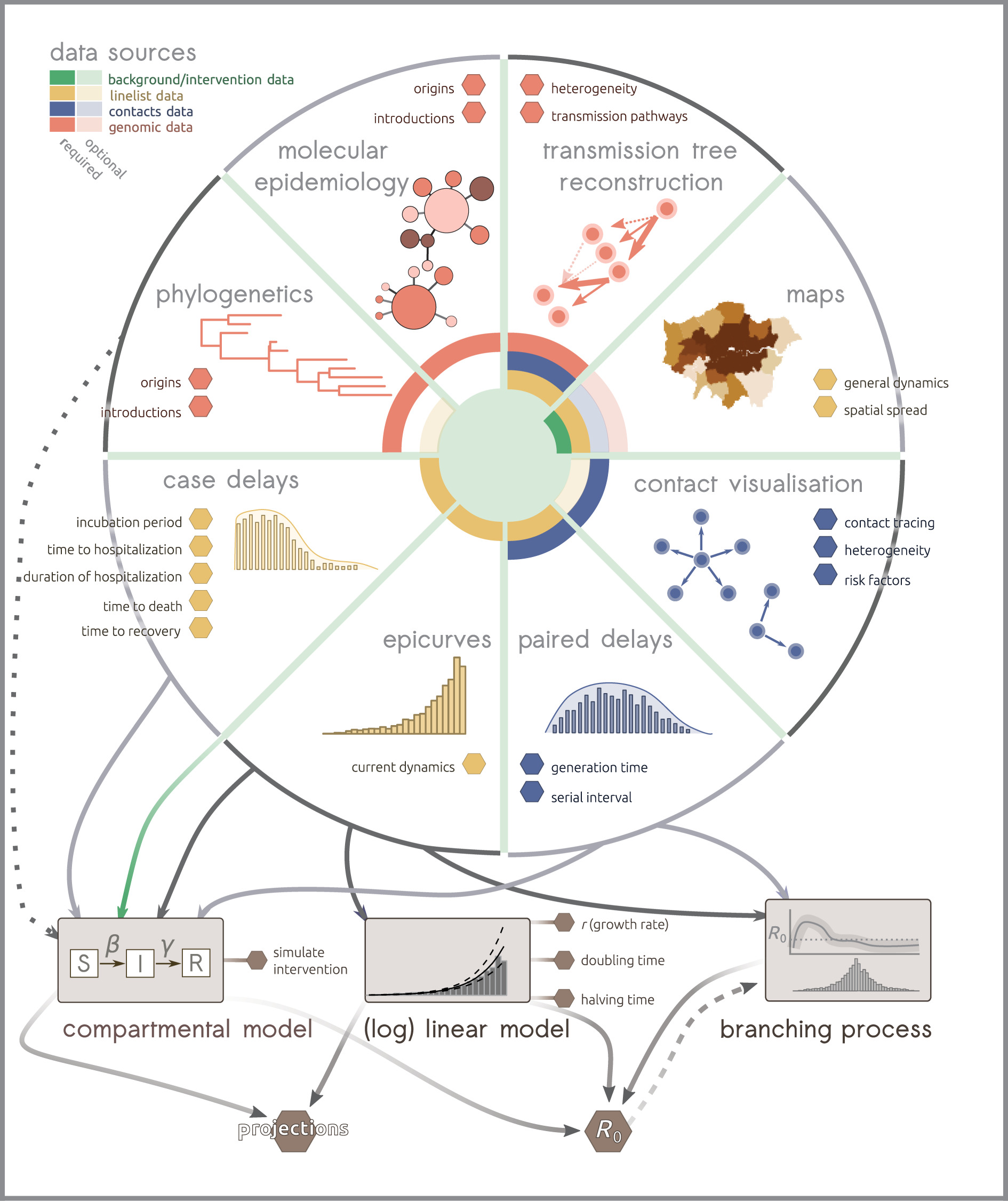
Abstract:
Despite continued efforts to improve health systems worldwide, emerging pathogen epidemics remain a major public health concern. Effective response to such outbreaks relies on timely intervention, ideally informed by all available sources of data. The collection, visualization and analysis of outbreak data are becoming increasingly complex, owing to the diversity in types of data, questions and available methods to address them. Recent advances have led to the rise of outbreak analytics, an emerging data science focused on the technological and methodological aspects of the outbreak data pipeline, from collection to analysis, modelling and reporting to inform outbreak response. In this article, we assess the current state of the field. After laying out the context of outbreak response, we critically review the most common analytics components, their inter-dependencies, data requirements and the type of information they can provide to inform operations in real time. We discuss some challenges and opportunities and conclude on the potential role of outbreak analytics for improving our understanding of, and response to outbreaks of emerging pathogens.
This article is part of the theme issue ‘Modelling infectious disease outbreaks in humans, animals and plants: epidemic forecasting and control‘. This theme issue is linked with the earlier issue ‘Modelling infectious disease outbreaks in humans, animals and plants: approaches and important themes’. -
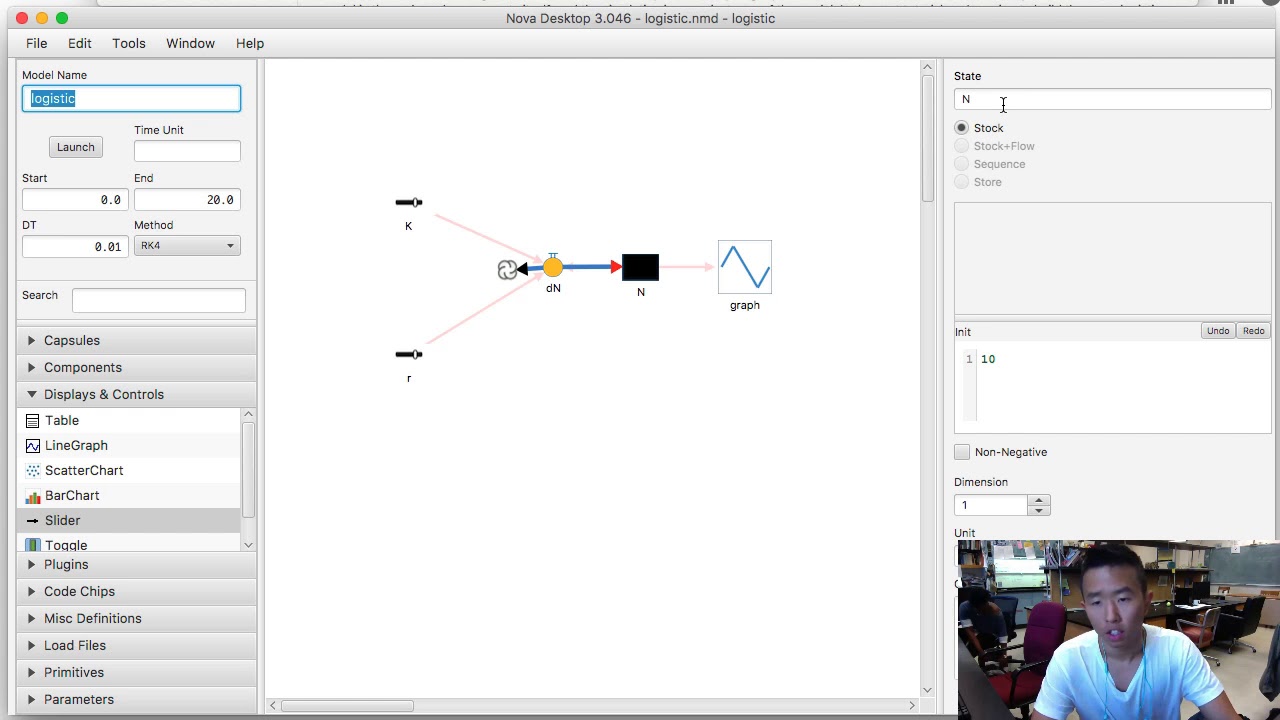
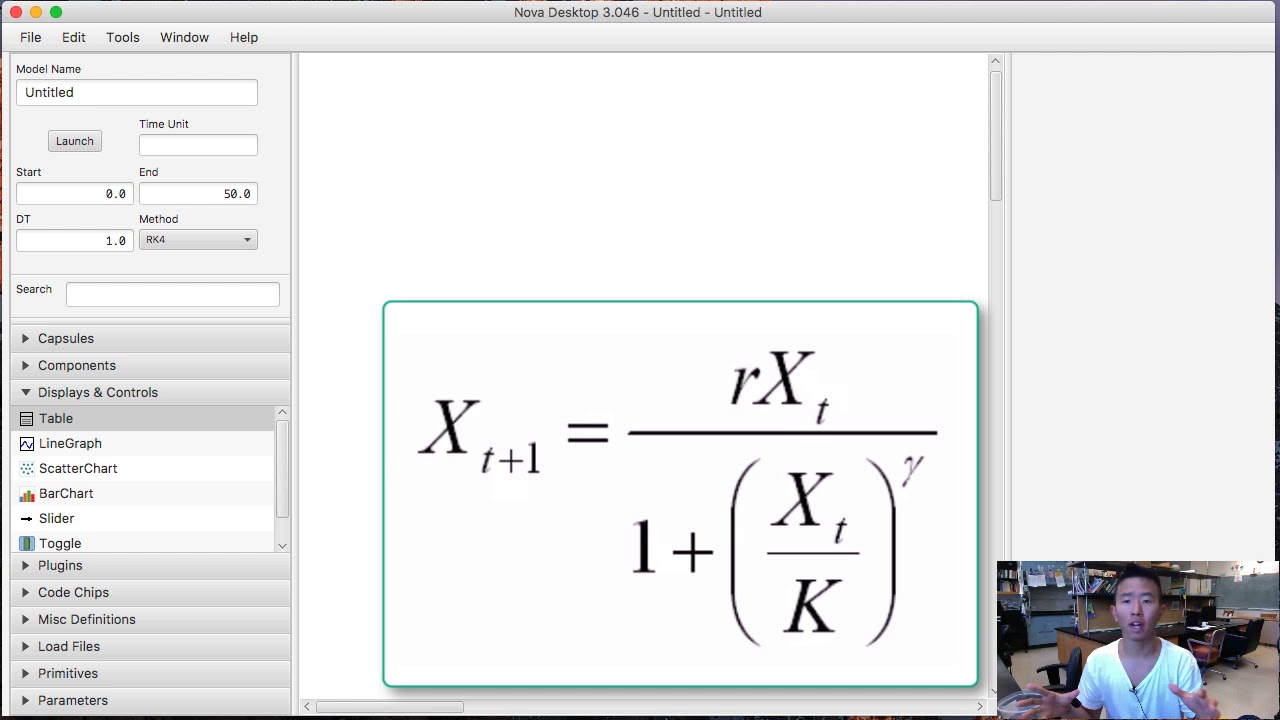
NOVA: An Interactive Graphics-Scripting Platform for Education and Computational Research
Nova: A Modern Platform for System Dynamics, Spatial, and Agent-Based Modeling - by Richard M. Salter (2013)
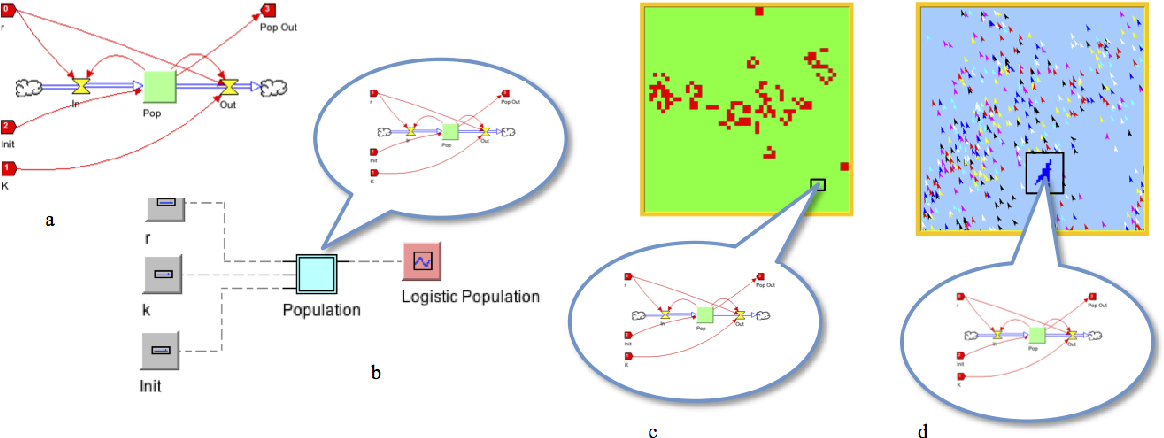
In this paper we describe Nova, a new Java-based modeling platform that naturally supports the creation of models in the system dynamics, spatial and agent-based modeling paradigms. Nova uses a visual language to express model design, and provides automatic conversion for such models to script form for execution. Nova's architecture promotes hierarchical design, code reuse, and extensibility through the use of plug-ins. The Nova Website, www.novamodeler.com, is being built to foster a vibrant user community by providing ample support for model and plug-in construction, and user services such as online repositories for user-contributed content.
Numerus Model Builder Tutorial 1a
-
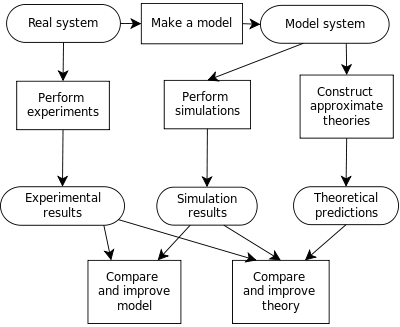
The process of mathematical modelling, performed on a computer, which is designed to predict the behaviour of and/or the outcome of a real-world or physical system. Simulation of a system is represented as the running of the system's model. It can be used to explore and gain new insights into new technology and to estimate the performance of systems too complex for analytical solutions.
Demystifying Simulation - Simulation software explained
-
Interview with Eric Trist (1909 – 1993), a British scientist and leading figure in the field of organizational development (OD). He was one of the founders of the Tavistock Institute.
-
ARIES - Artificial Intelligence for Ecosystem Services
ARIES is a networked software technology that redefines ecosystem service assessment and valuation for decision-making. The ARIES approach to mapping natural capital, natural processes, human beneficiaries, and service flows to society is a powerful new way to visualize, value, and manage the ecosystems on which the human economy and well-being depend.